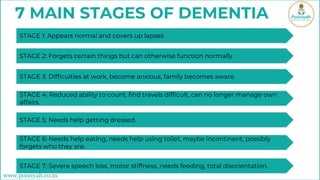
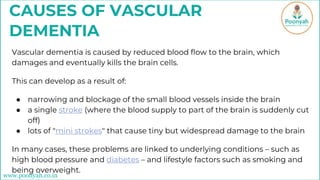
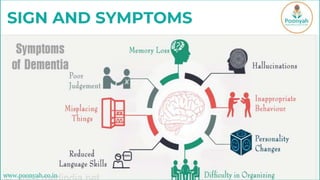
Vascular dementia, the second most common form of dementia, is caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often due to strokes or underlying conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. It presents in stages, with symptoms progressively worsening and currently has no cure, though treatment can help slow its progression. Prevention strategies include managing blood pressure, maintaining healthy cholesterol and weight, exercising, and quitting smoking.