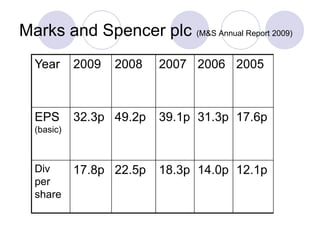
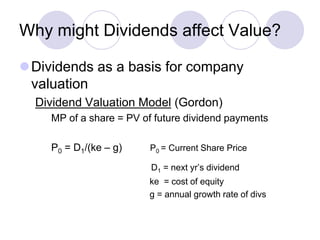
Dividend policy refers to a company's decision to pay dividends to shareholders. Companies pay dividends for reasons such as rewarding shareholders and signaling future profitability. There is no consensus on whether dividend policy directly affects share value, as share prices are influenced by many factors. While dividends may attract certain types of investors, changing dividend amounts could also convey new information to the market. Ultimately, the complex interplay of clientele effects, signaling, and other share price determinants makes the impact of dividends on value difficult to isolate.