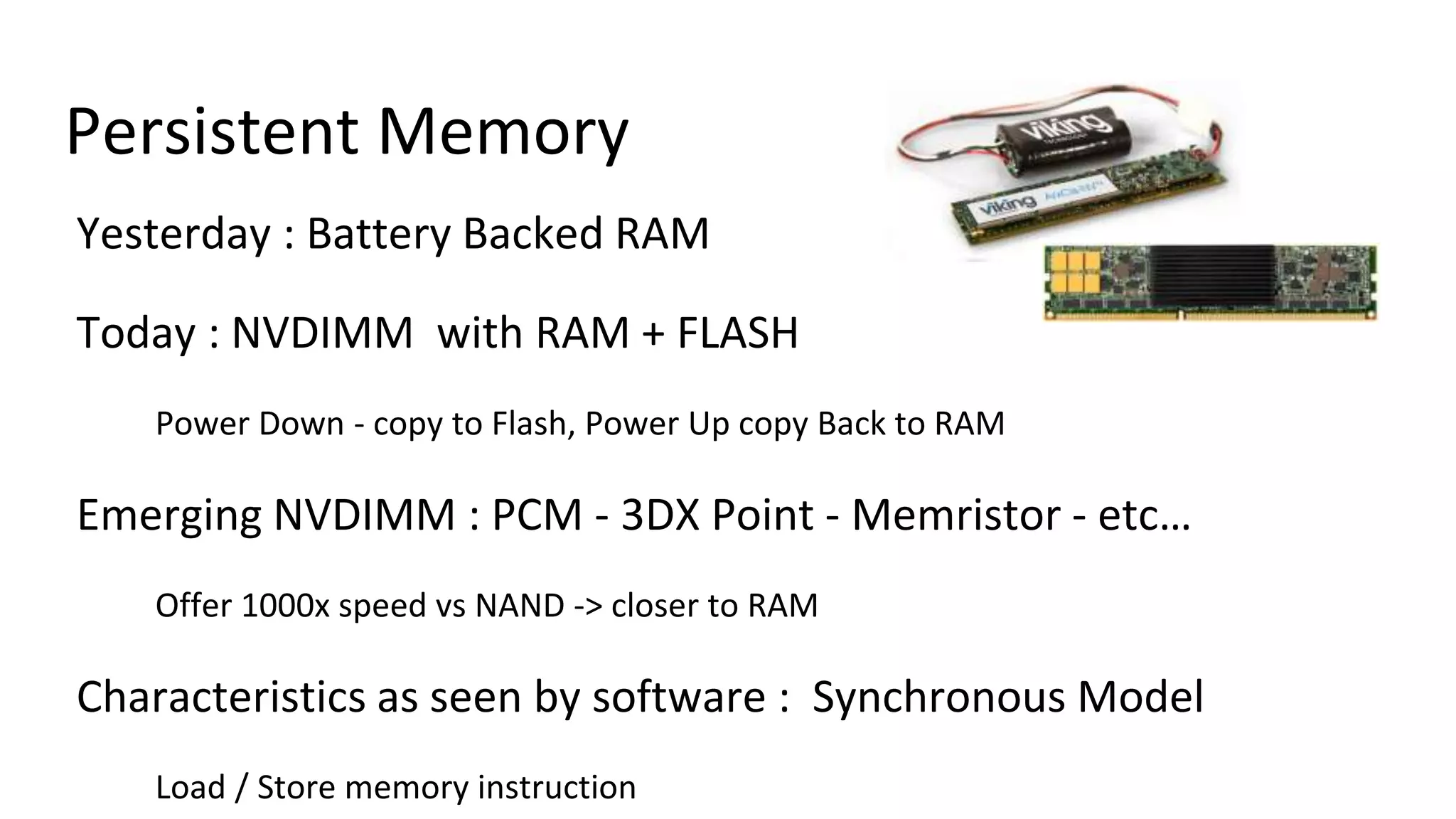
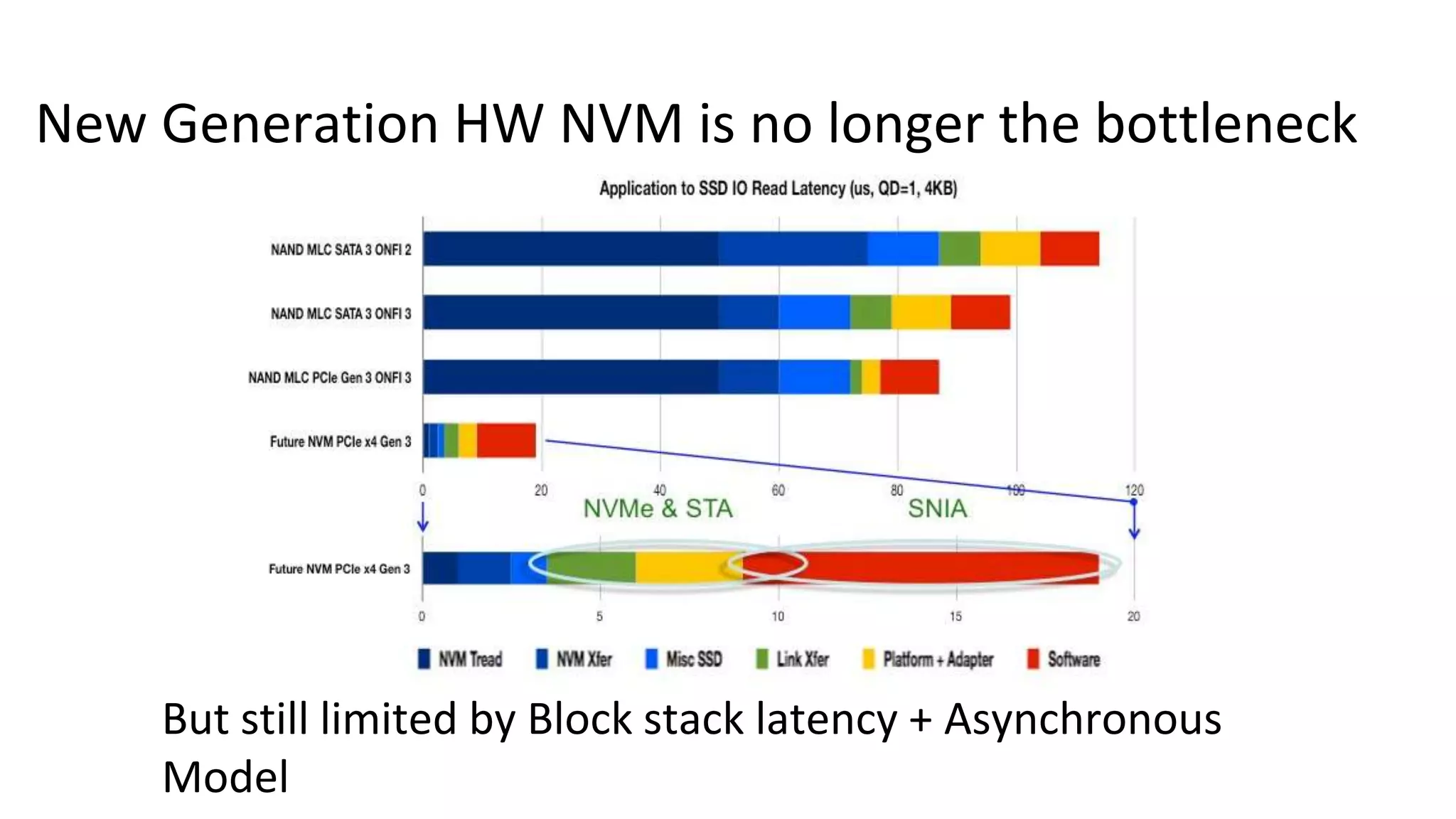
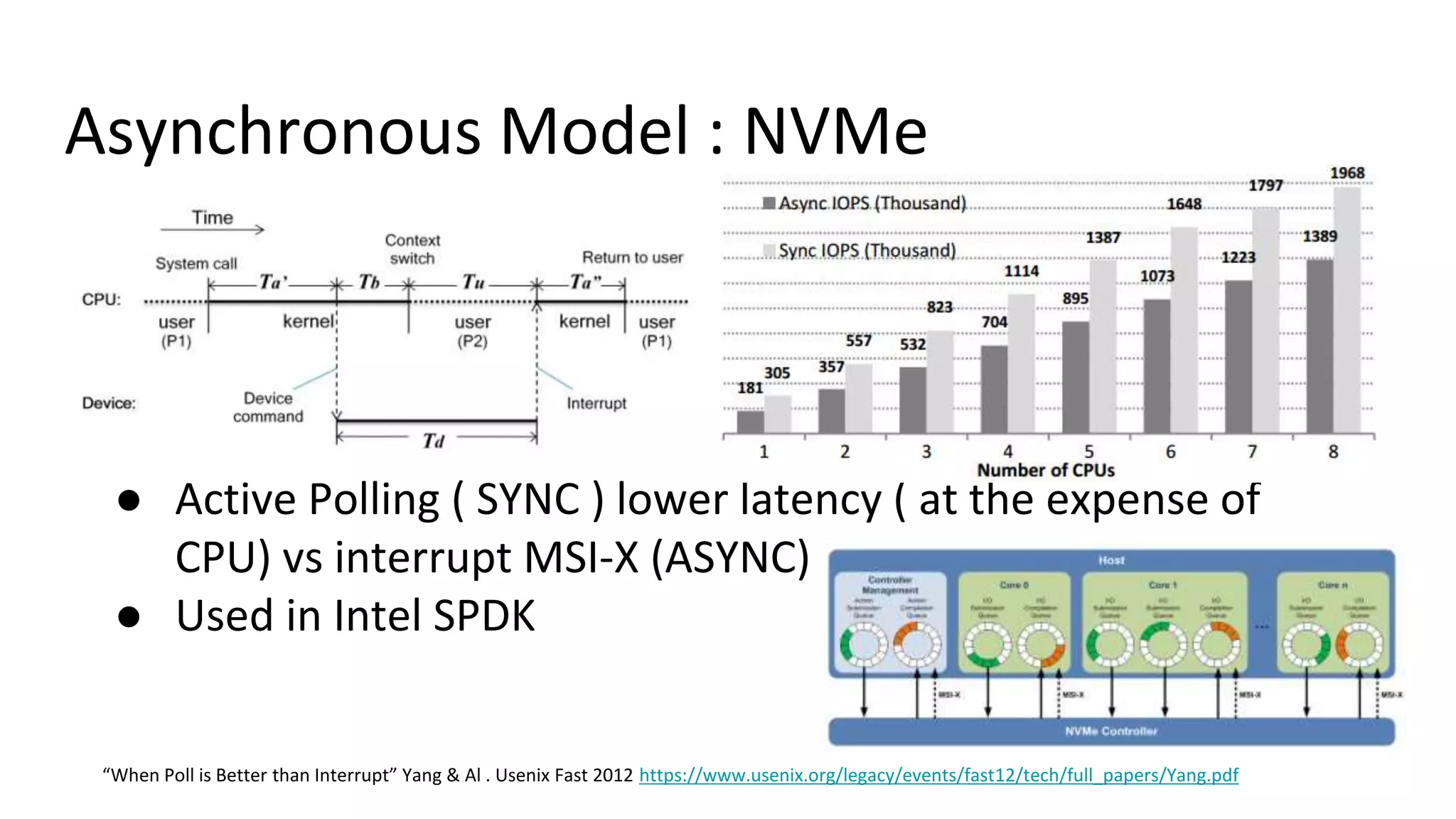
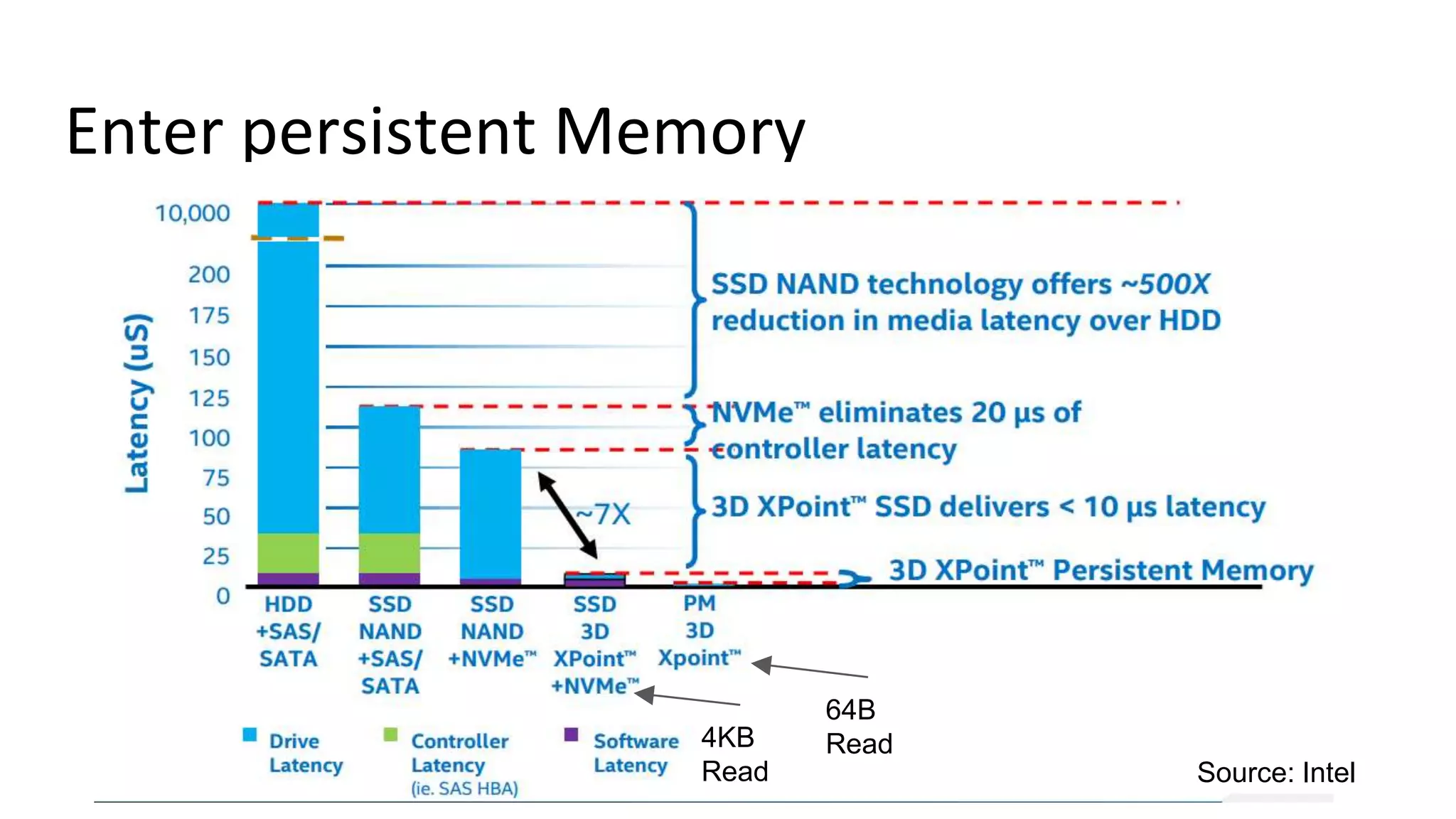
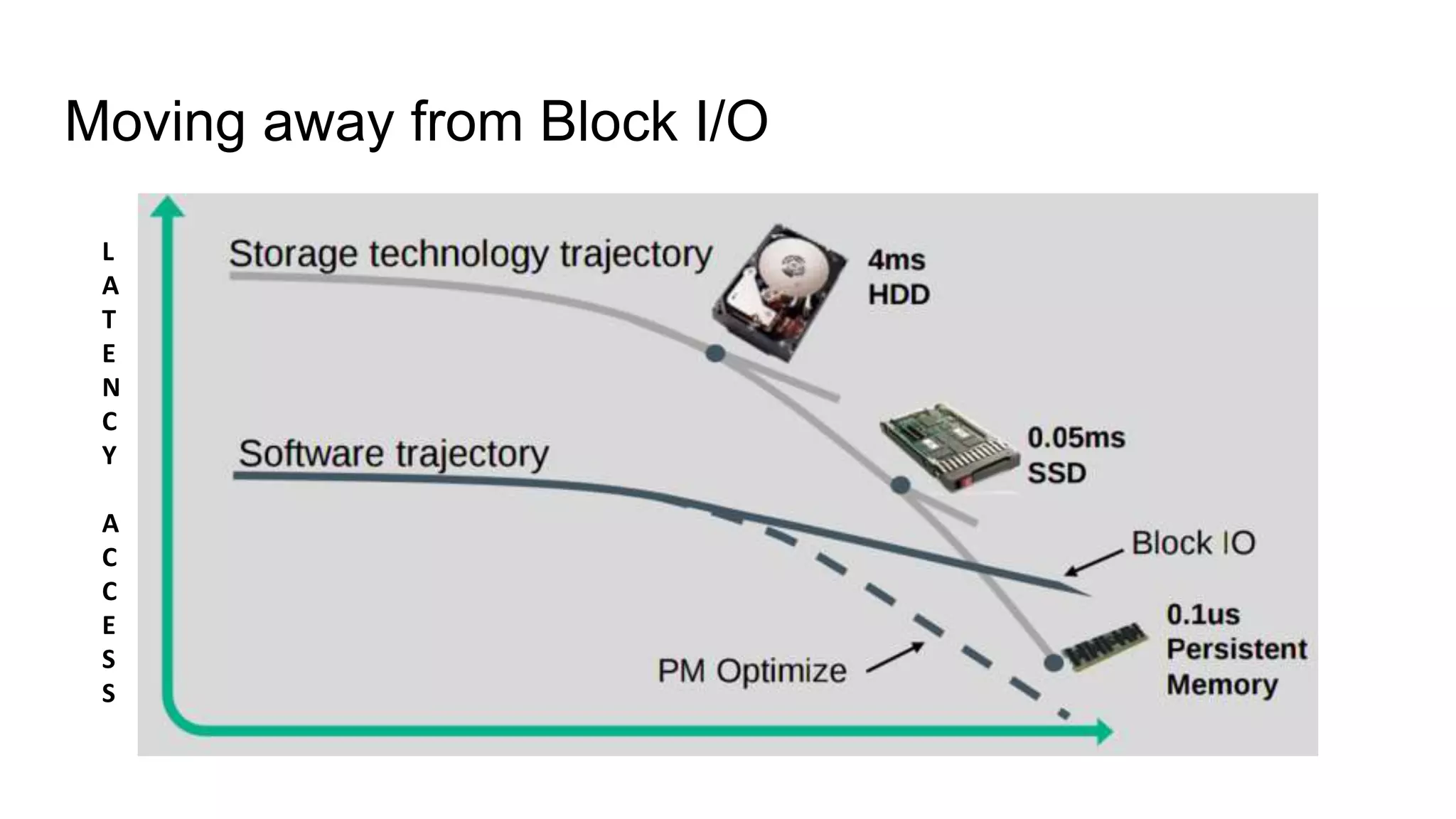
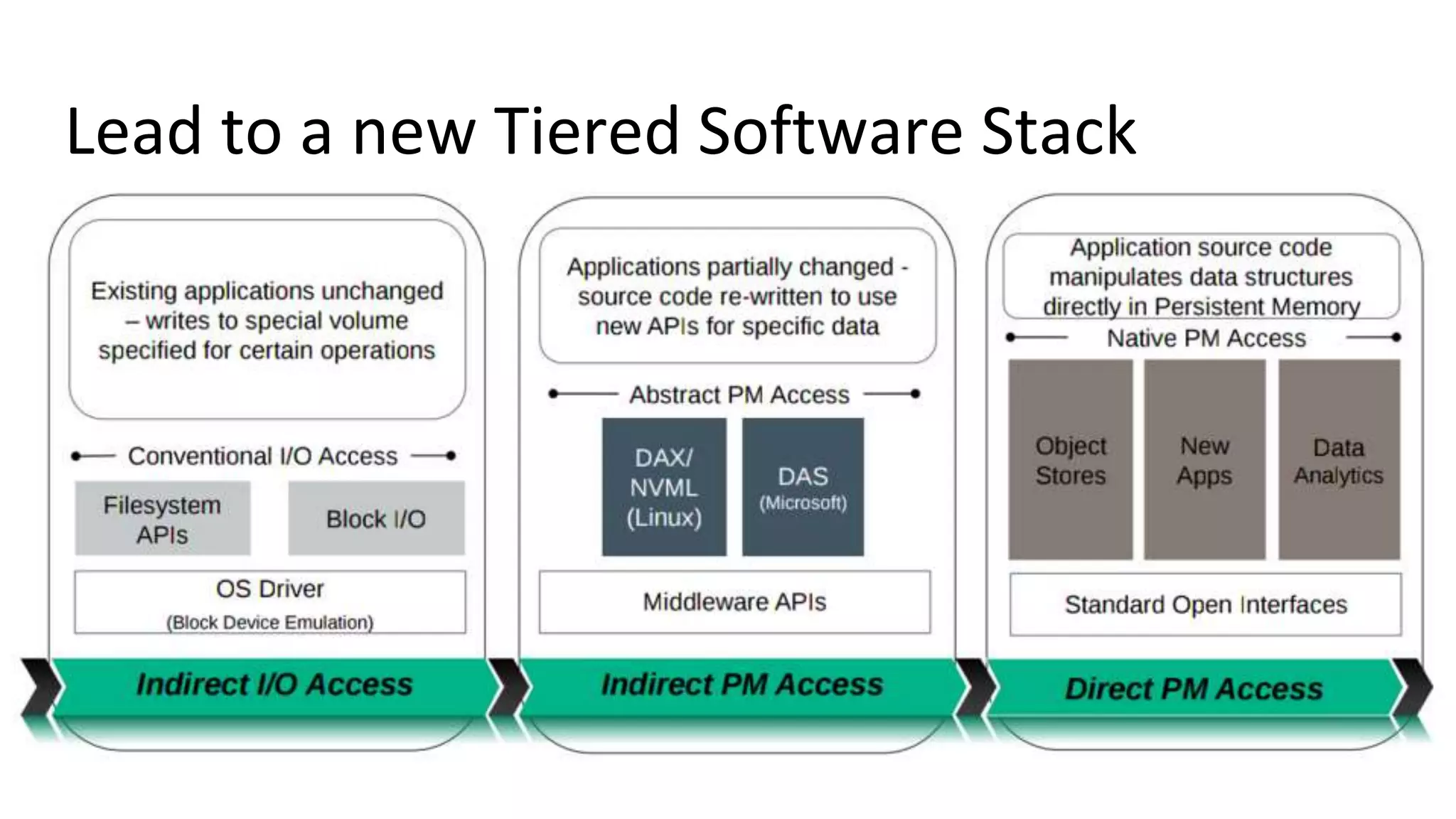
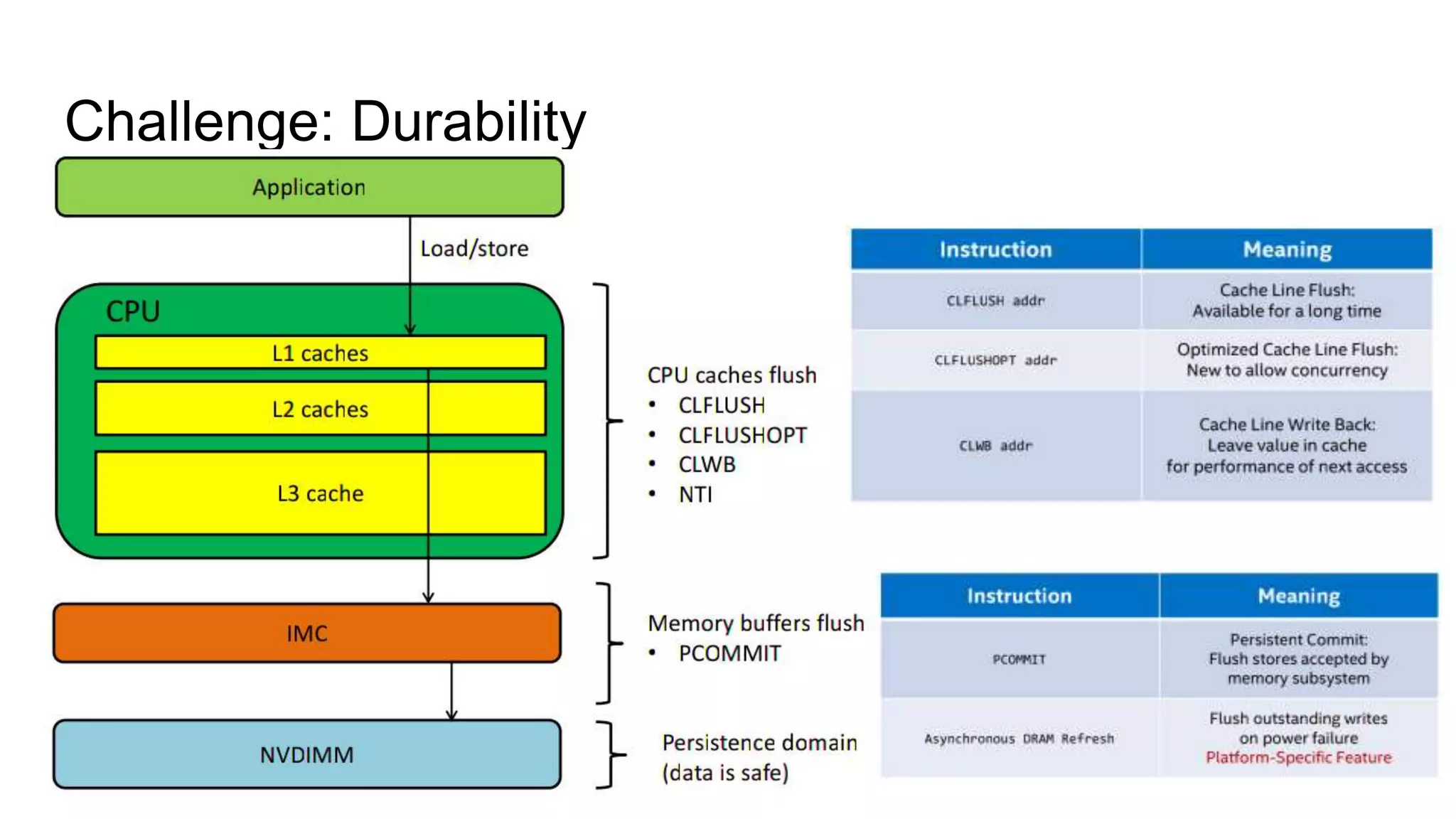
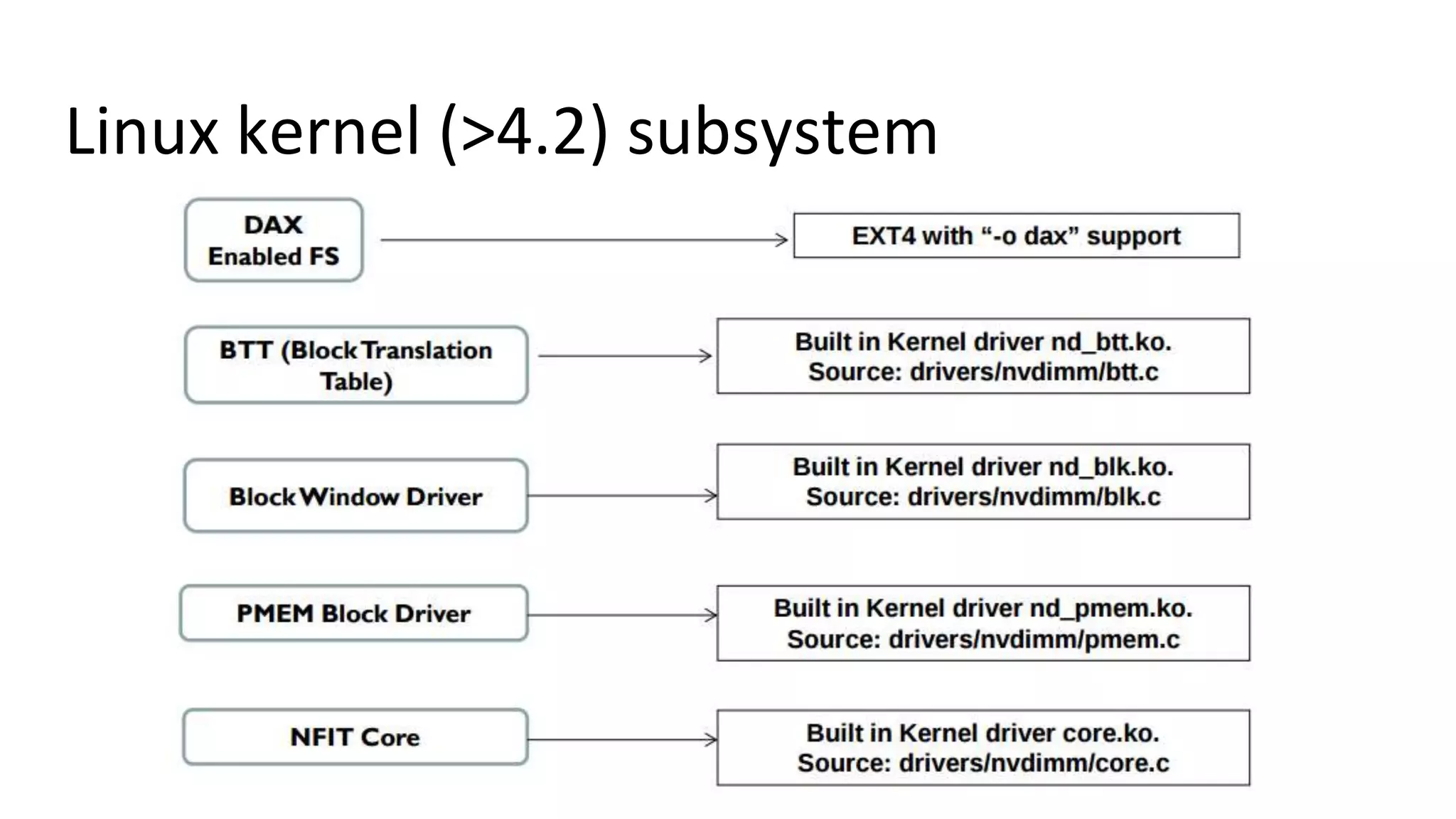
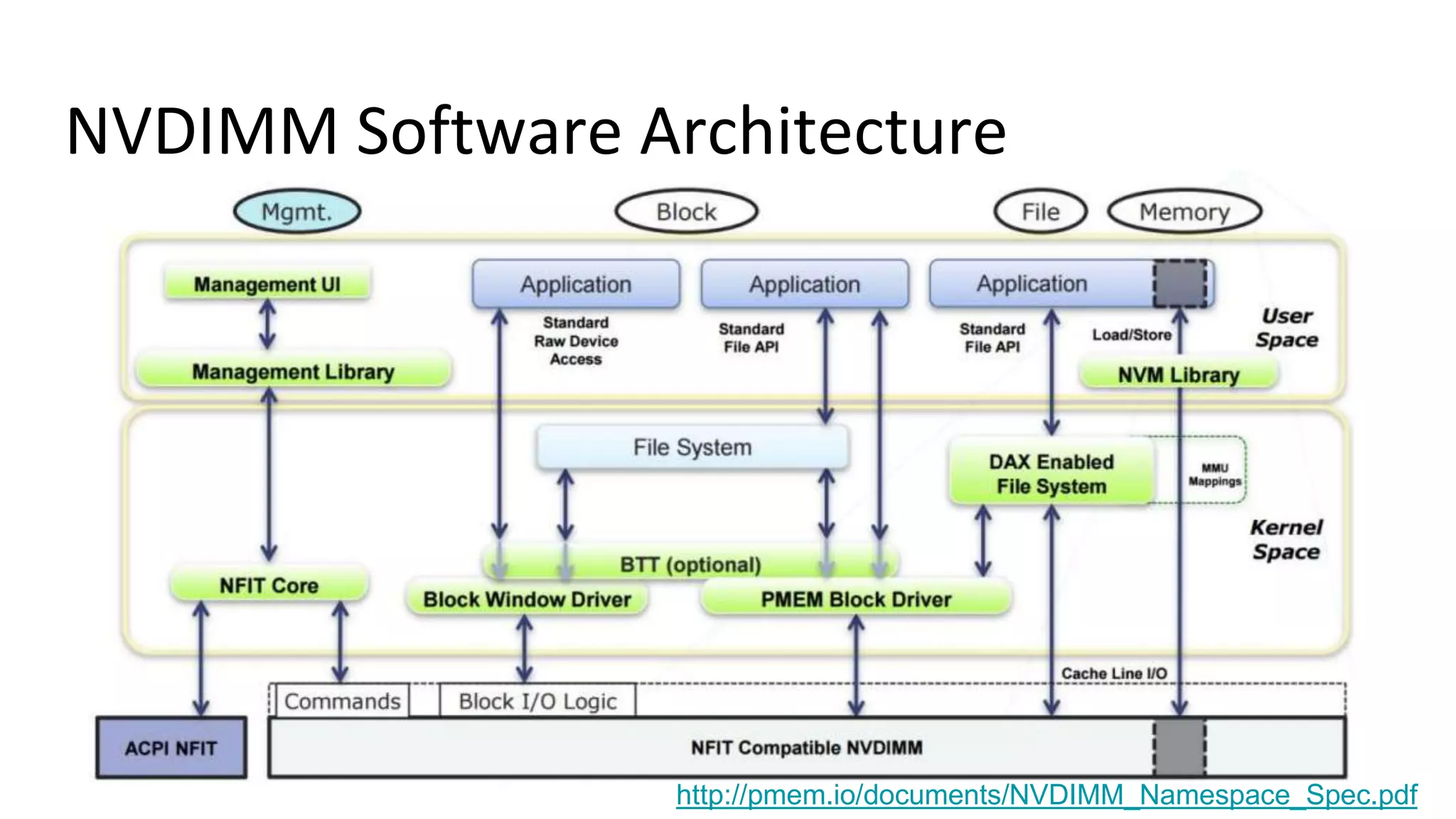
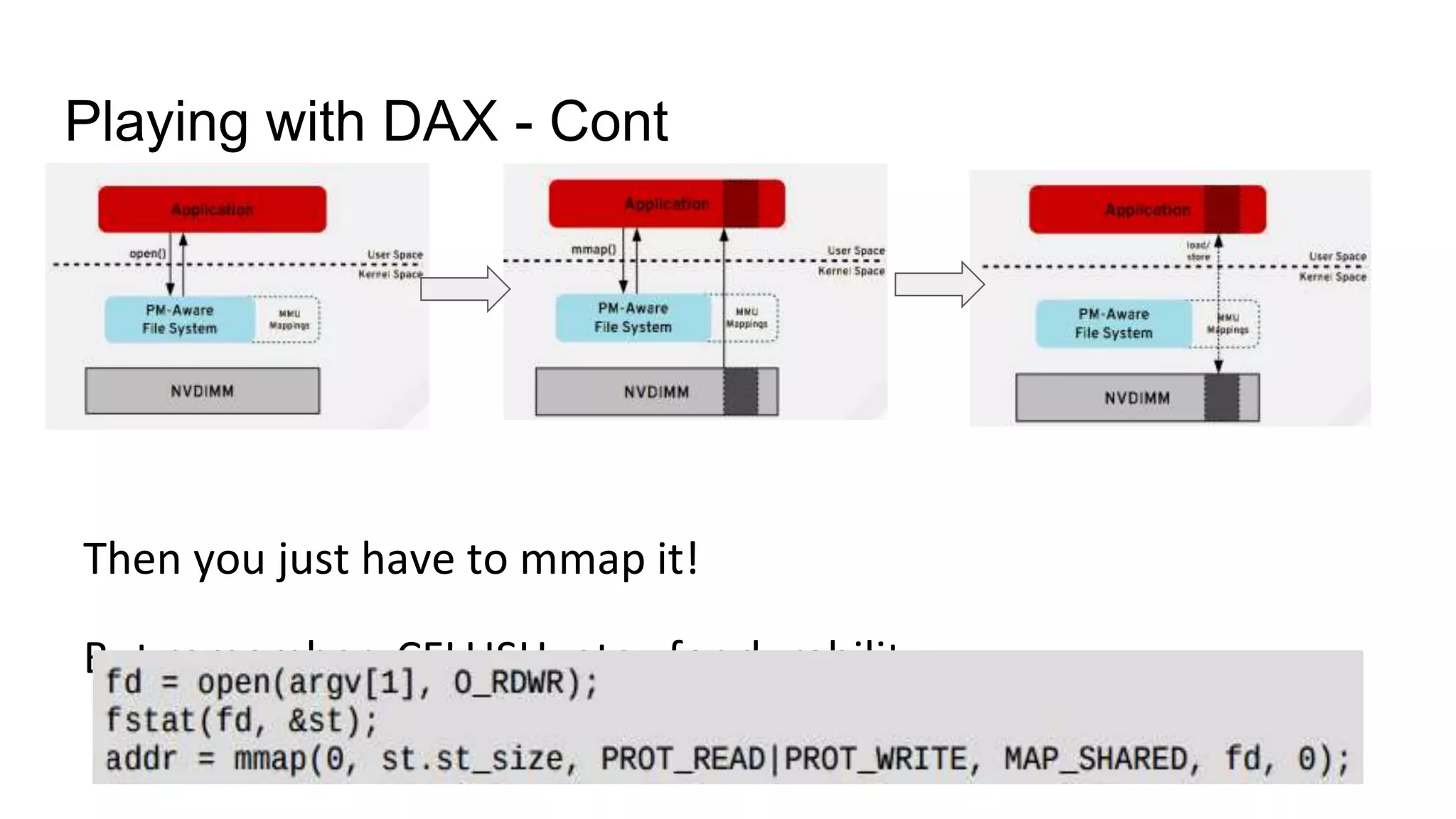
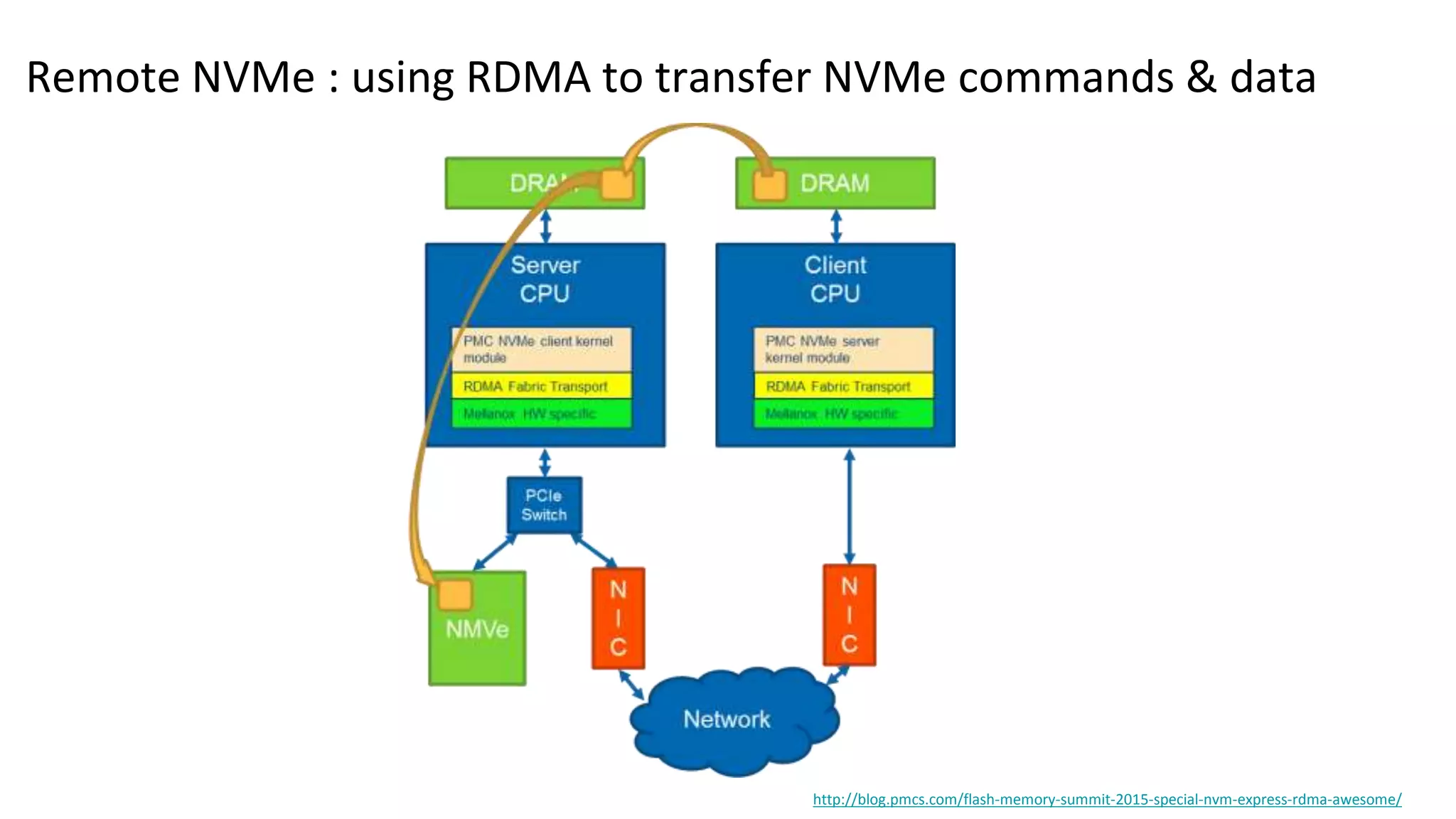
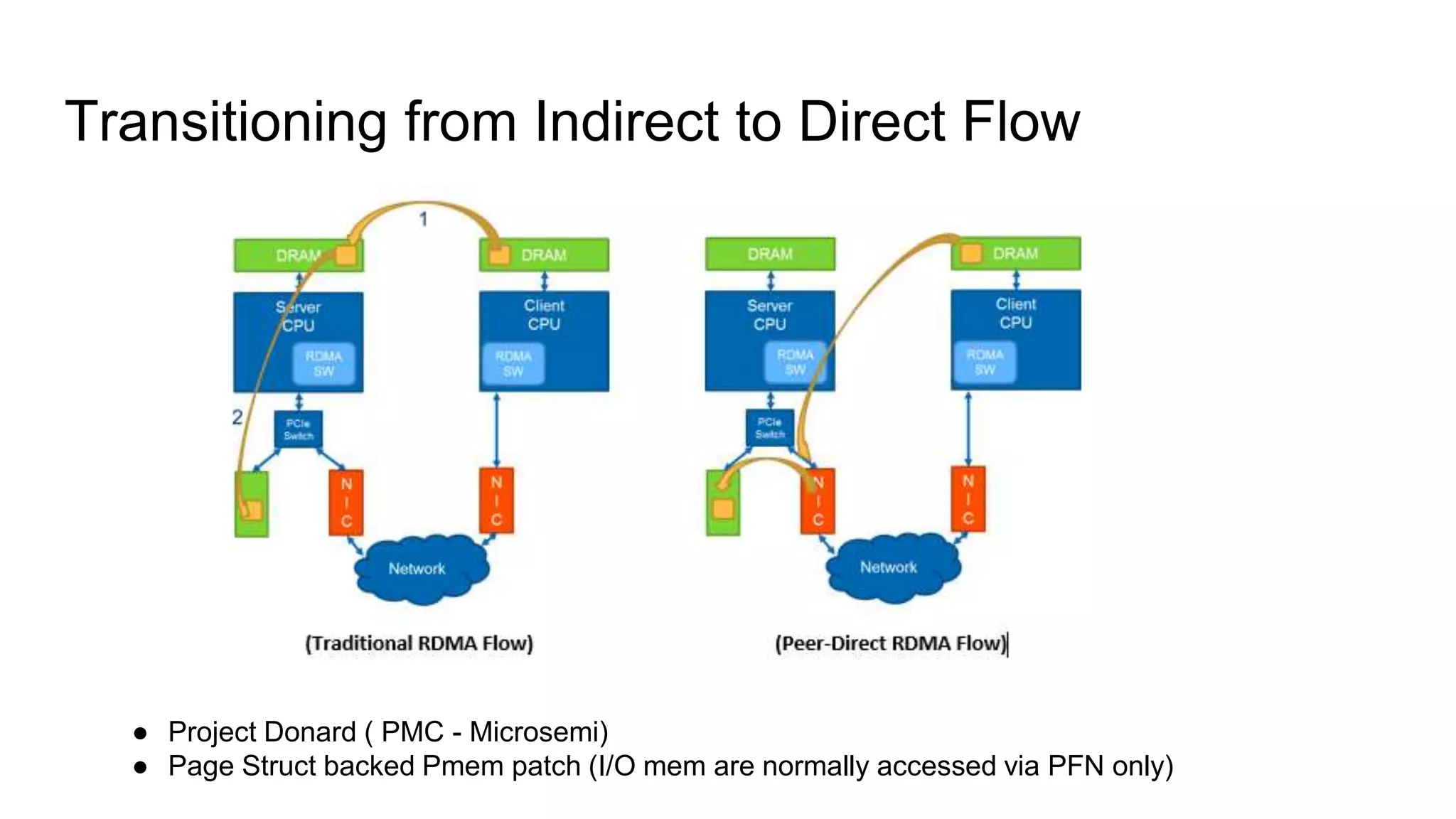
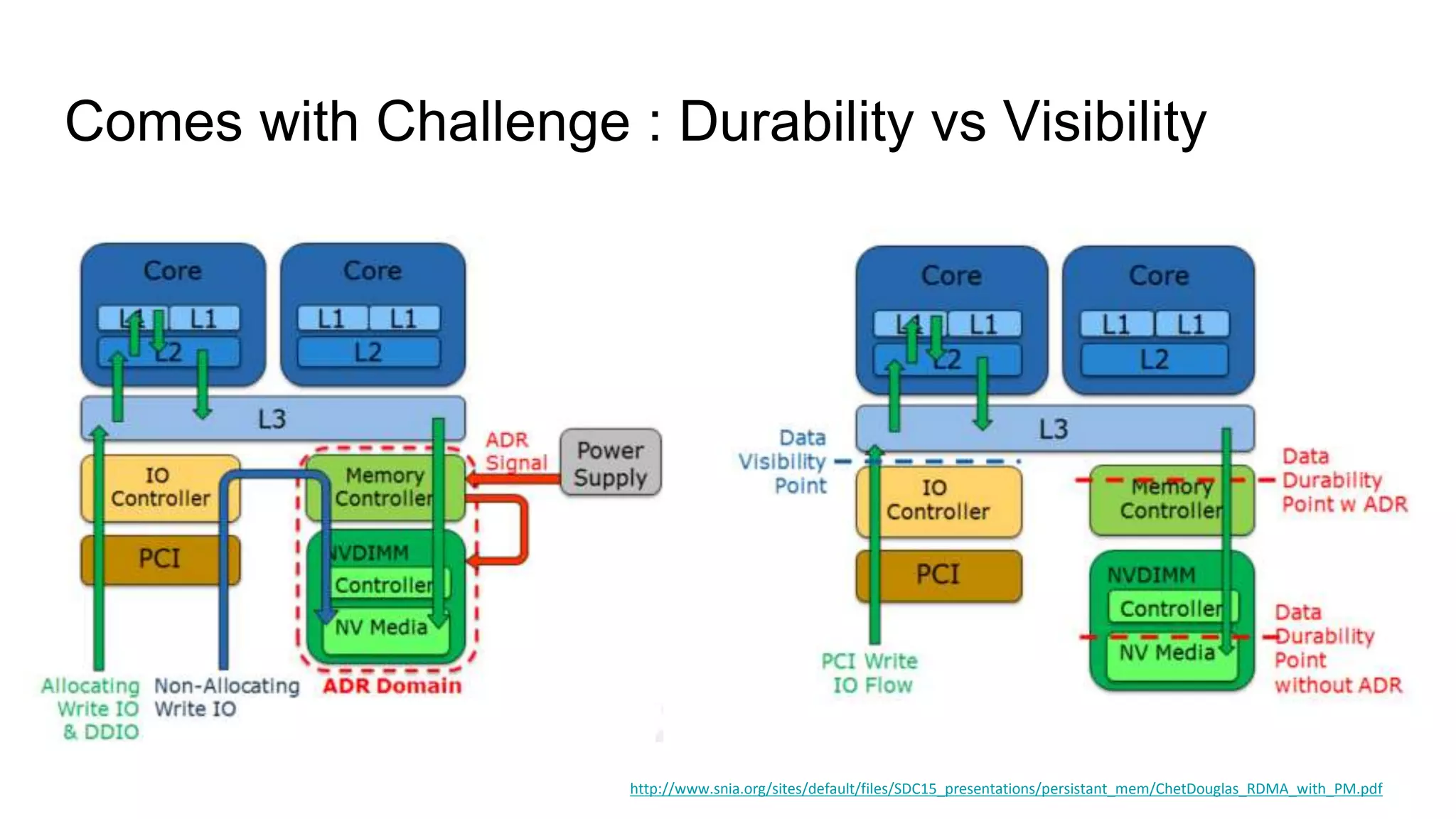
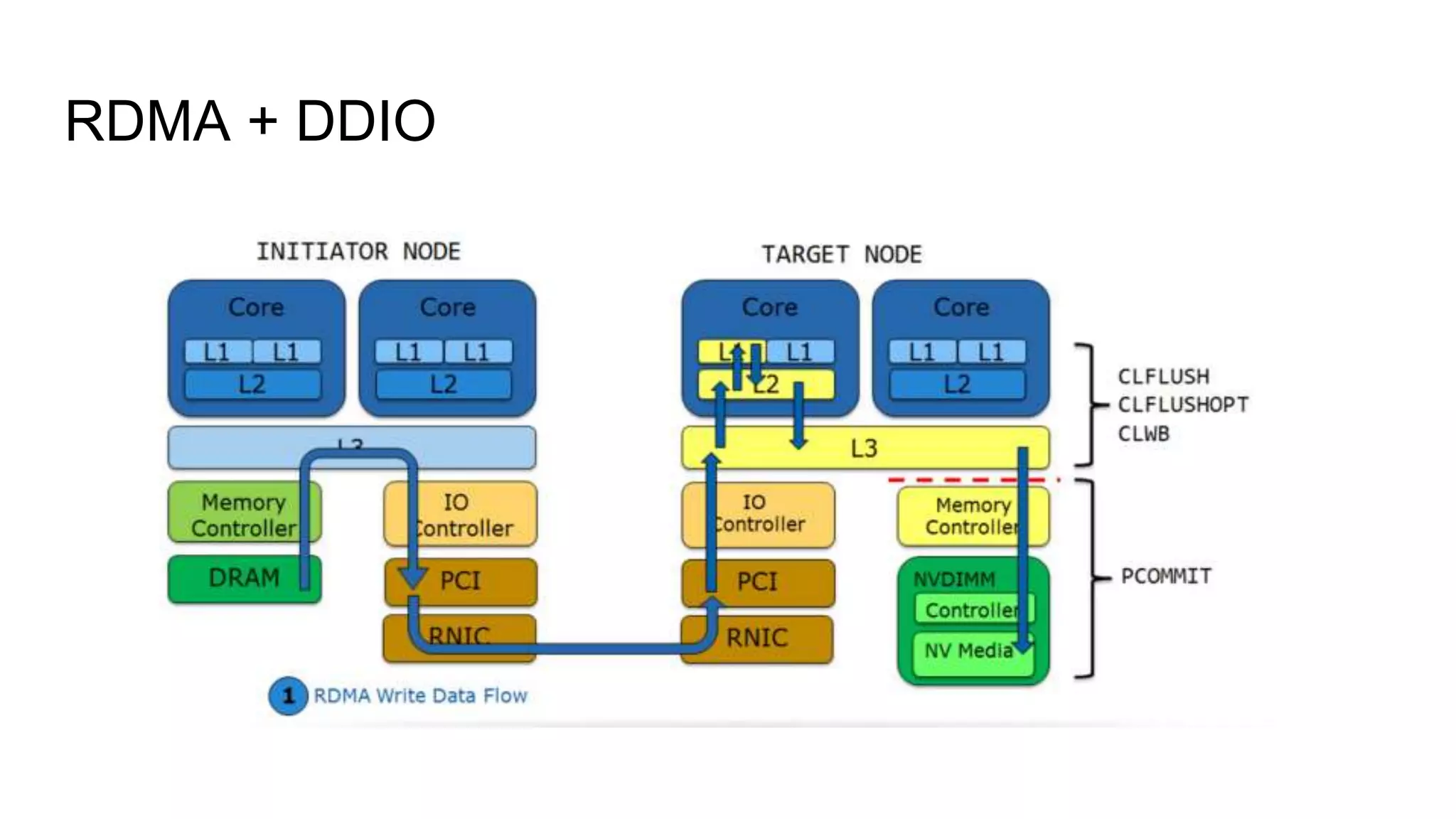
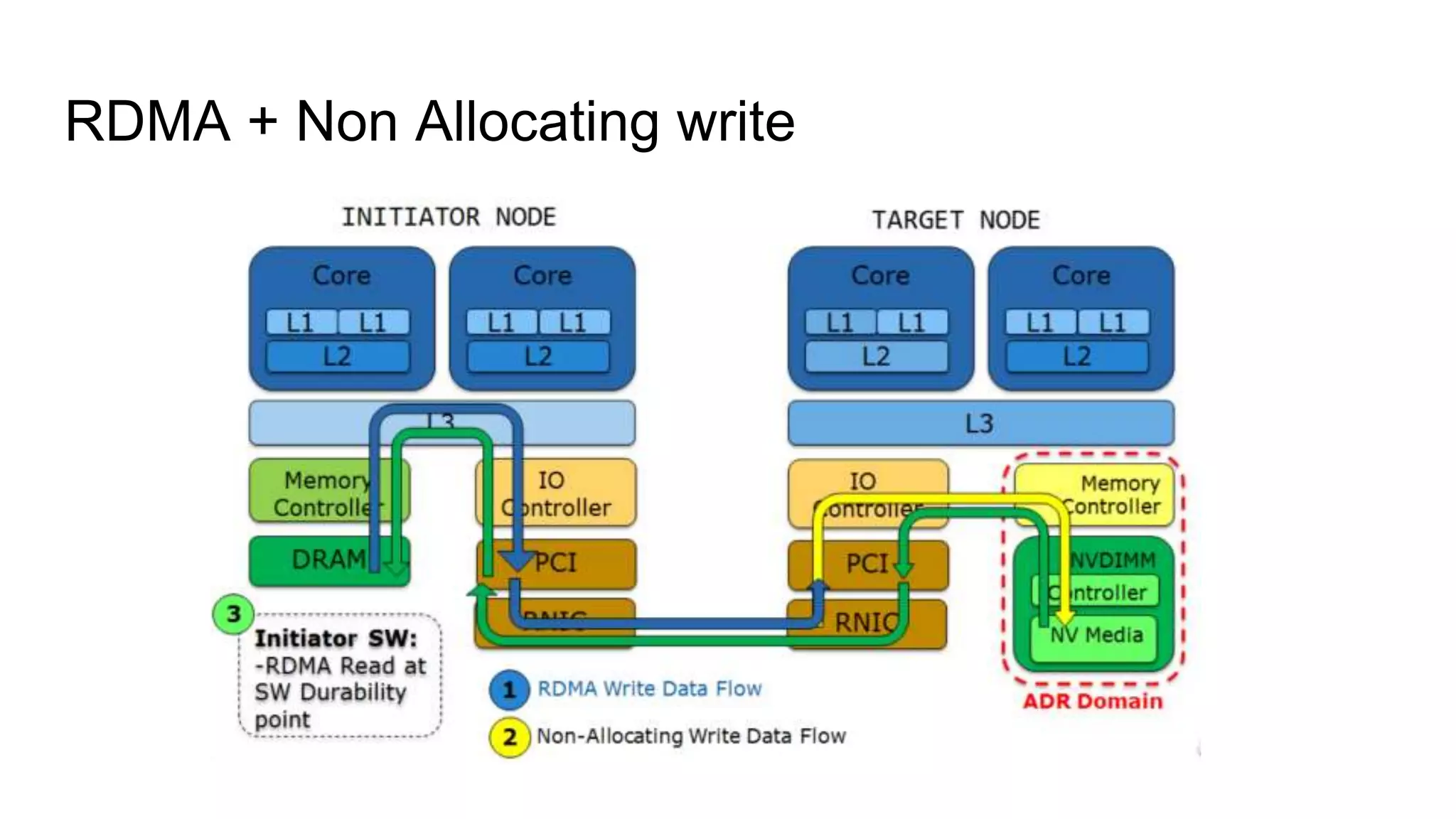
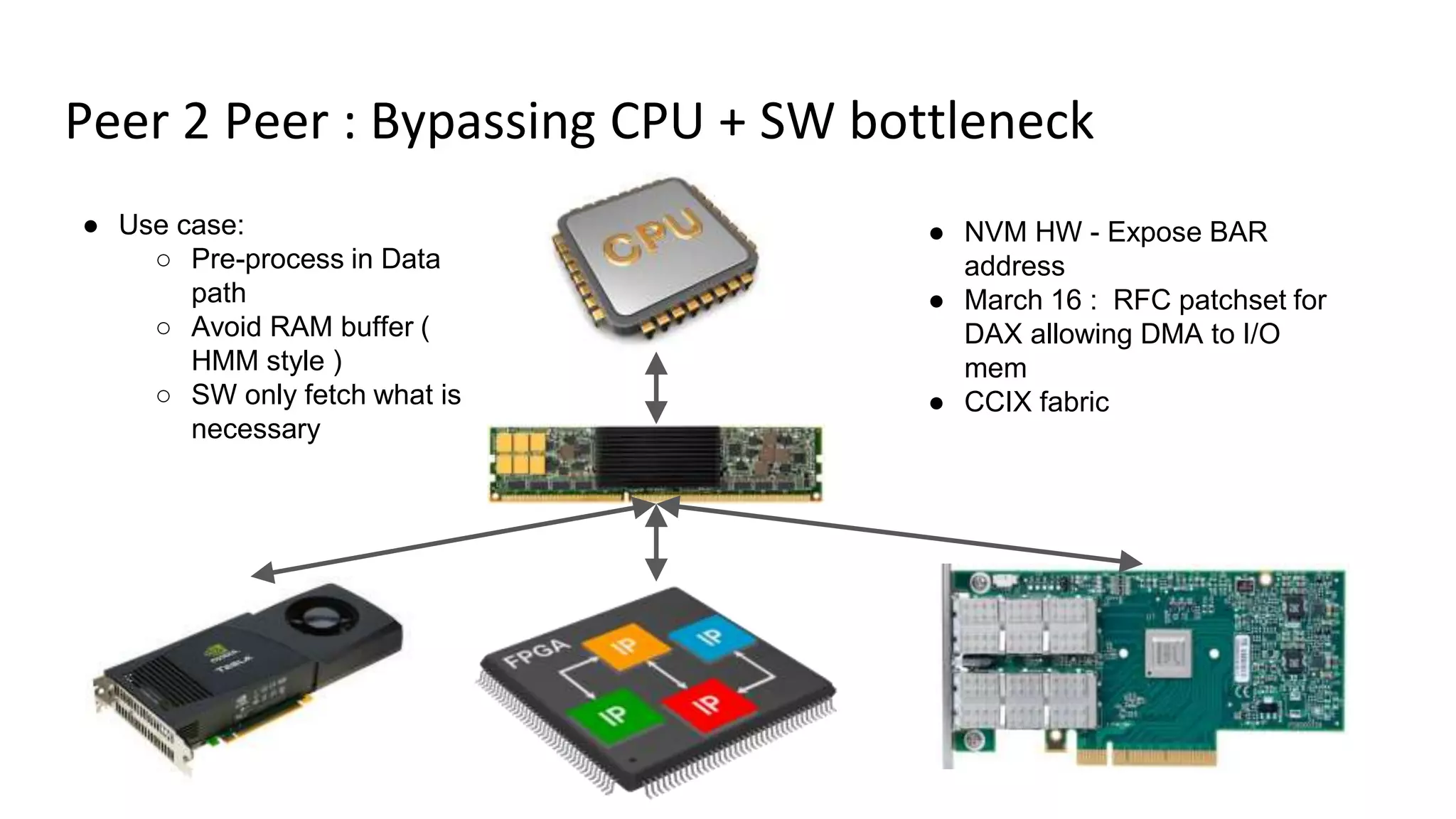
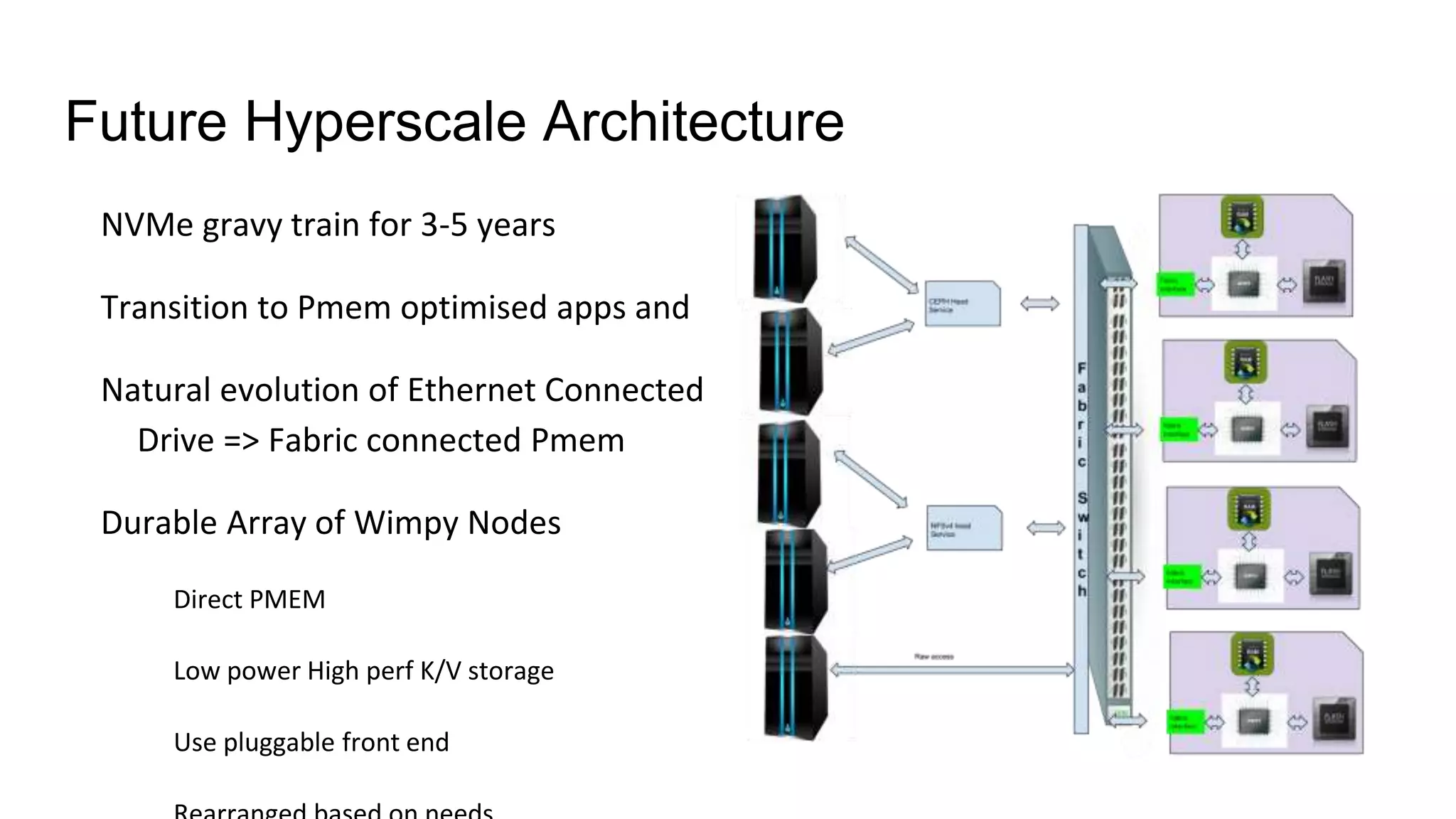
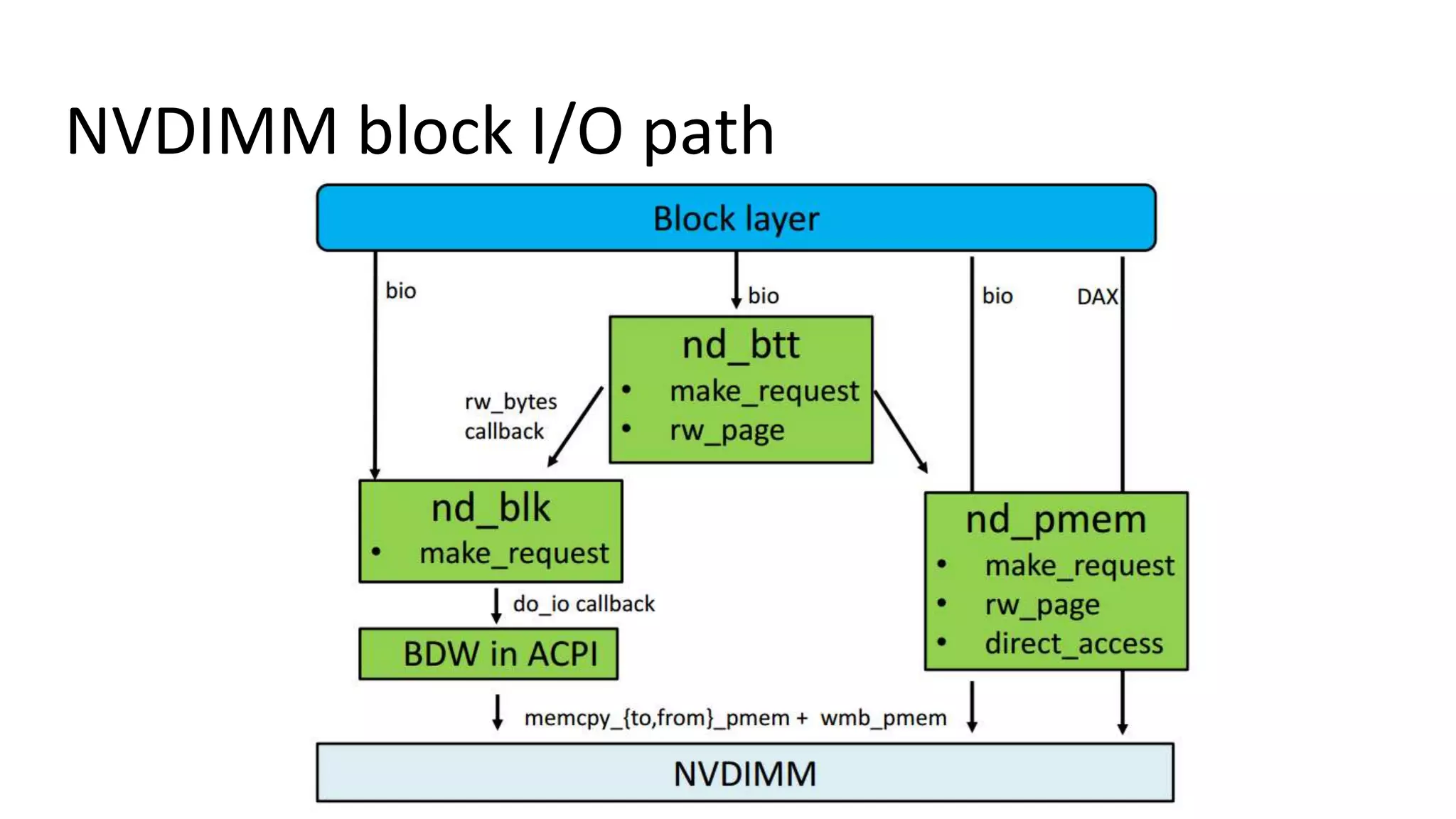
This document discusses persistent memory and the Linux software stack. It begins by covering the evolution of non-volatile memory from battery backed RAM to emerging technologies like PCM and memristors. It then outlines the persistent memory Linux software stack, including the kernel subsystem and NVDIMM architecture. Finally, it discusses using and emulating persistent memory on Linux, including kernel configuration, hardware options, and libraries for programming with persistent memory.