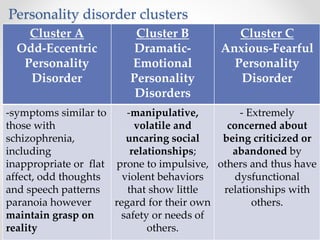
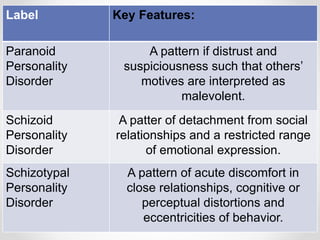
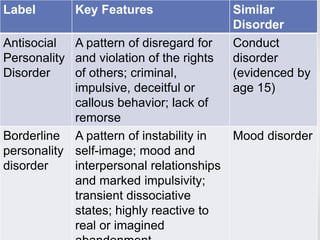
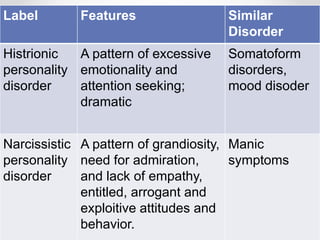
Personality disorders are enduring patterns of thinking, feeling and behaving that deviate from a person's culture and are evident by early adulthood. They are categorized into three clusters: odd-eccentric behaviors for Cluster A; dramatic-emotional behaviors for Cluster B; and anxious-fearful behaviors for Cluster C. Borderline personality disorder is characterized by instability in self-image, mood, and relationships as well as impulsivity and is more commonly diagnosed in females. It is frequently accompanied by depression, anxiety or anger.