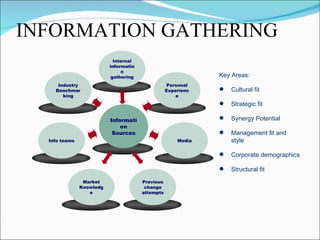
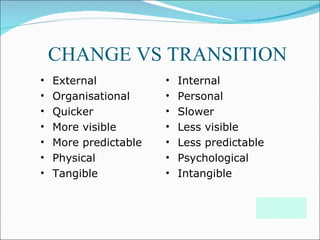
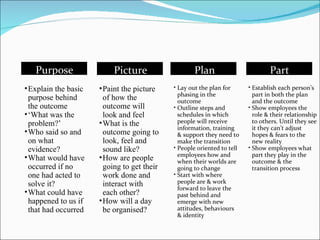
This document discusses change management and provides information on various aspects of managing organizational change. It defines change management as a structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from their current state to a desired future state. It also lists common reasons for the need for change in organizations, such as new strategies, technology, competition, and mergers/acquisitions. The document outlines several models and approaches for managing change, including establishing a sense of urgency, creating a vision and communication plan, empowering others, and institutionalizing new approaches. It also discusses potential pitfalls to avoid and keys to leading successful change initiatives.