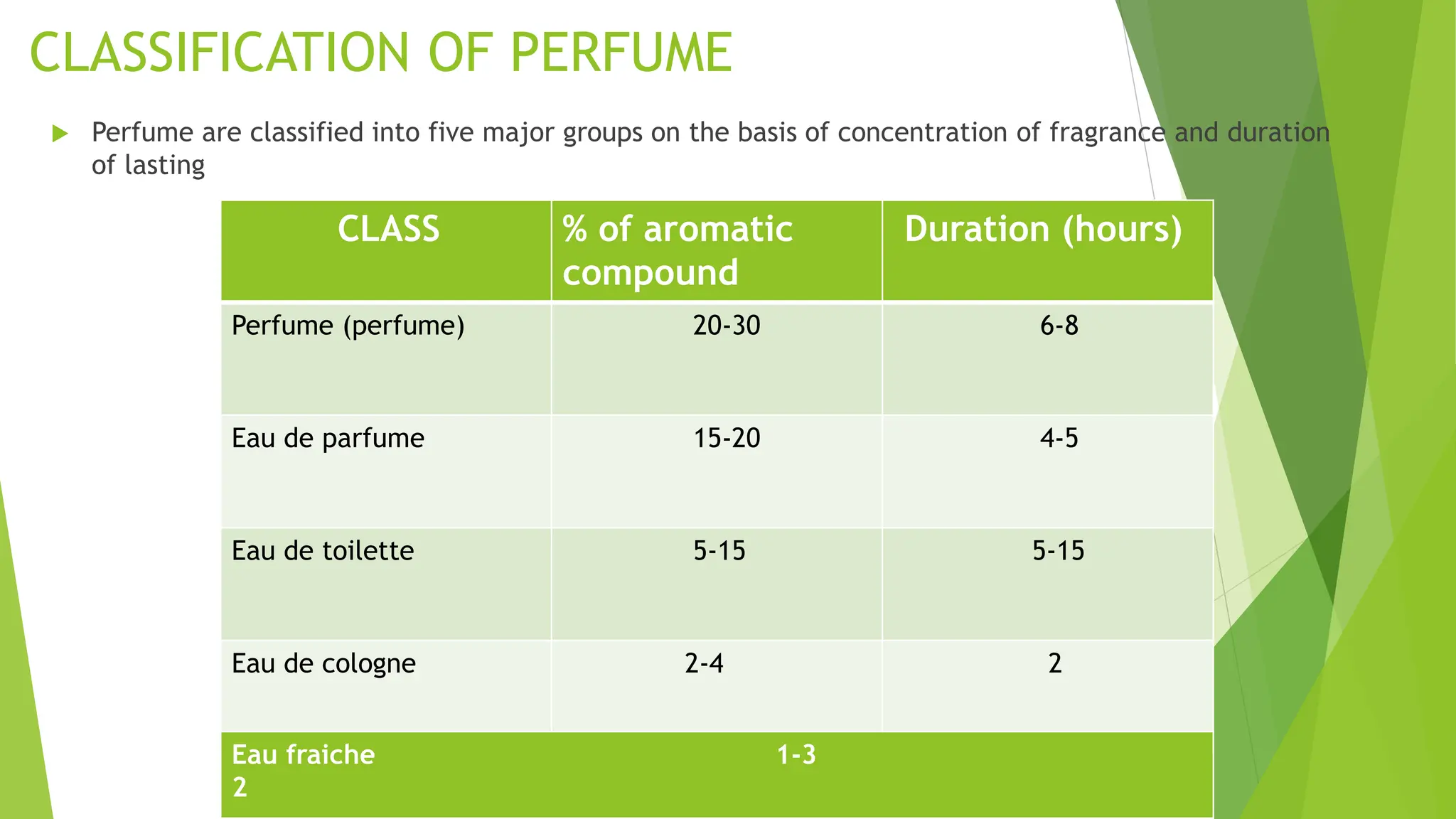
The document discusses perfumes, detailing their definition, history, classification, and manufacturing processes. It highlights the evolution of perfume from ancient religious uses to modern luxury items, outlines different types and classifications based on fragrance concentration, and describes the steps in perfume production. Additionally, it addresses the advantages and disadvantages of wearing perfumes.