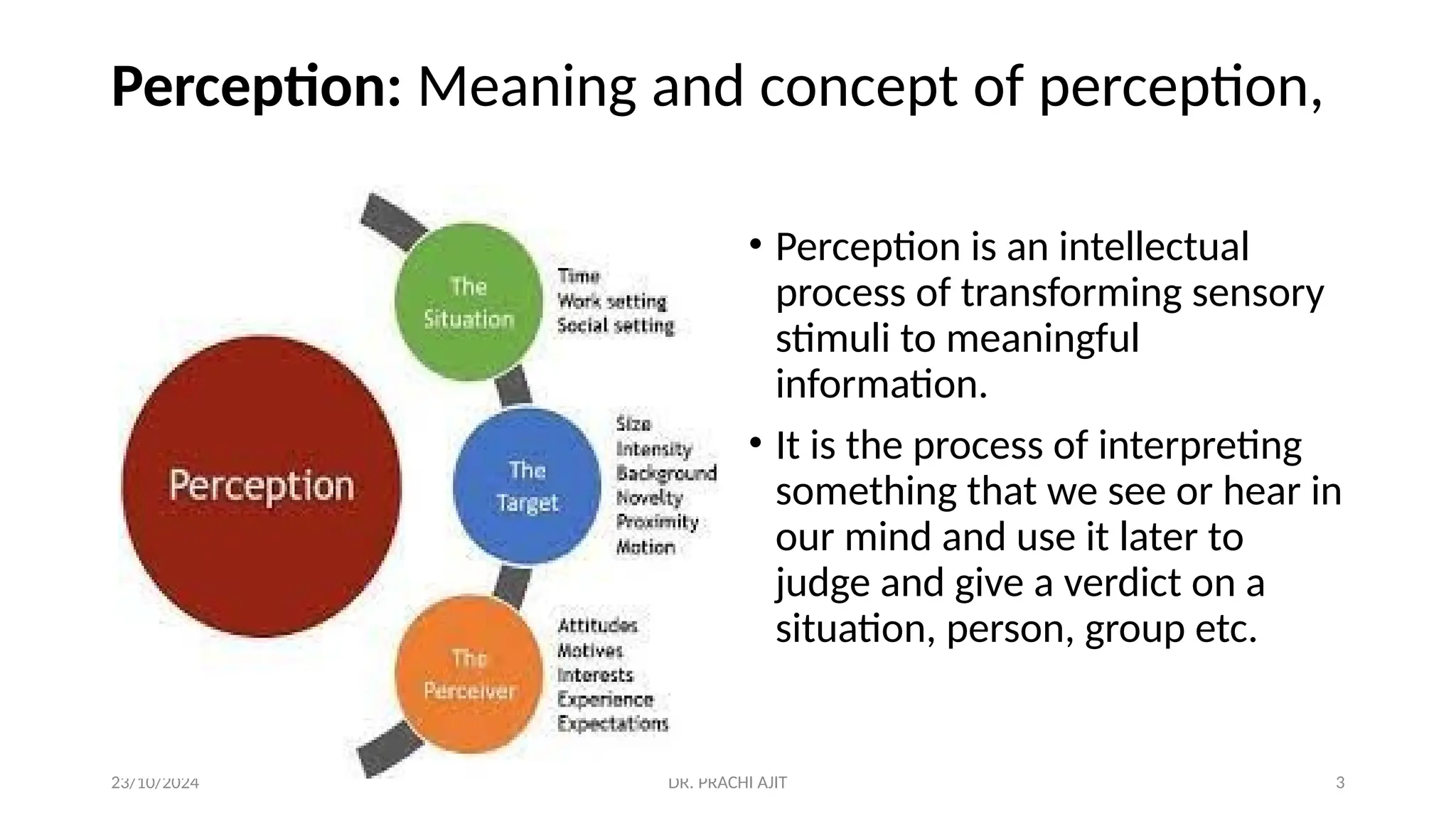
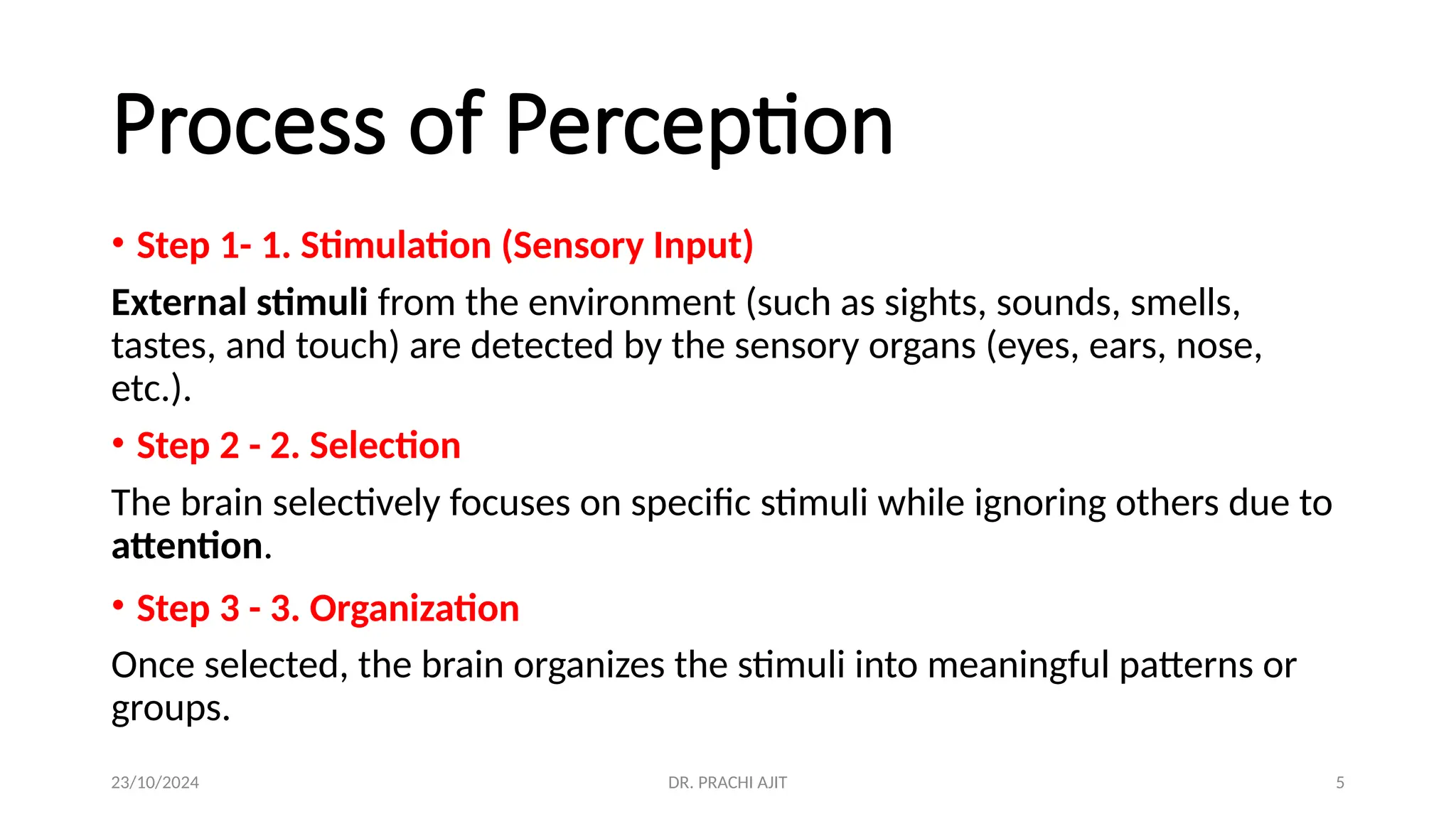
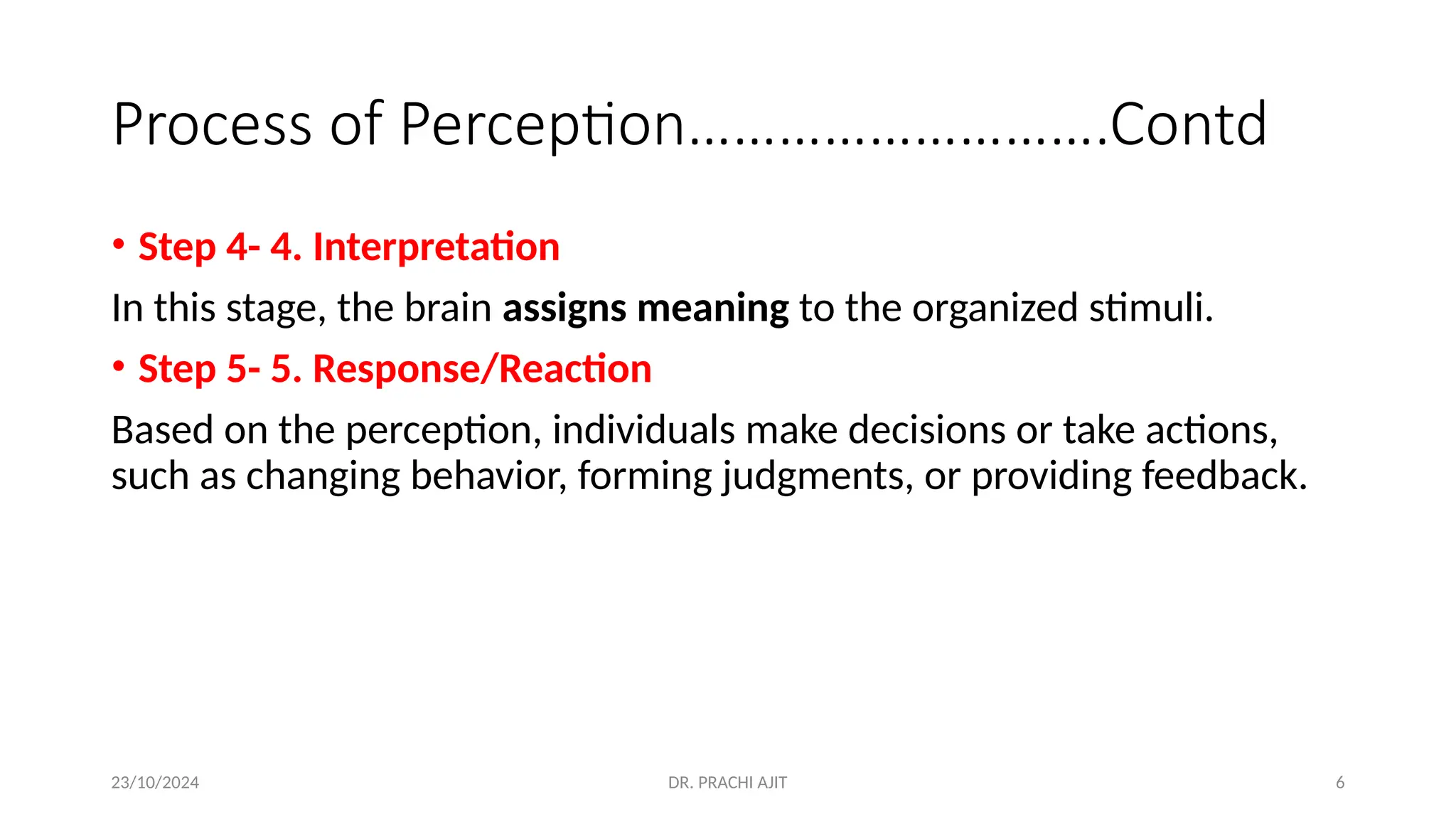
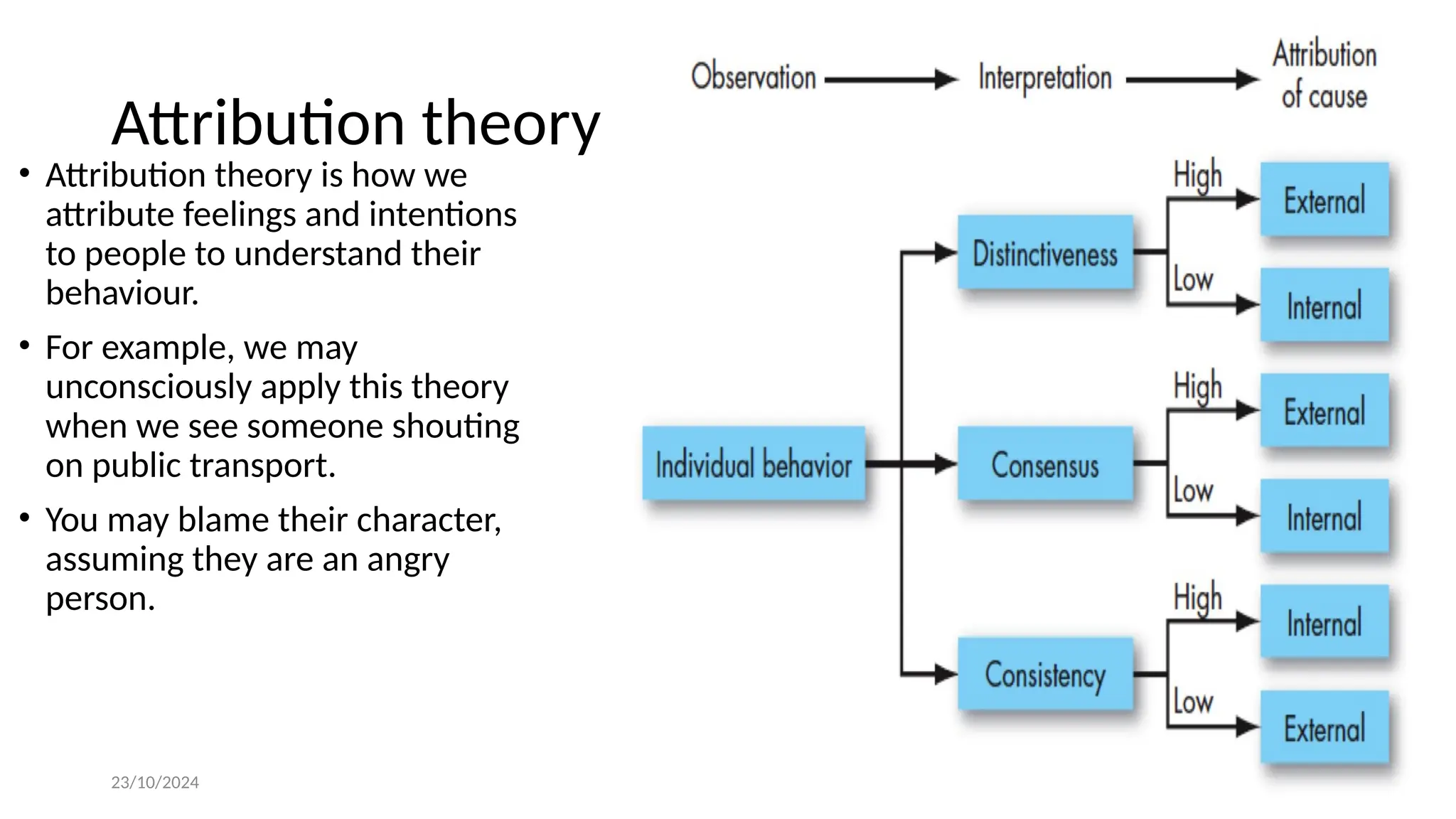
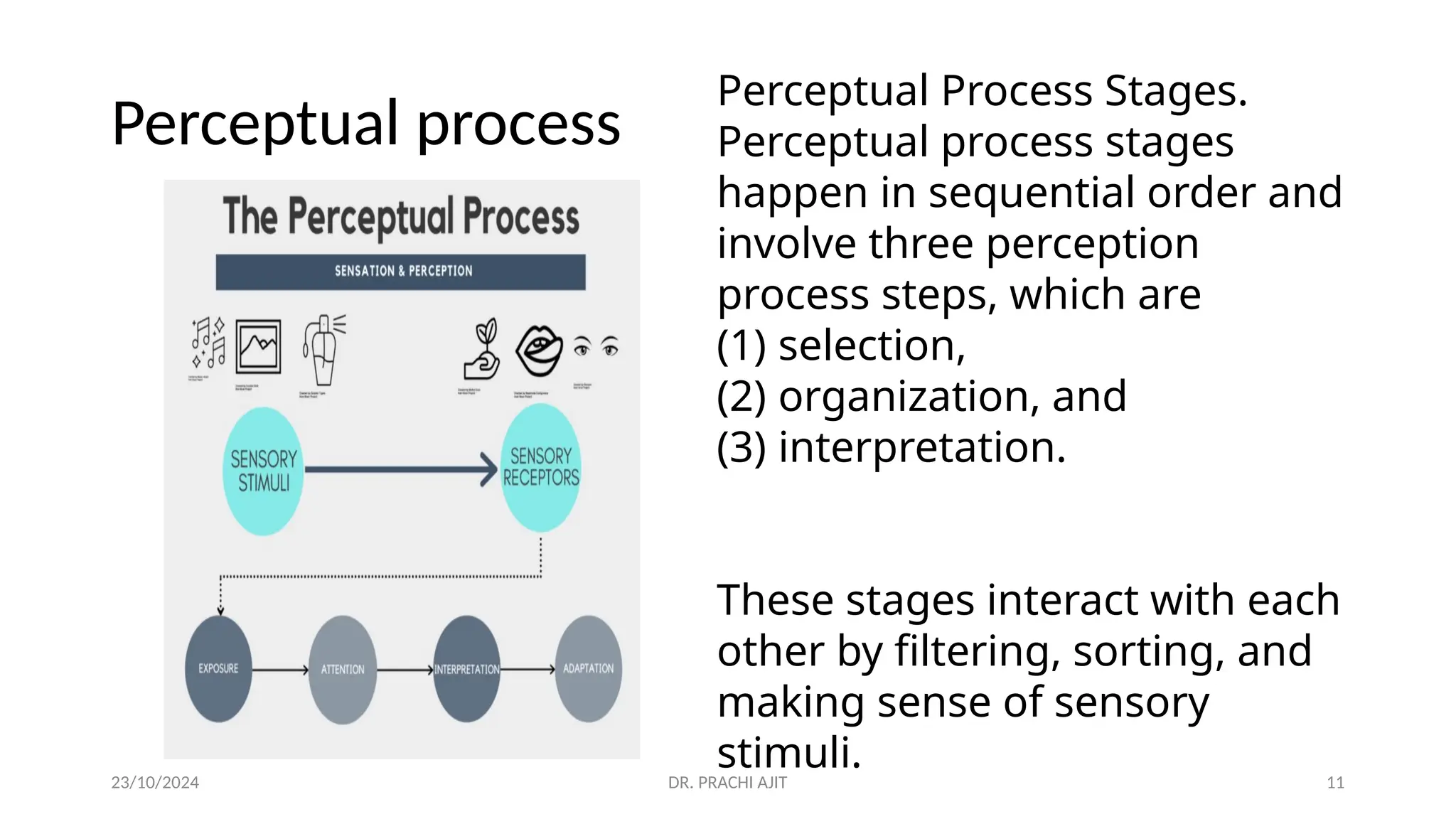
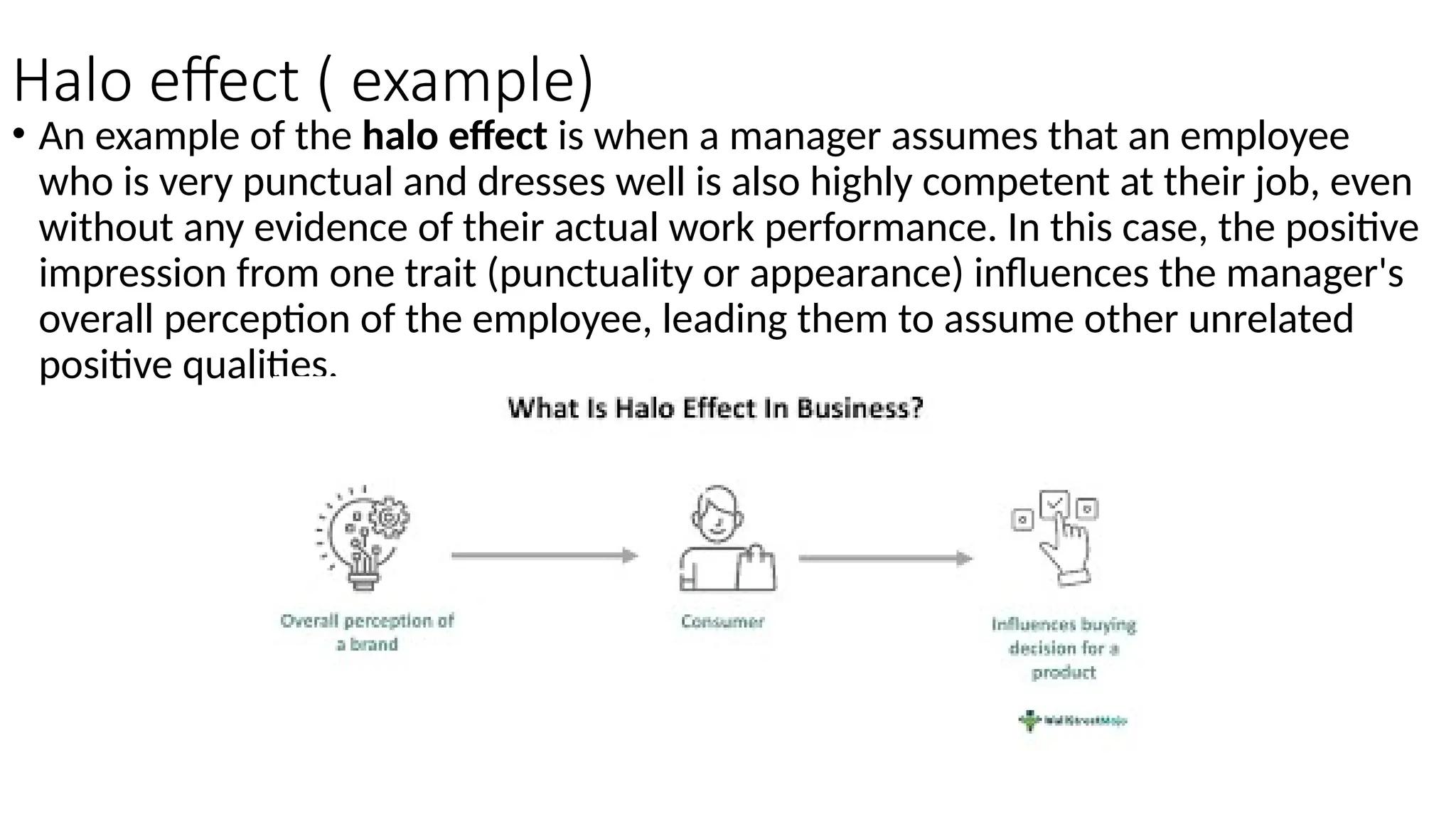
The document discusses the concept of perception, outlining its definition, process, and factors that influence it, such as personal, situational, and social factors. It details the perceptual process in five steps: stimulation, selection, organization, interpretation, and response, and introduces theories like selective perception and attribution theory. Additionally, it examines social perception, including stereotyping and the halo effect, providing examples of how these concepts can lead to biases in judgment.