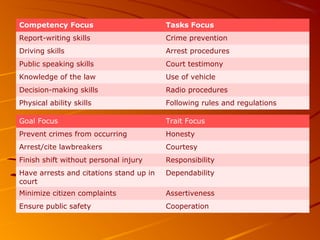
Performance evaluation involves assessing an employee's accomplishment of tasks through effort, commitment, skills and account for factors that may help or hinder performance. It is done to provide feedback to employees, determine salary increases and promotions, and assess productivity. The process involves setting goals and standards mutually agreed upon by the employee and supervisor, monitoring progress through reviews, feedback and documentation, and finally providing an evaluation, feedback, and plans for future development. Dimensions can be focused on traits, competencies, tasks, or goals, with competency-focused being most useful for providing feedback and suggestions to improve.