This document discusses different types of carpets, including their materials, manufacturing processes, uses, and maintenance. Some key points covered include:
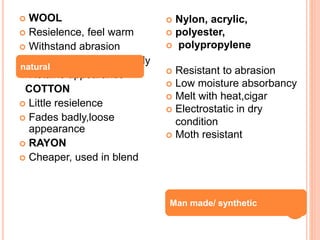
- Carpets originated in the East and are now commonly used for warmth, appearance, safety, and sound insulation. Materials include natural fibers like wool and synthetic fibers like nylon.
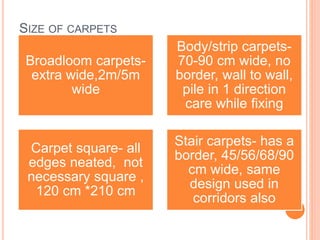
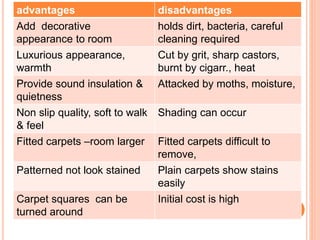
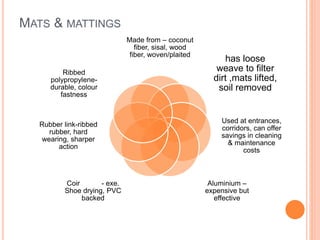
- Carpet selection depends on factors like cost, durability, appearance, safety properties, and comfort. Woven carpets include Wilton, Brussels, and Axminster carpets while nonwoven carpets are tufted, pile bonded, or needle punched.
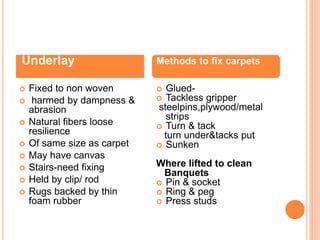
- Proper carpet care involves regular vacuuming, protecting edges, and periodic deep cleaning methods like sh