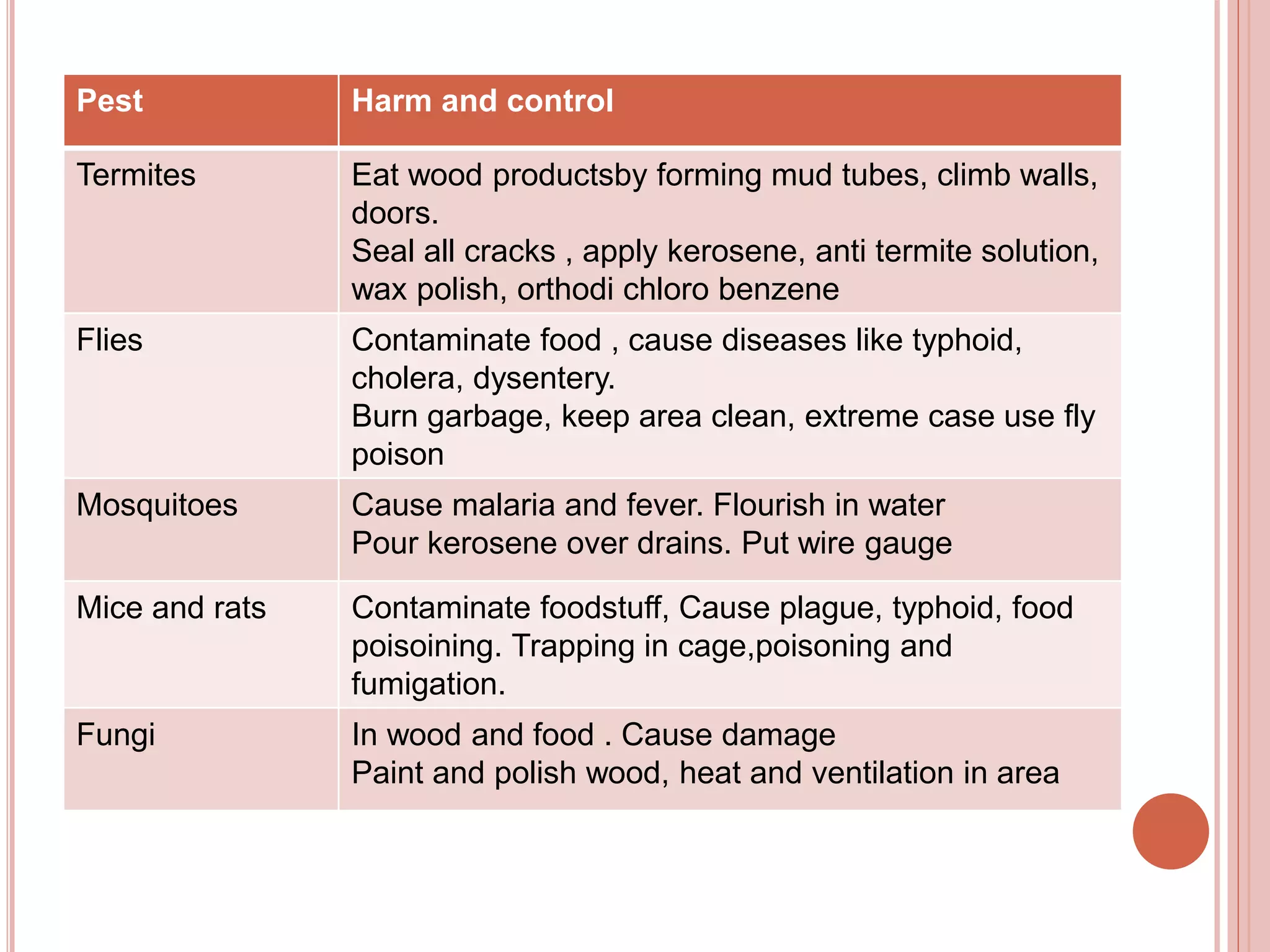
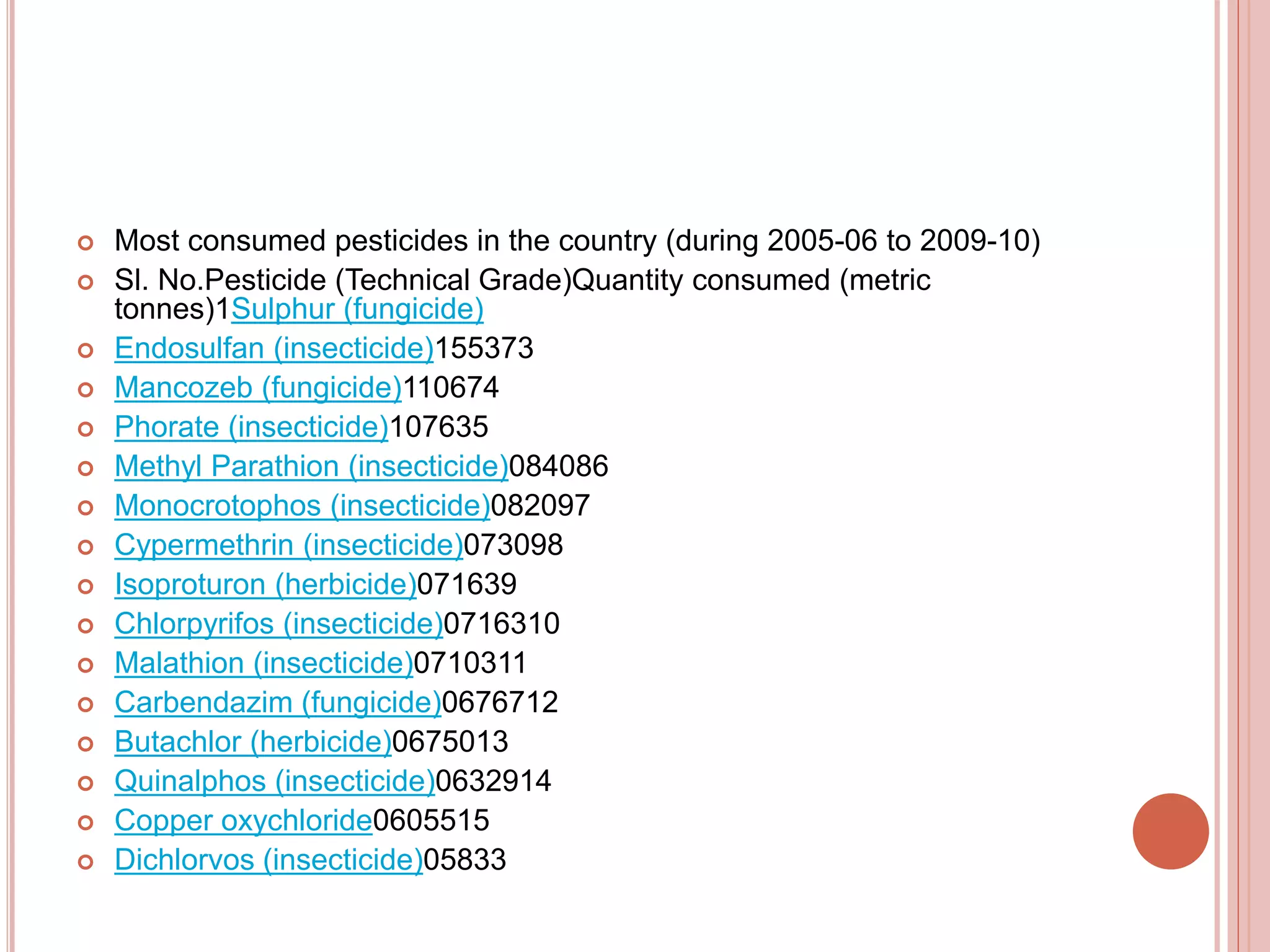
This document discusses pest control. It describes common pests like insects, rodents, and fungi that damage homes, food, and property. The goals of pest control are prevention, suppression, and eradication of pest populations. Various control methods are outlined, including natural, biological, mechanical, and chemical using pesticides. Guidelines are provided for safe pesticide use to protect human health. Common pests and their impacts are explained along with recommended control strategies.