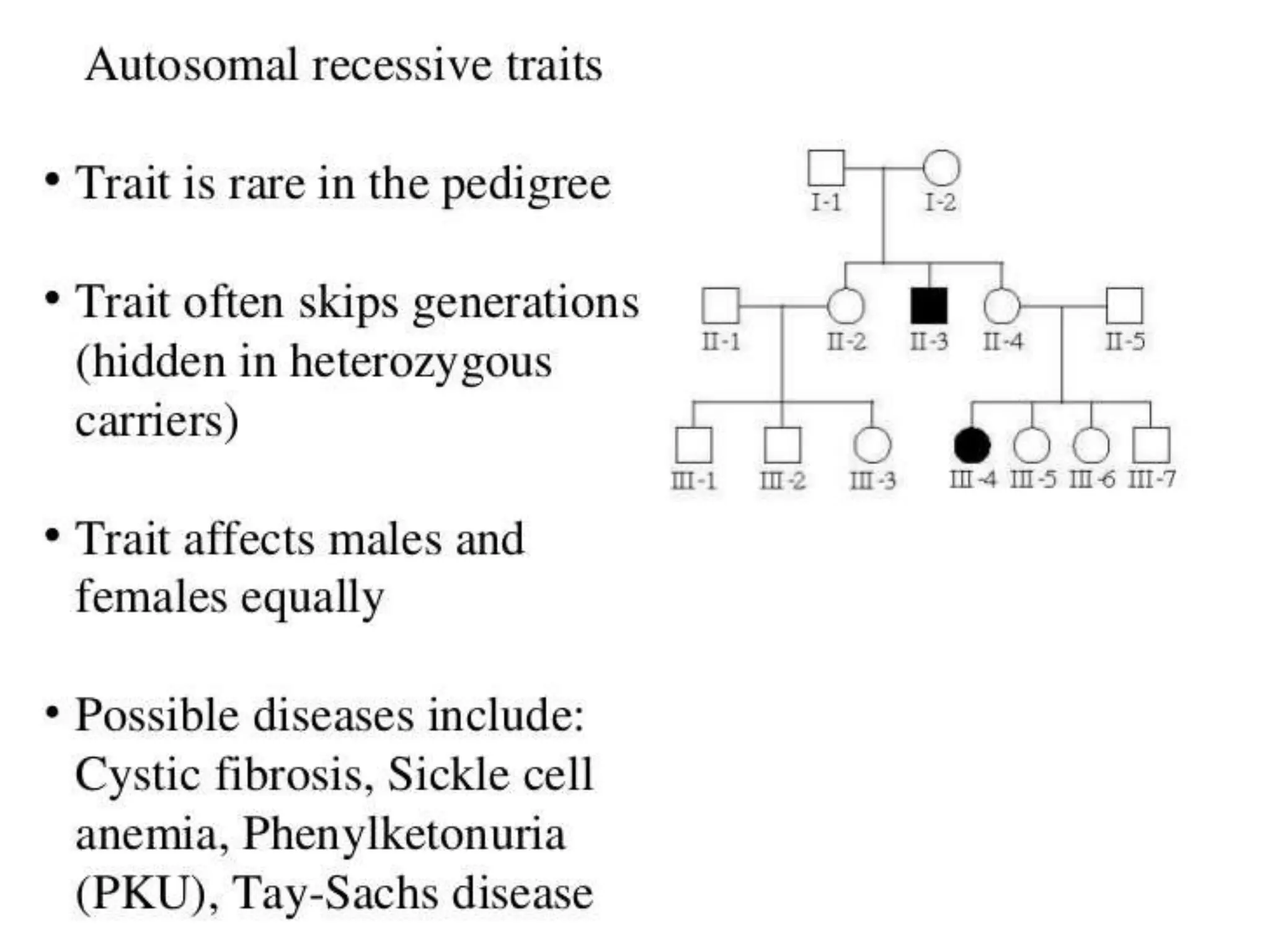
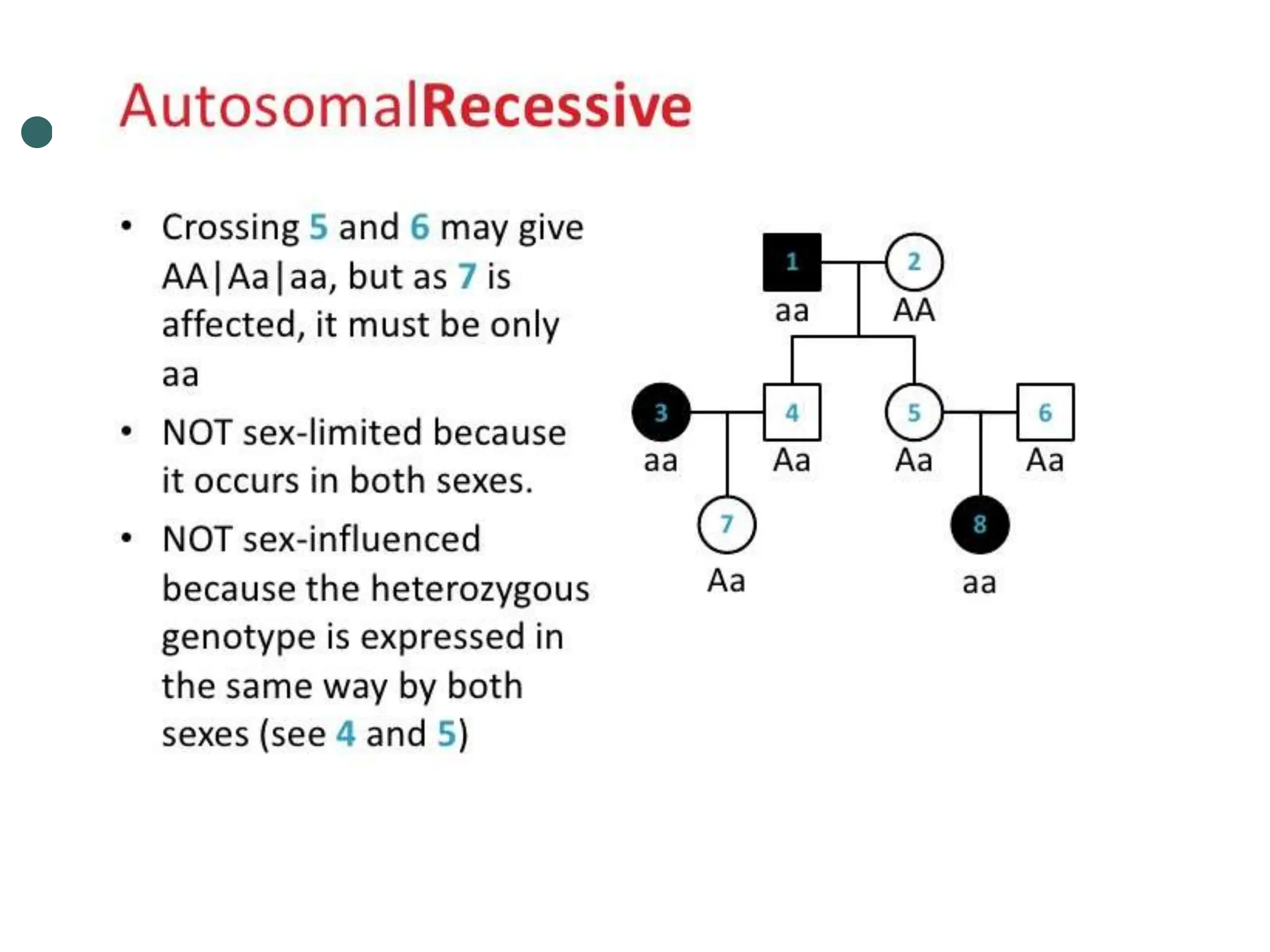
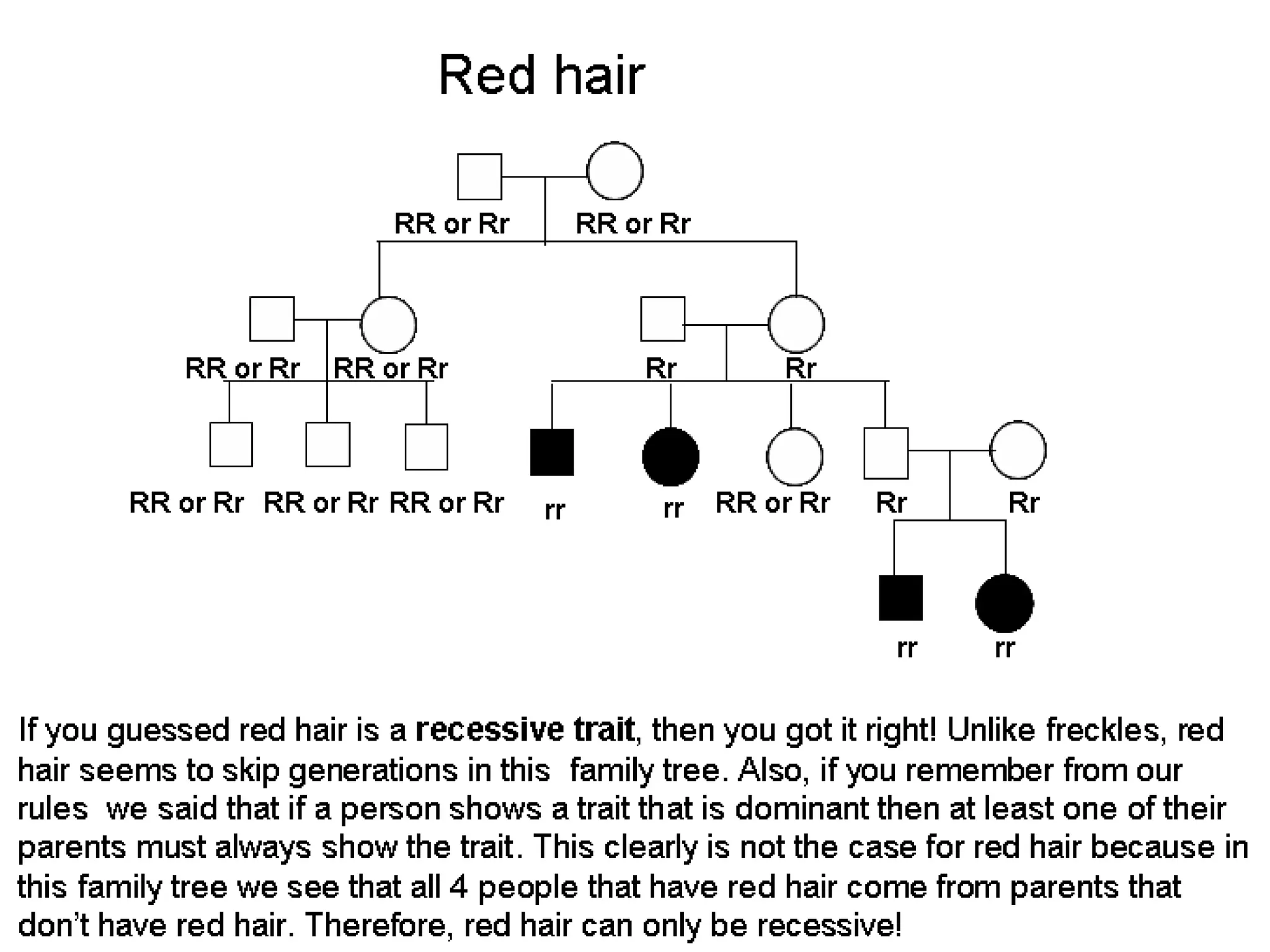
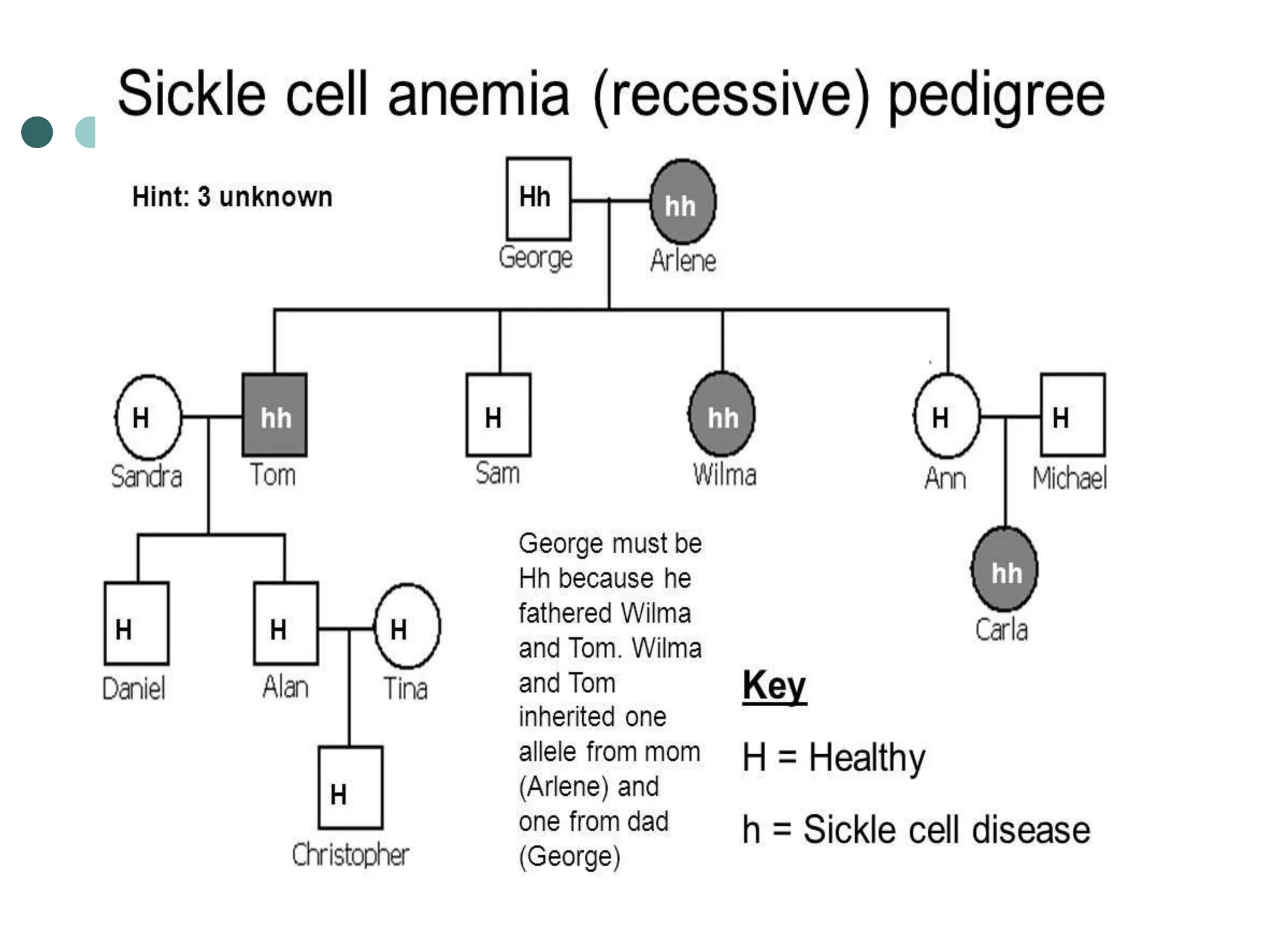
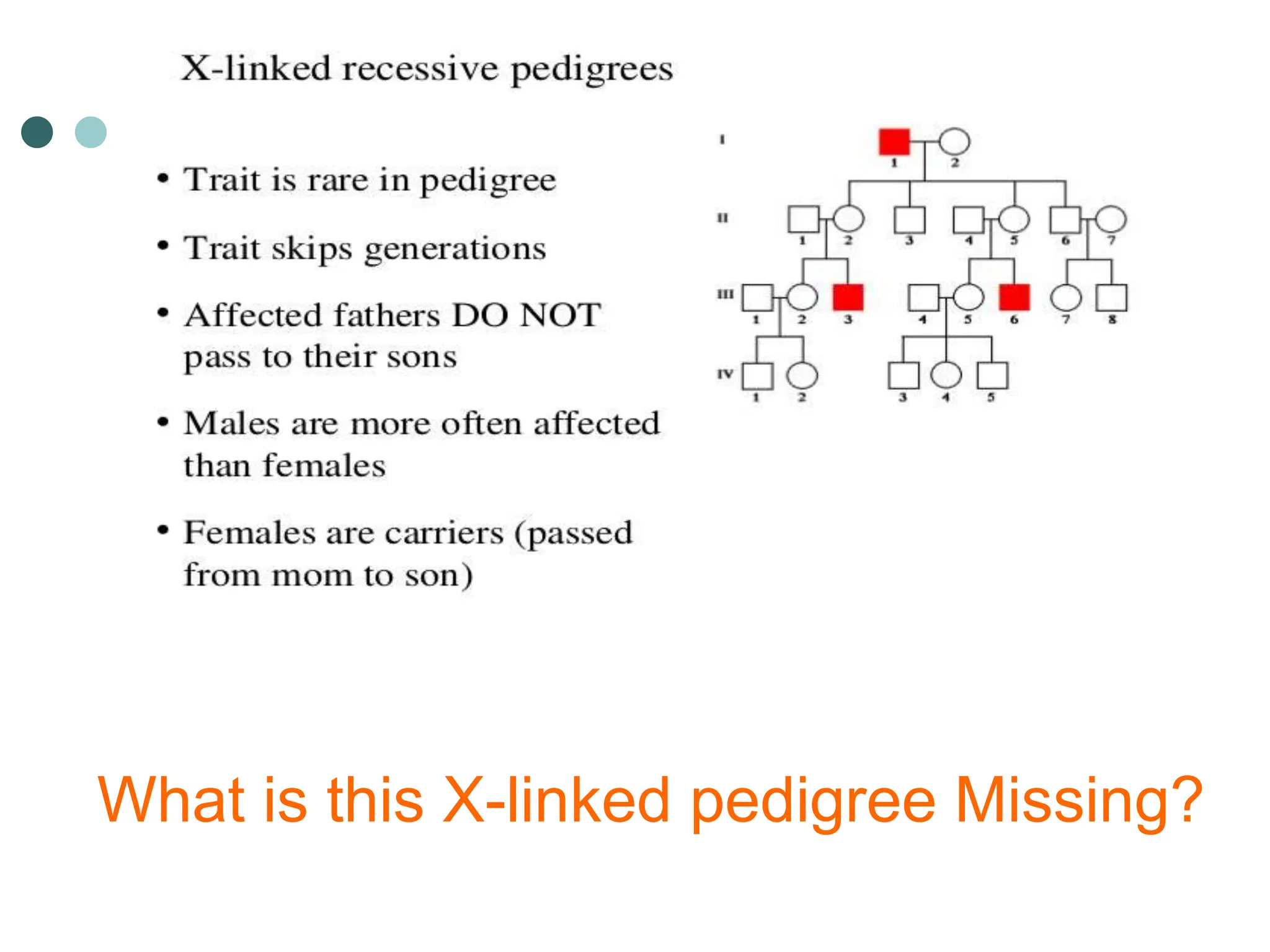
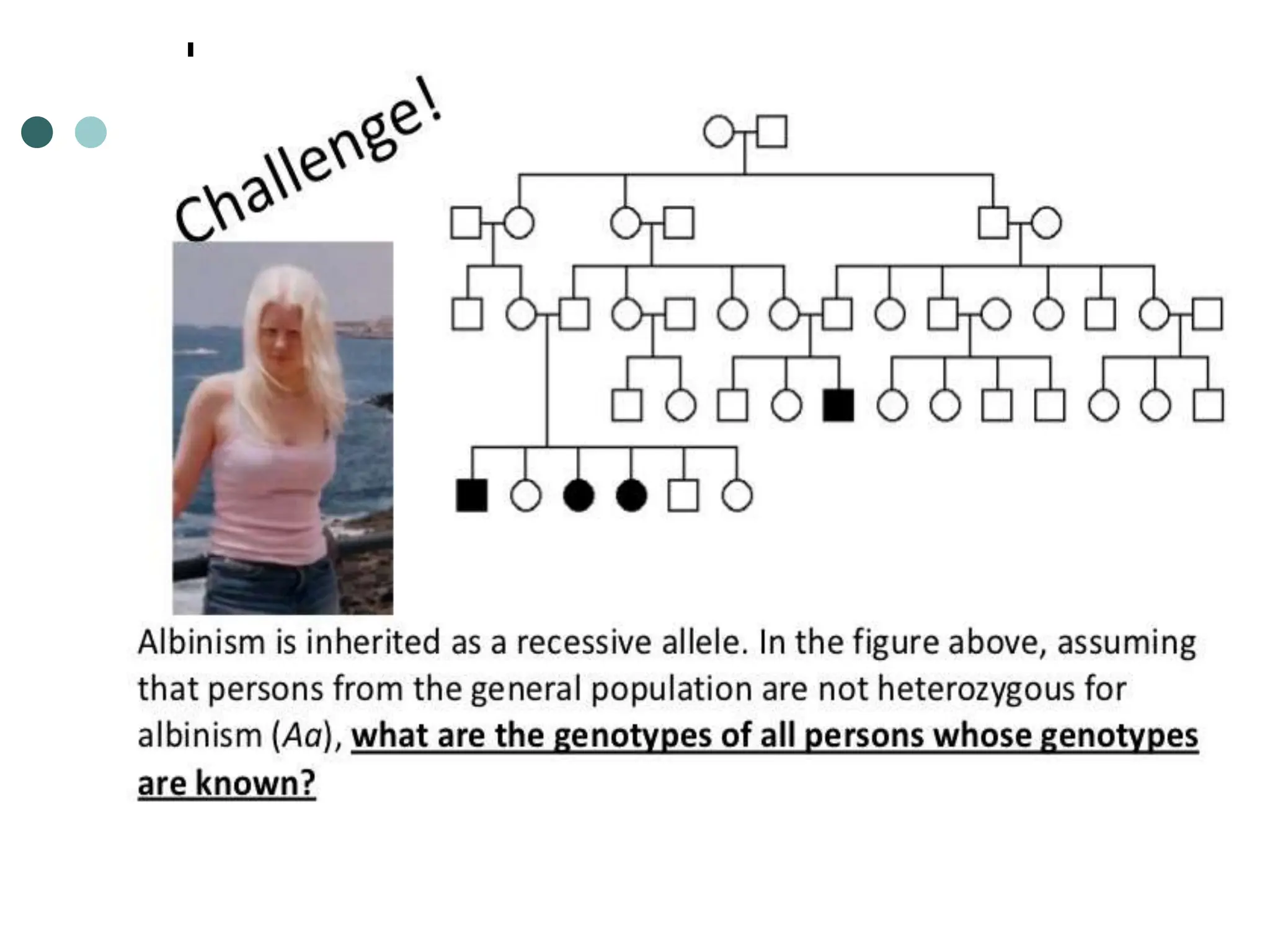
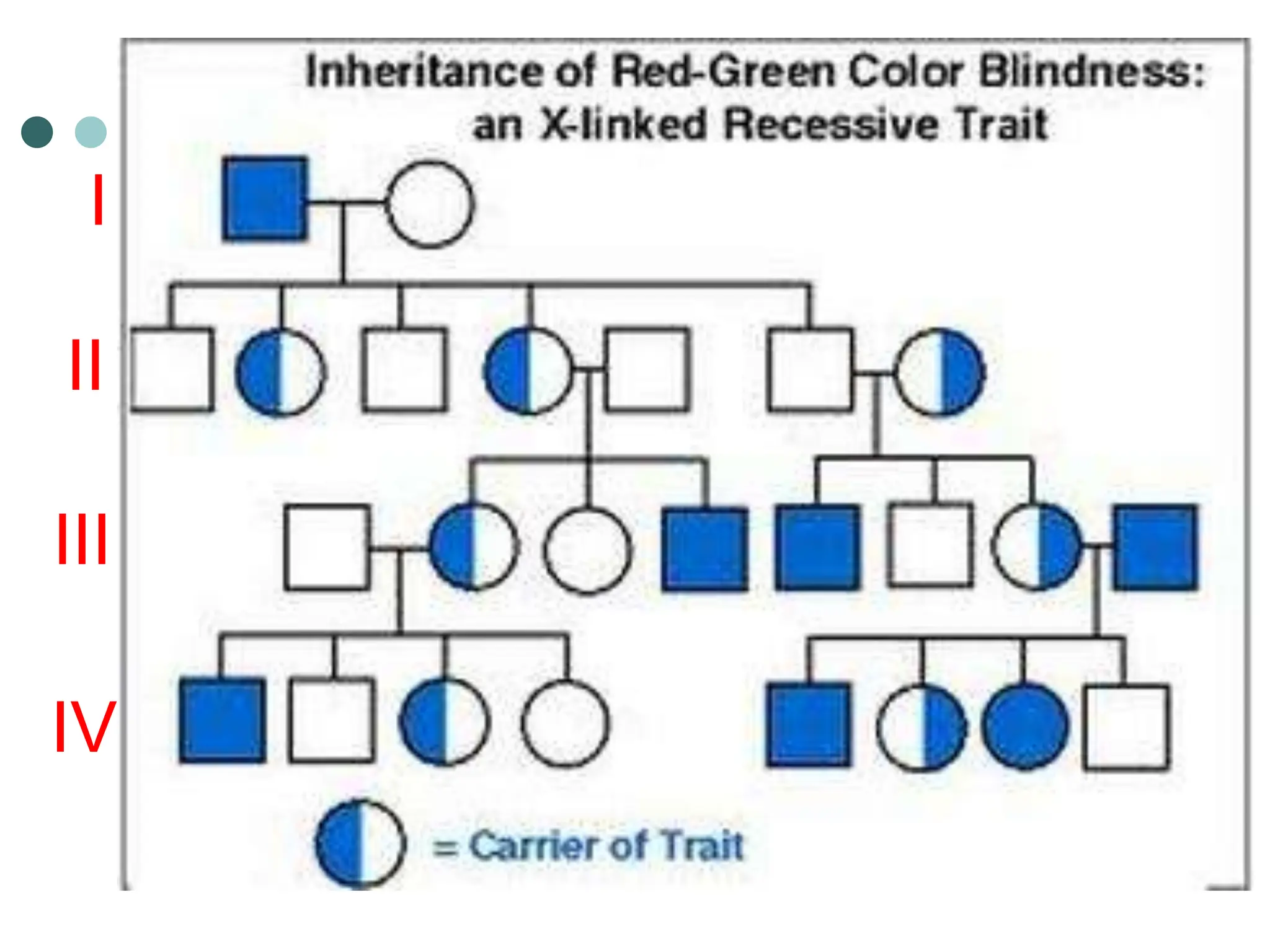
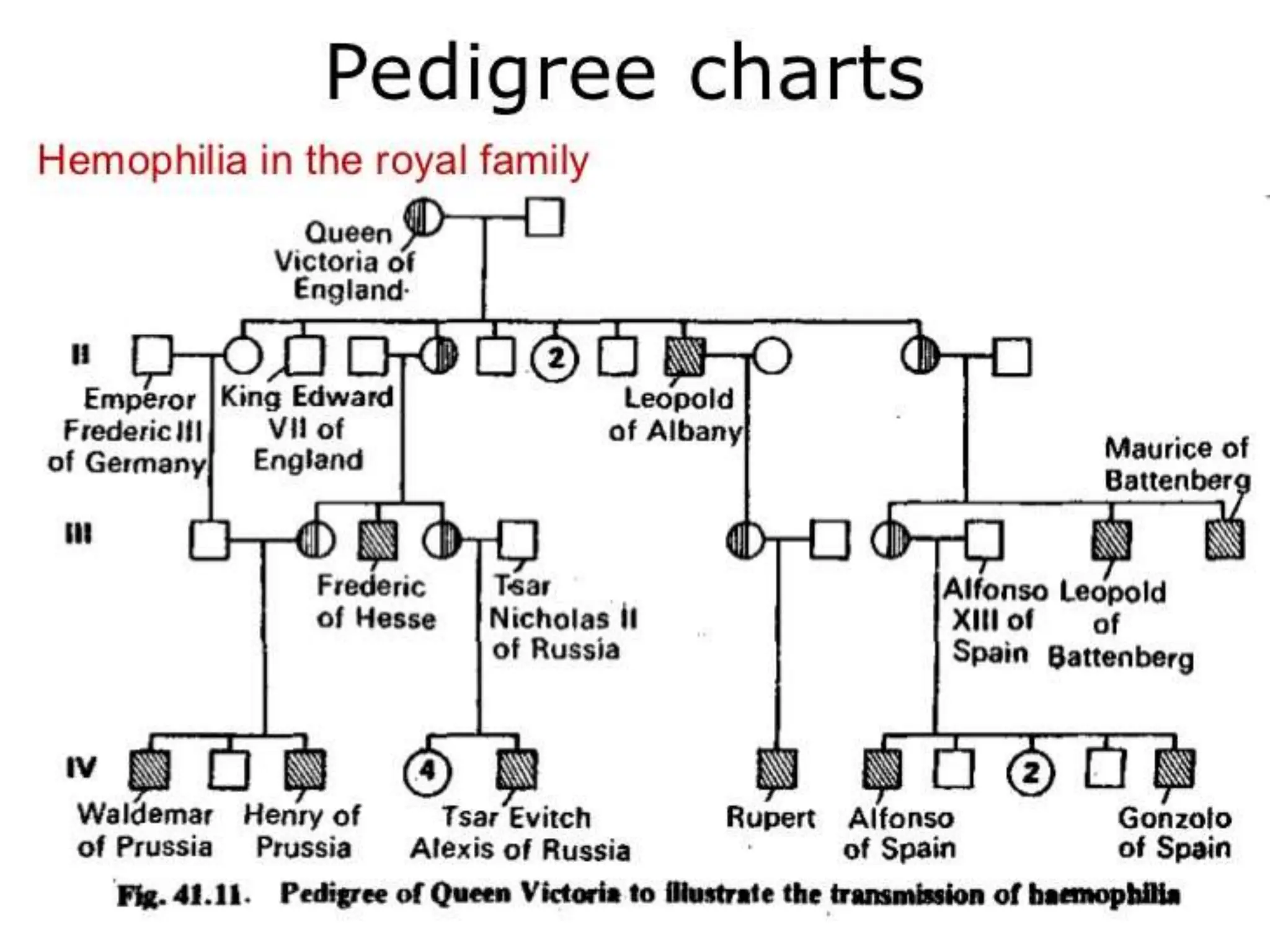
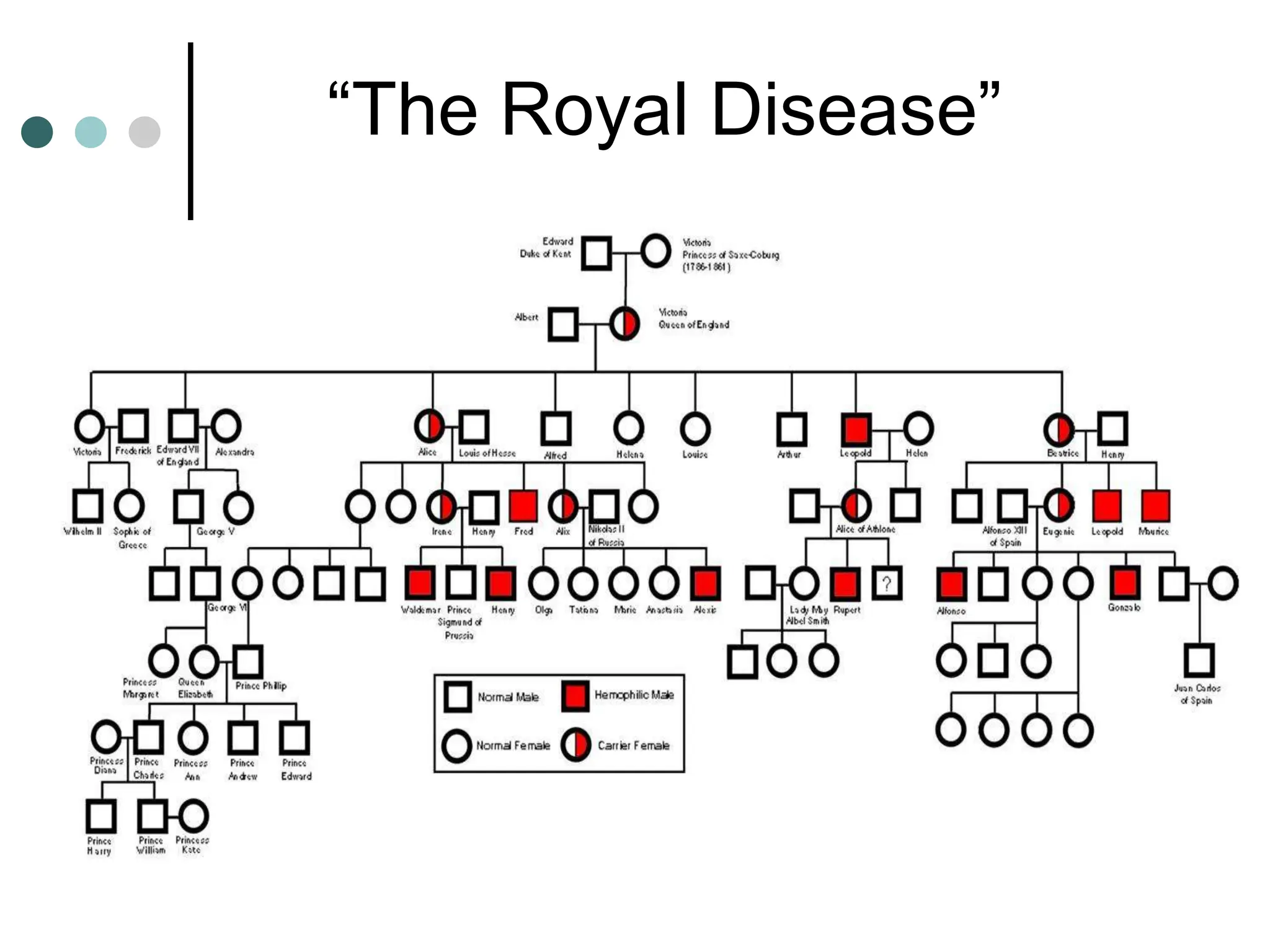
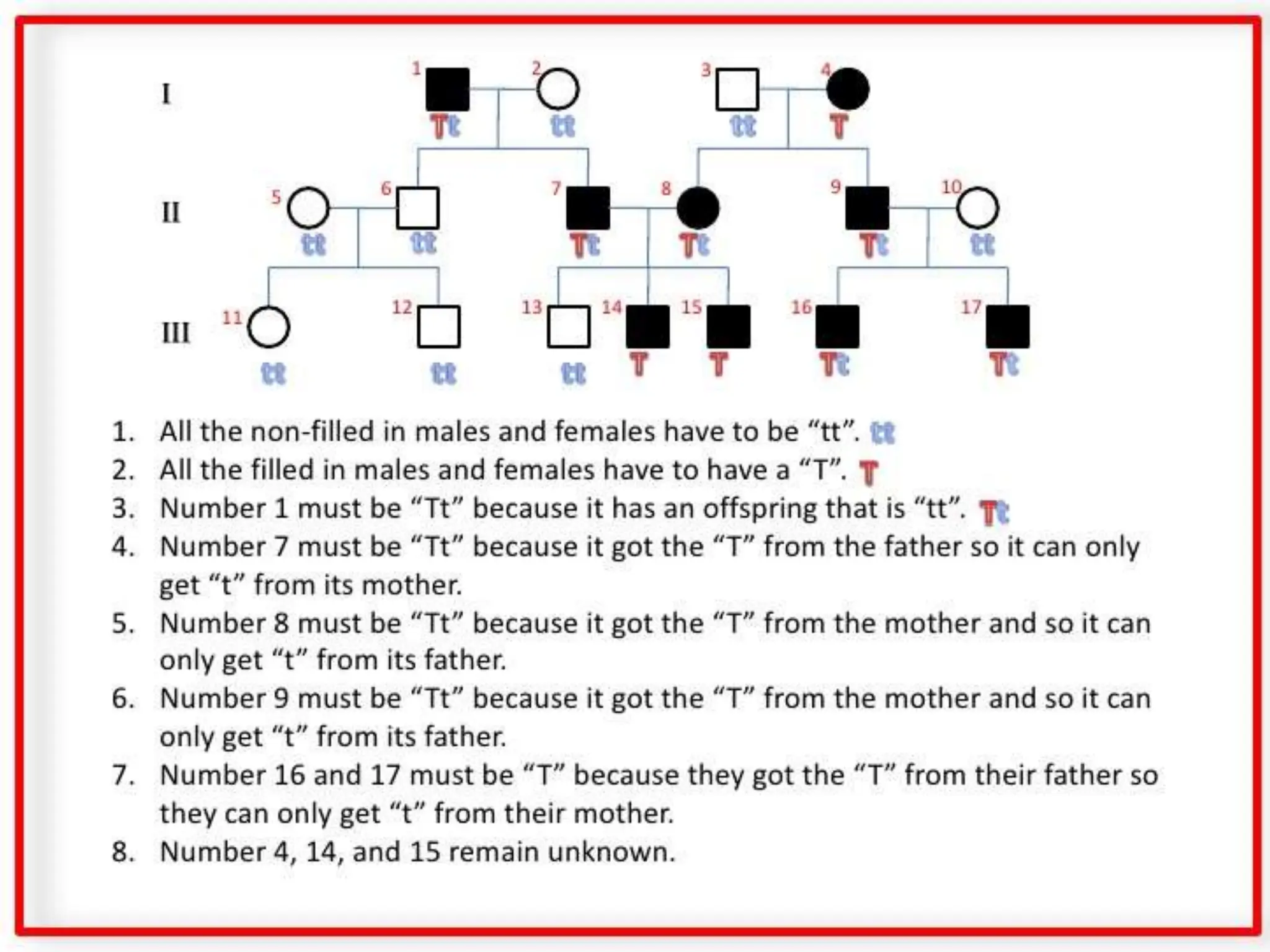
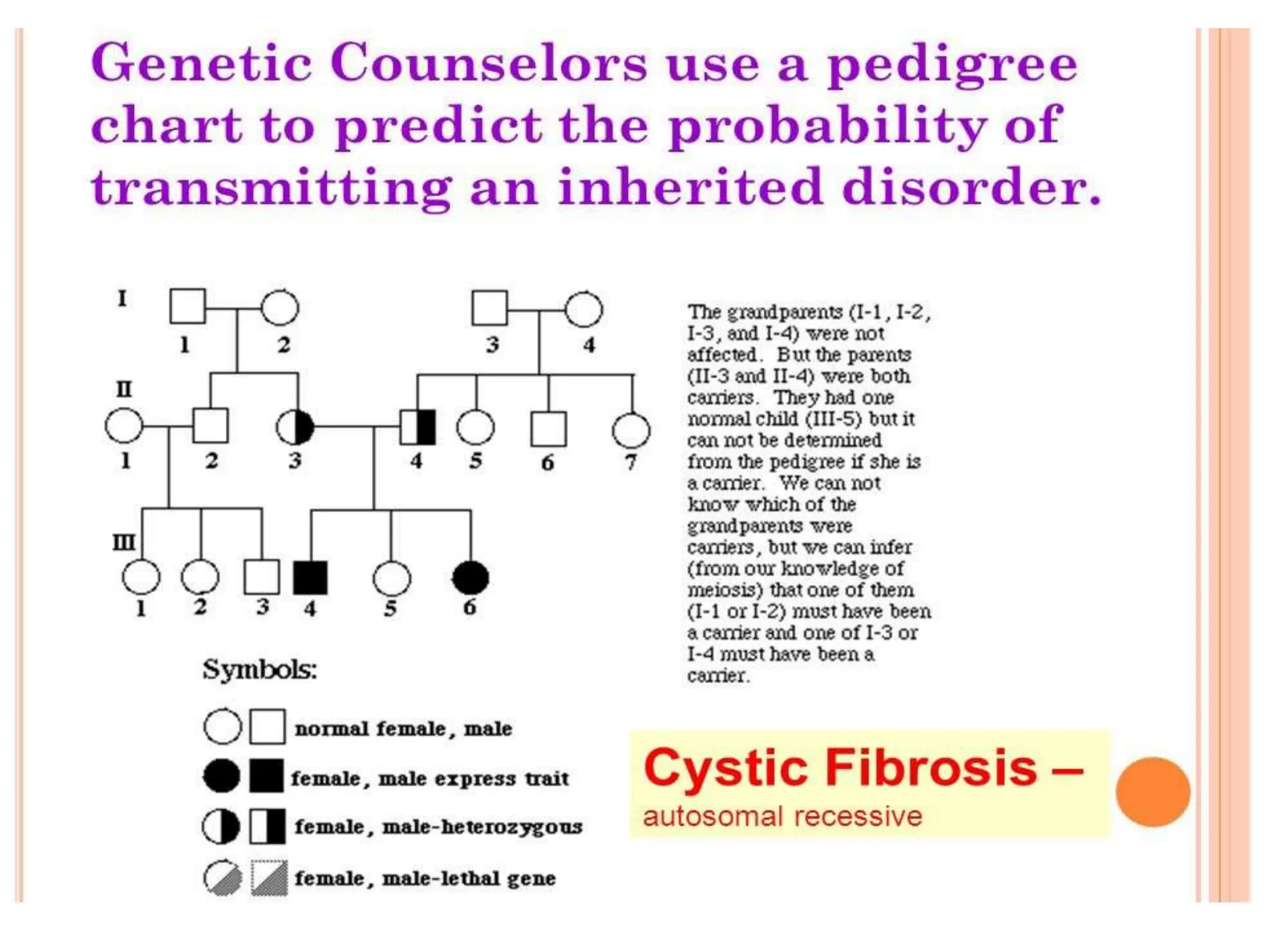
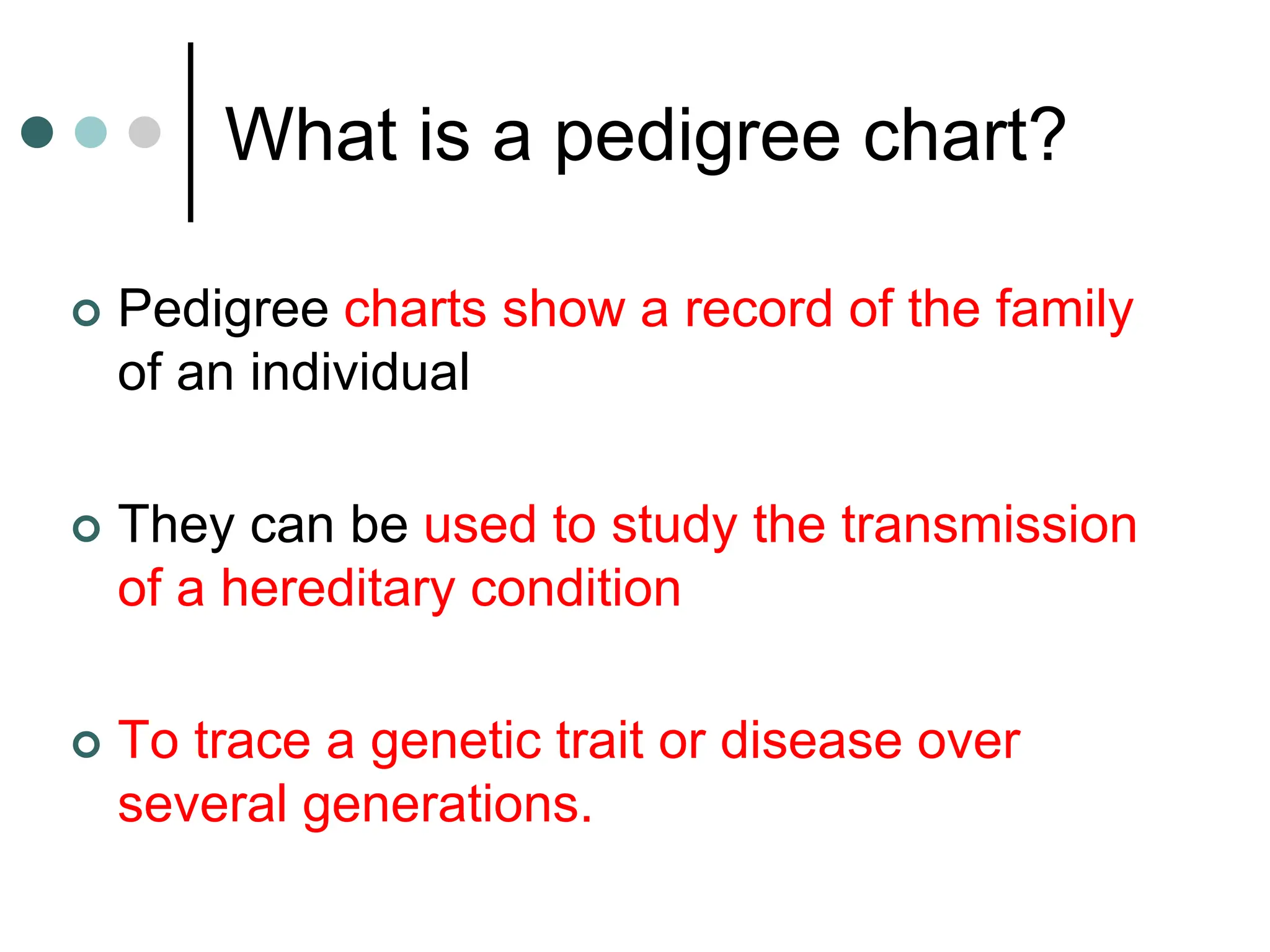
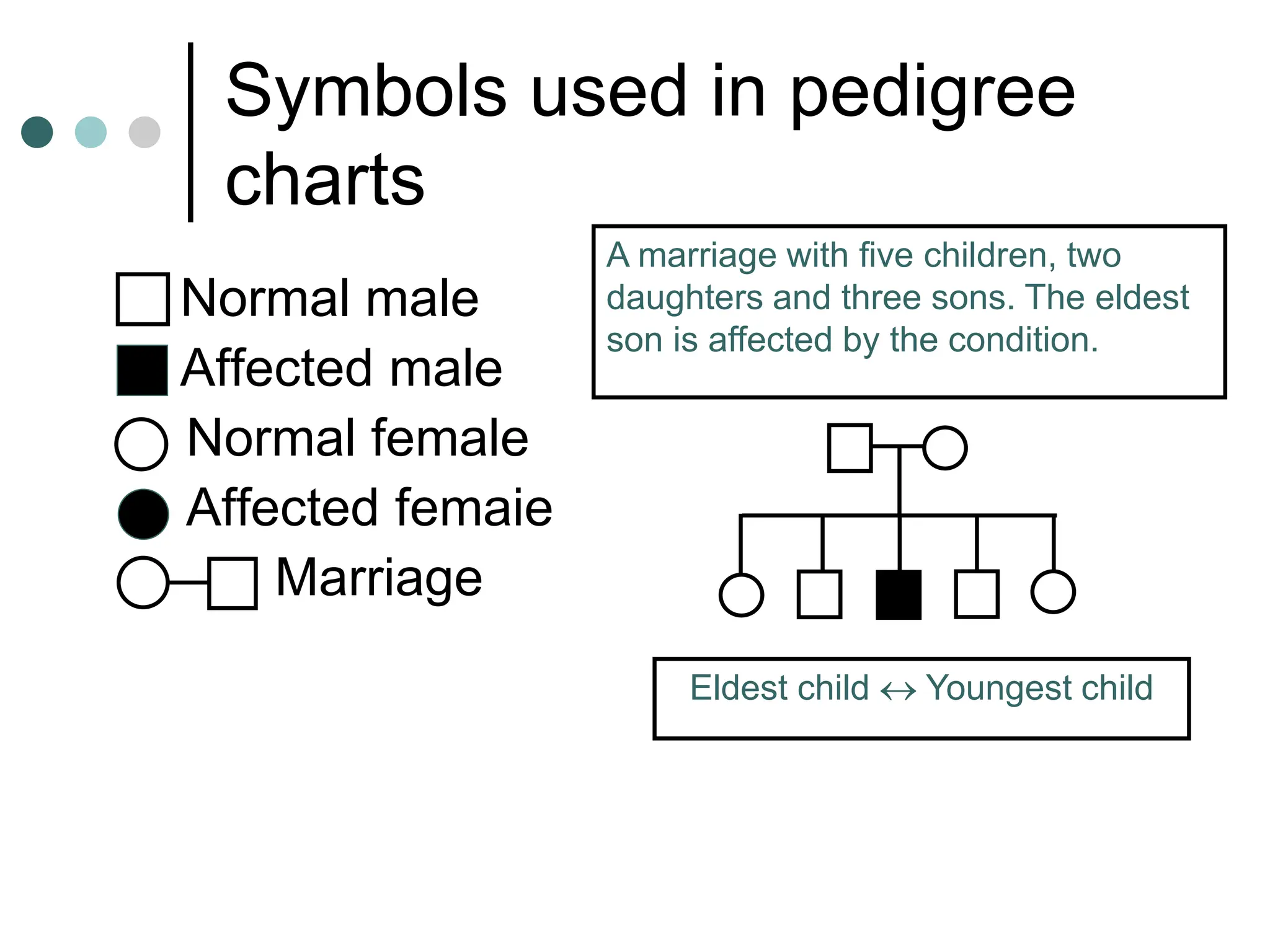
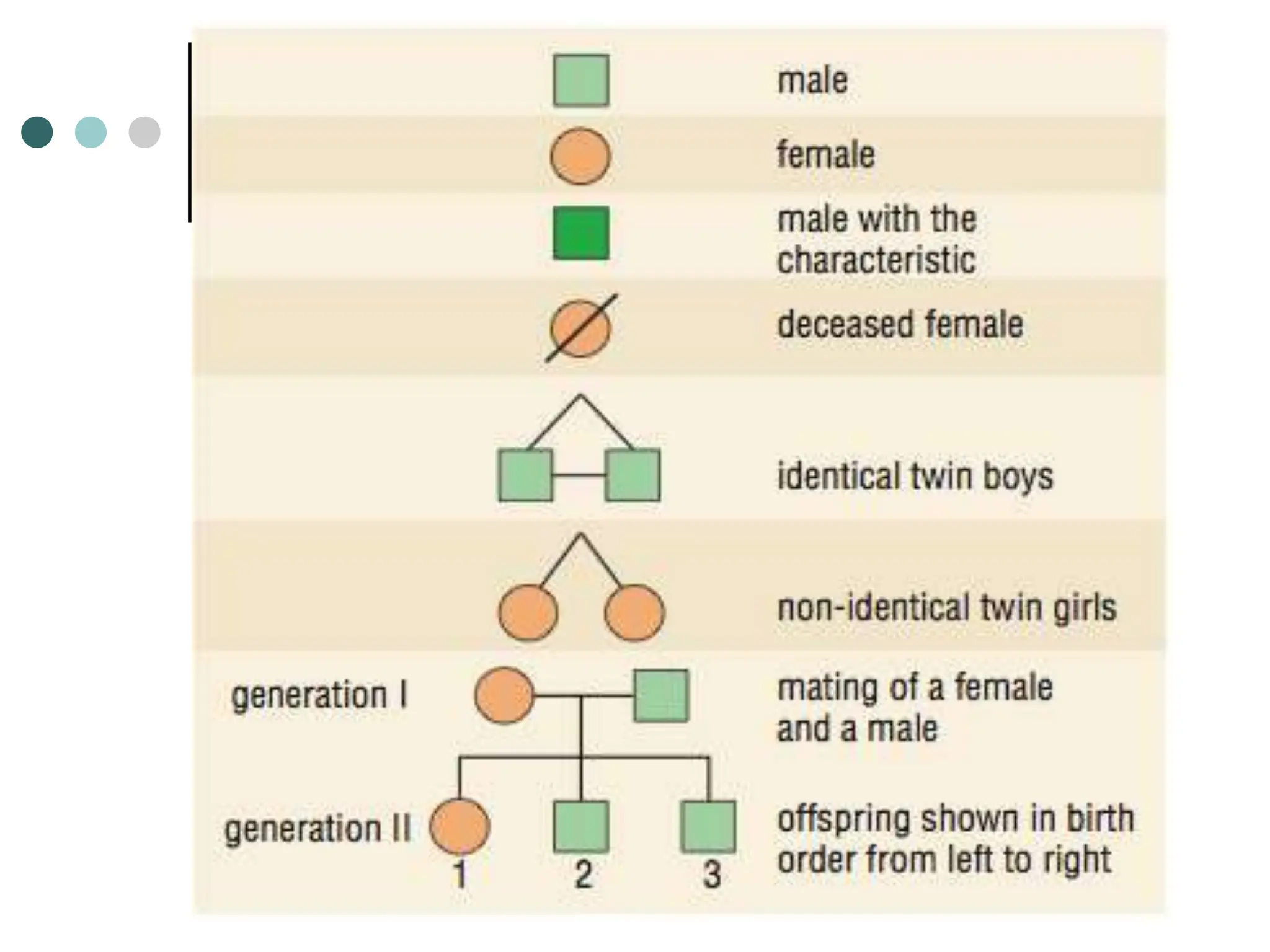
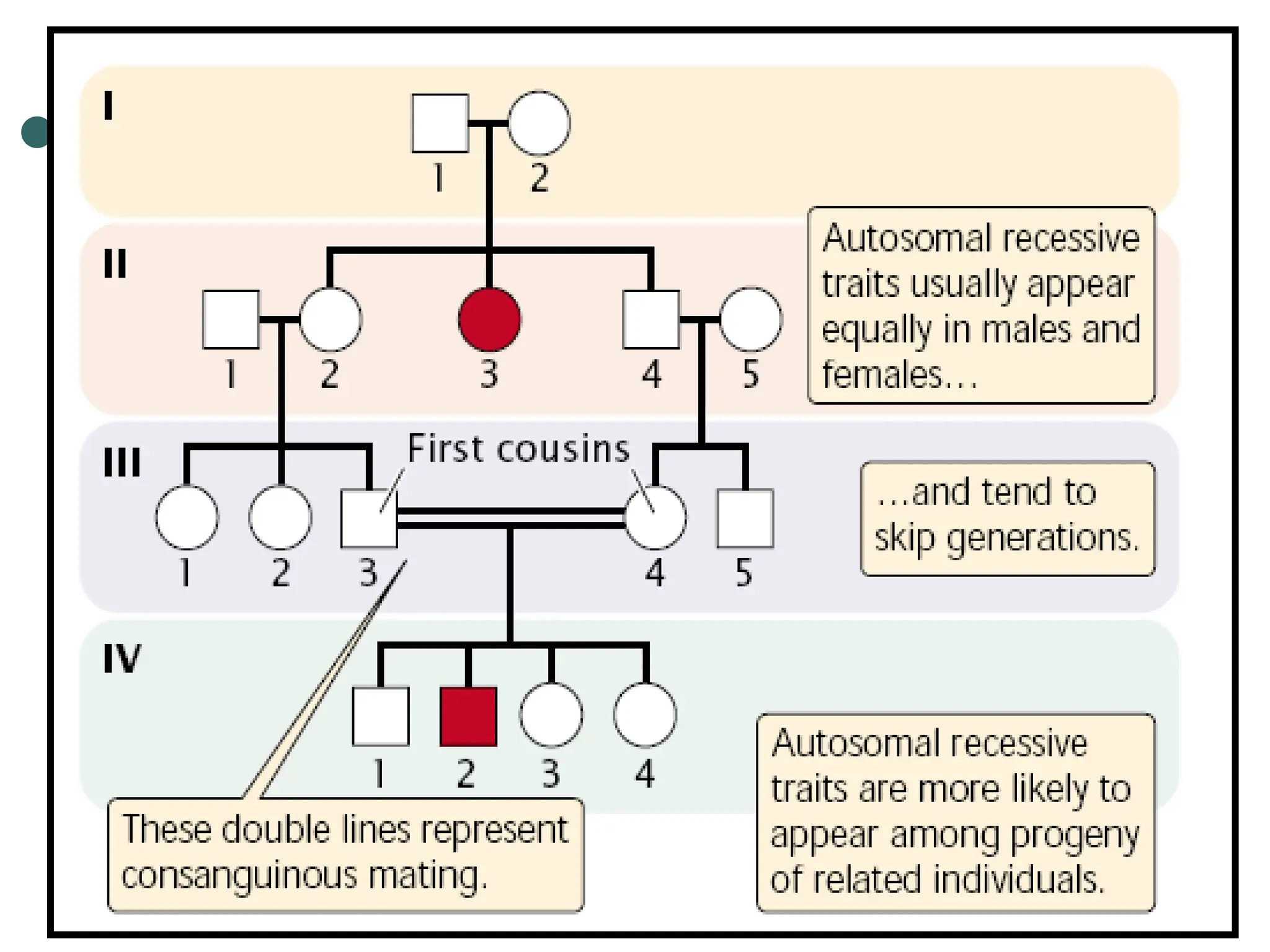
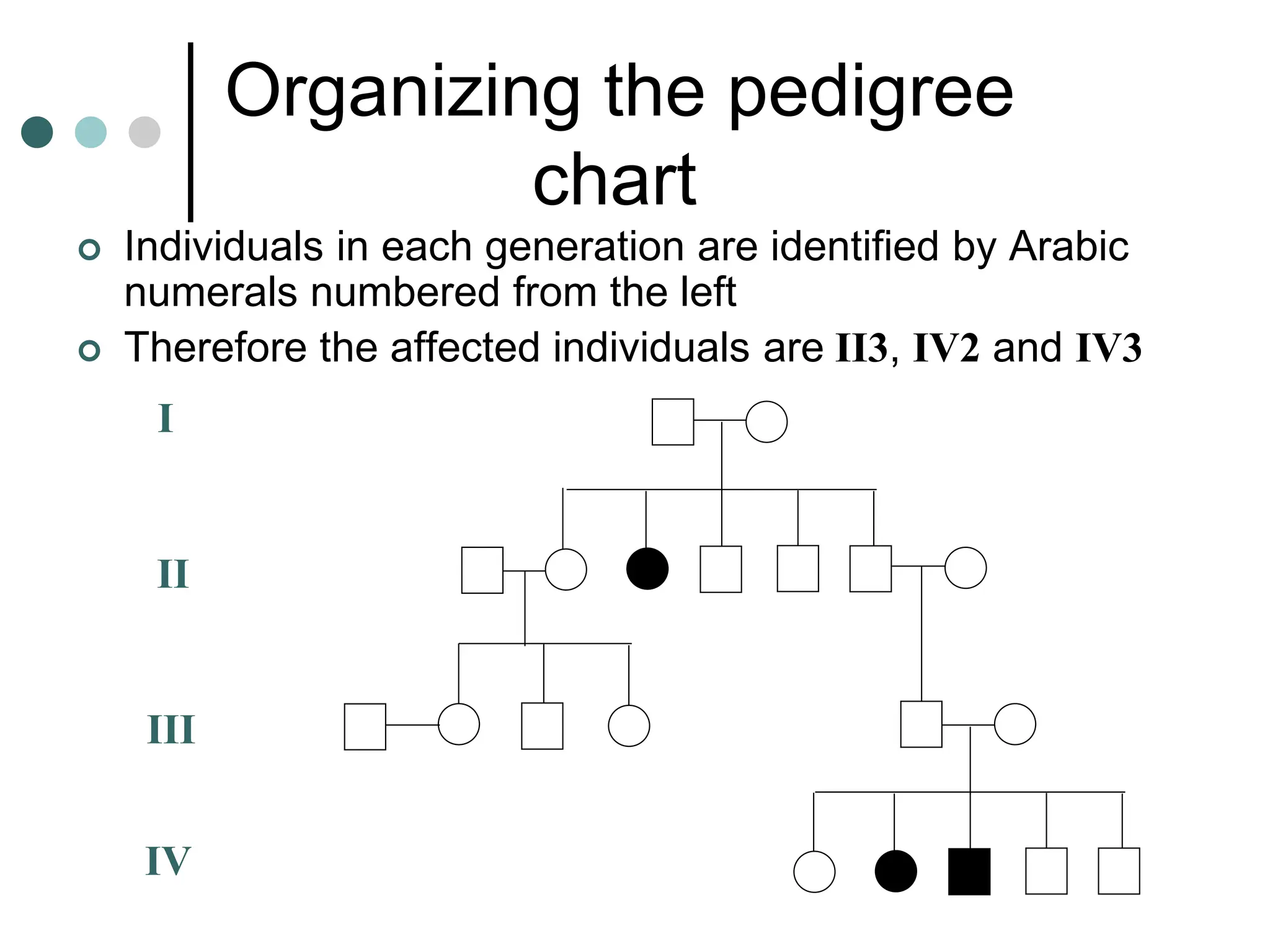
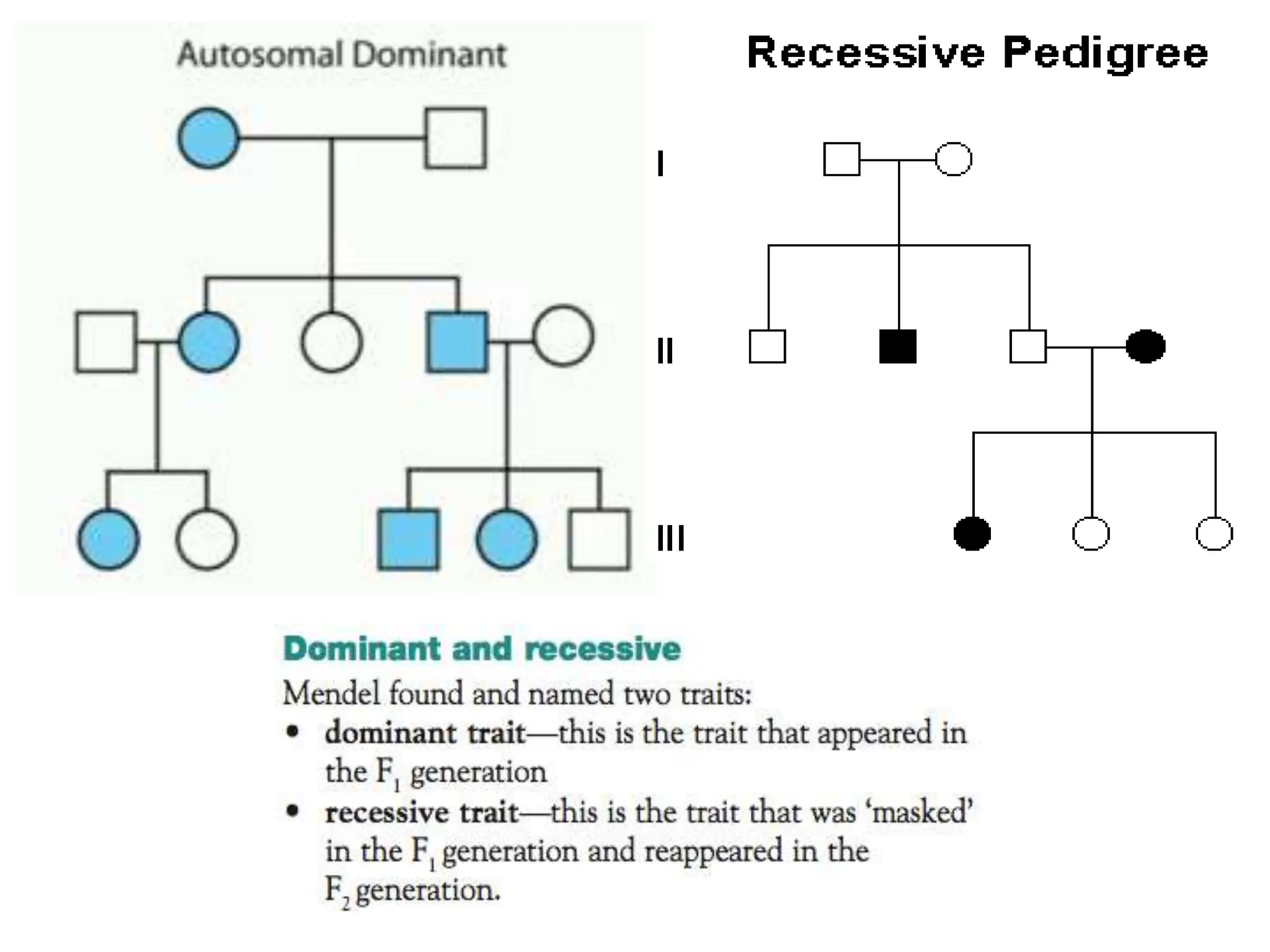
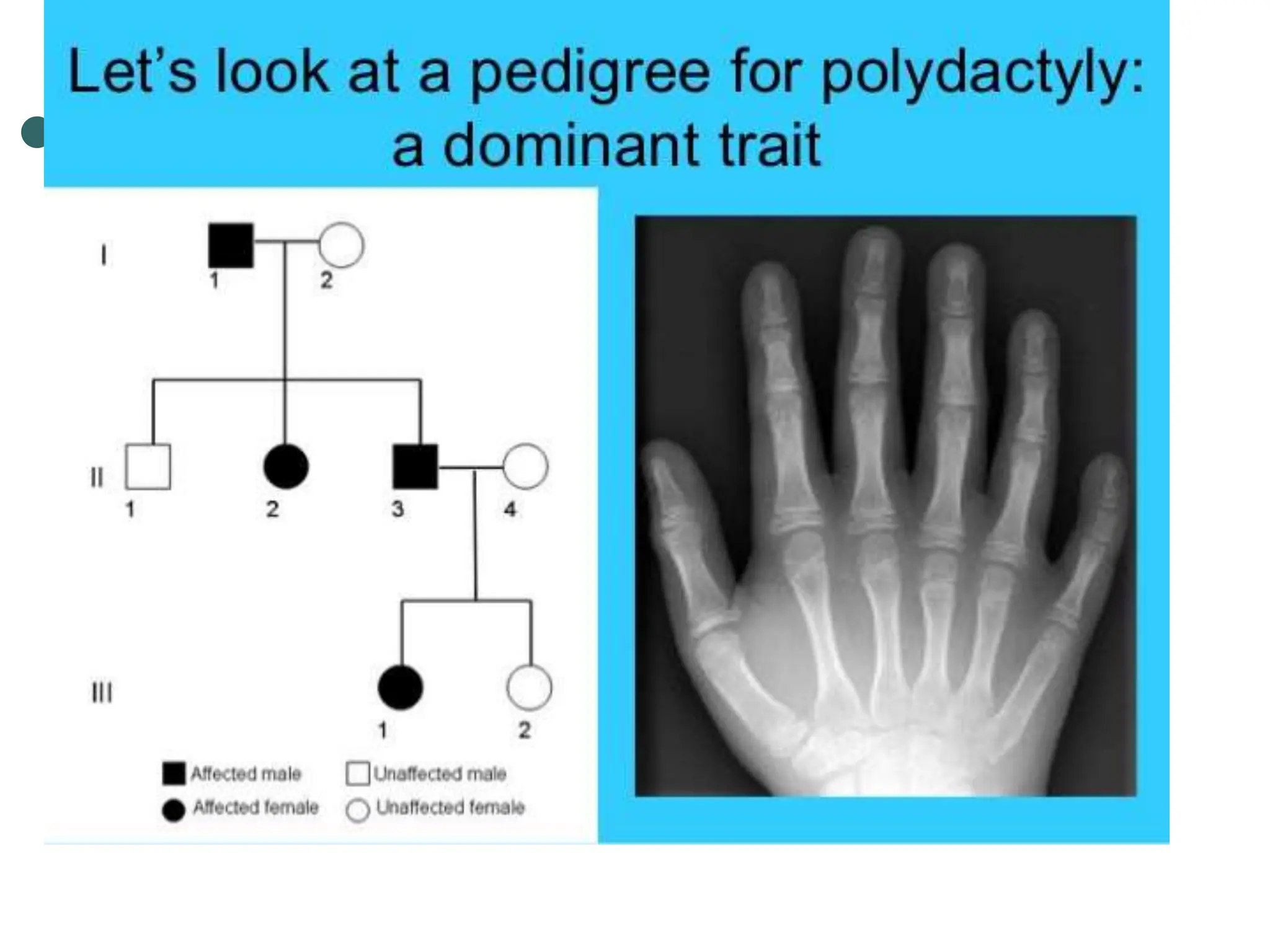
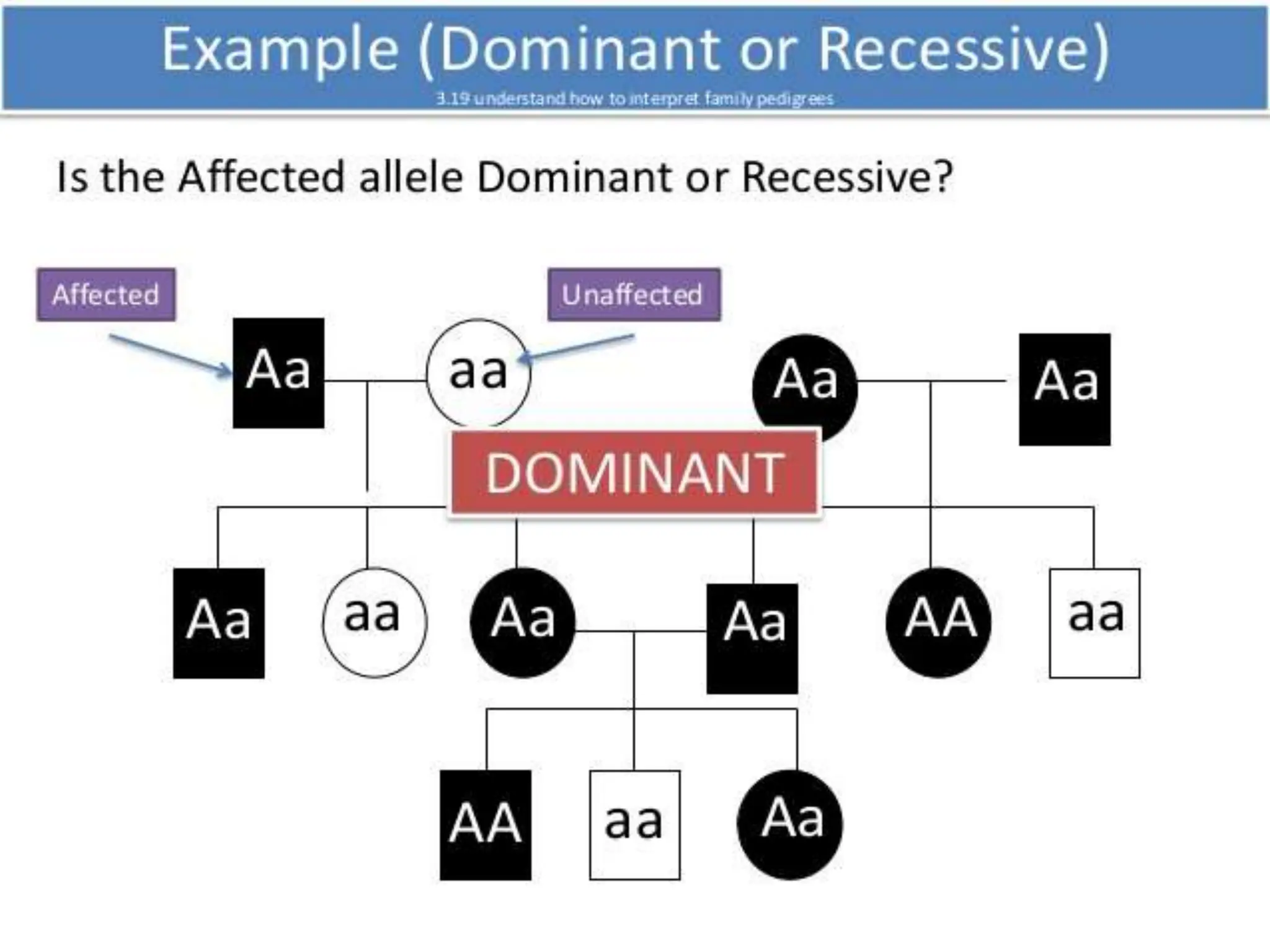
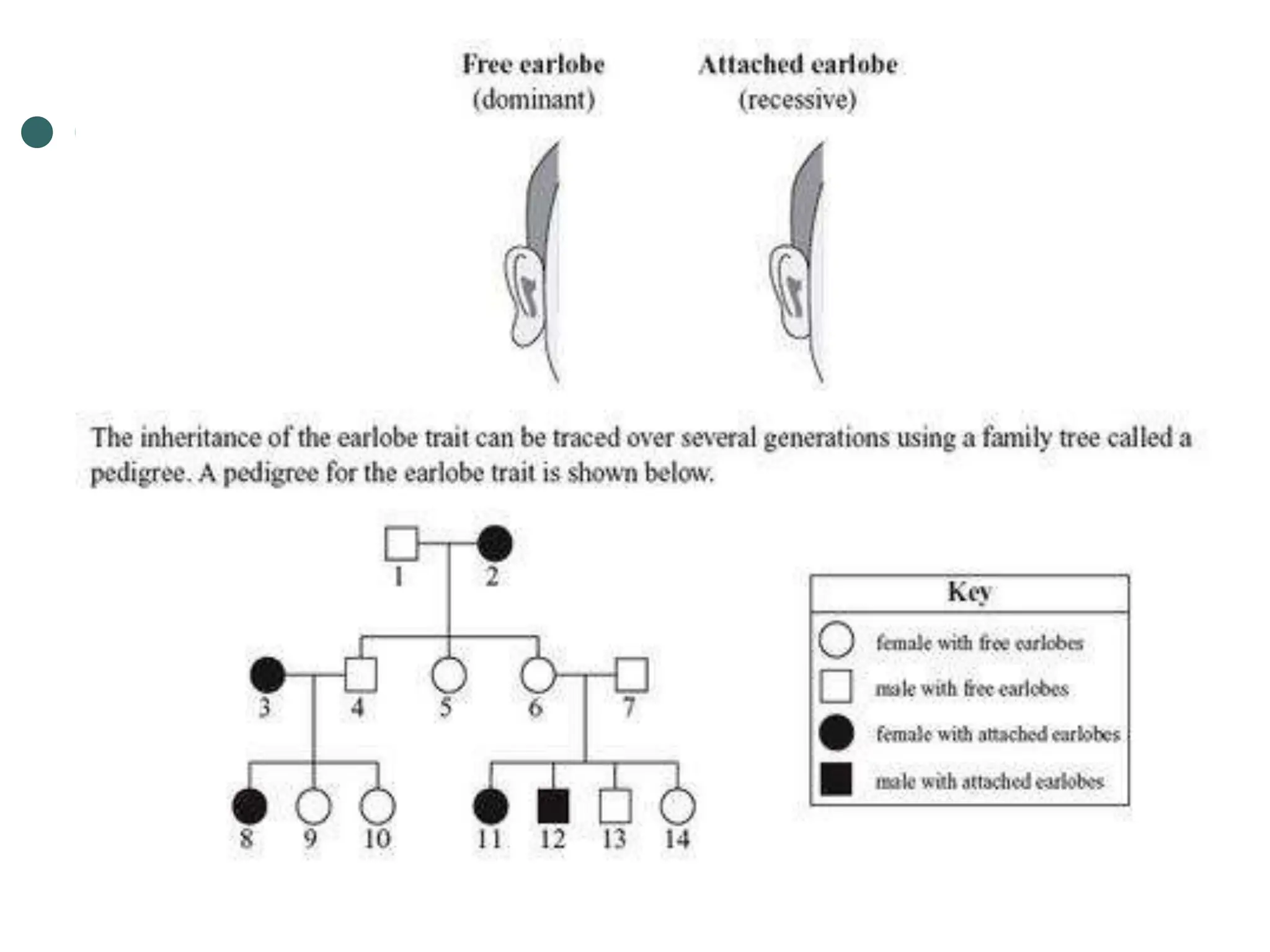
This document provides information about pedigree charts and how they are used to study the transmission of genetic traits and diseases over multiple generations. It defines what a pedigree chart is and explains that they offer an ethical way to study human genetics compared to forcing different types of humans to breed. Pedigree charts use symbols to represent individuals and their characteristics and relationships. They are organized with individuals in each generation numbered from left to right. Pedigree charts can be used to determine if a trait is dominant or recessive and to calculate the probability of offspring inheriting traits when parents with different genotypes are crossed. The document provides examples of homework involving creating a pedigree chart and performing test crosses for traits like earlobes, freckles and hair color in a






![Pedigree Project
If you have special cases divorce, half
sibling or you don’t know the name of
someone, death of a child or baby, see me
for help. [Ask your folks for help if possible]
Do both sides of your family if possible on
the Same pedigree. (Hint: draw it out on
paper first to work out all problems, once you
get it right, then put it on poster board).
Did you have to do any test crosses to figure
out the genotype of a family member?
Write the words test cross about the Punnett
squares you did on paper.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pedigreeppt-240107184225-62f858d2/75/PEDIGREE-ppt-ppt-17-2048.jpg)