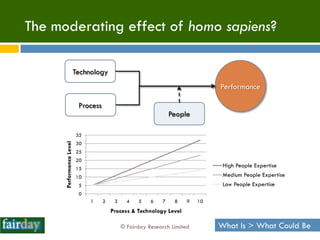
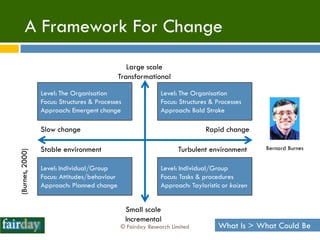
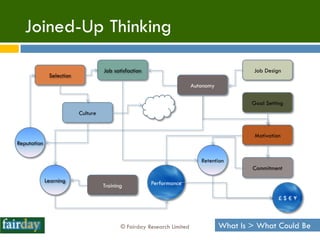
The document discusses the importance of 'people expertise' in Information Technology Service Management (ITSM), emphasizing that human factors significantly influence project success. It argues for the integration of psychological principles into ITSM practices to enhance motivation, culture, and performance among teams. The overall thesis posits that combining ITIL with people science can lead to improved outcomes in service management projects.