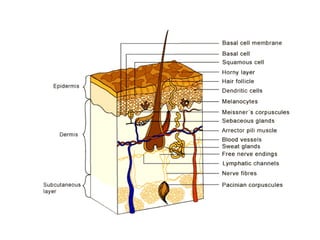
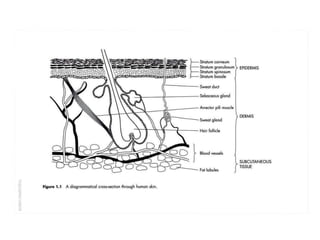
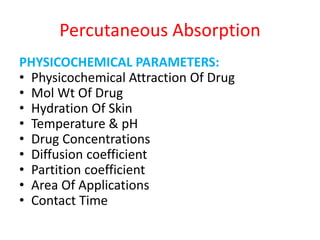
This document discusses percutaneous absorption, which is the absorption of drugs through the skin. It describes the structure of skin, which consists of the epidermis and dermis layers. Percutaneous absorption involves drugs diffusing through the stratum corneum barrier and into the skin microcirculation. The rate of absorption is affected by factors like the drug's physicochemical properties, skin conditions, and techniques used to enhance delivery like hydration, ultrasound, or chemical enhancers. The goal is to maximize bioavailability by overcoming the stratum corneum barrier through various approaches.