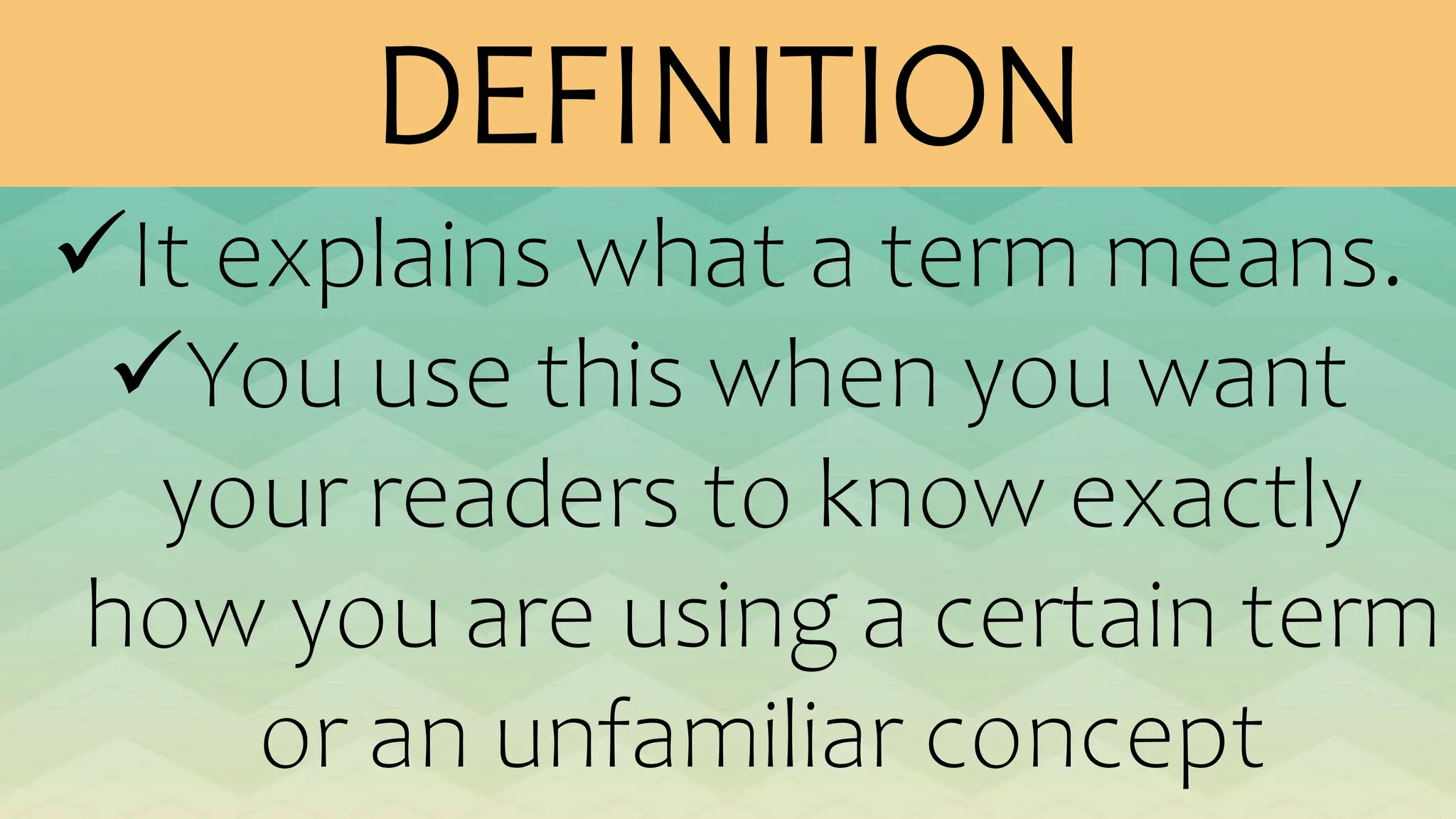
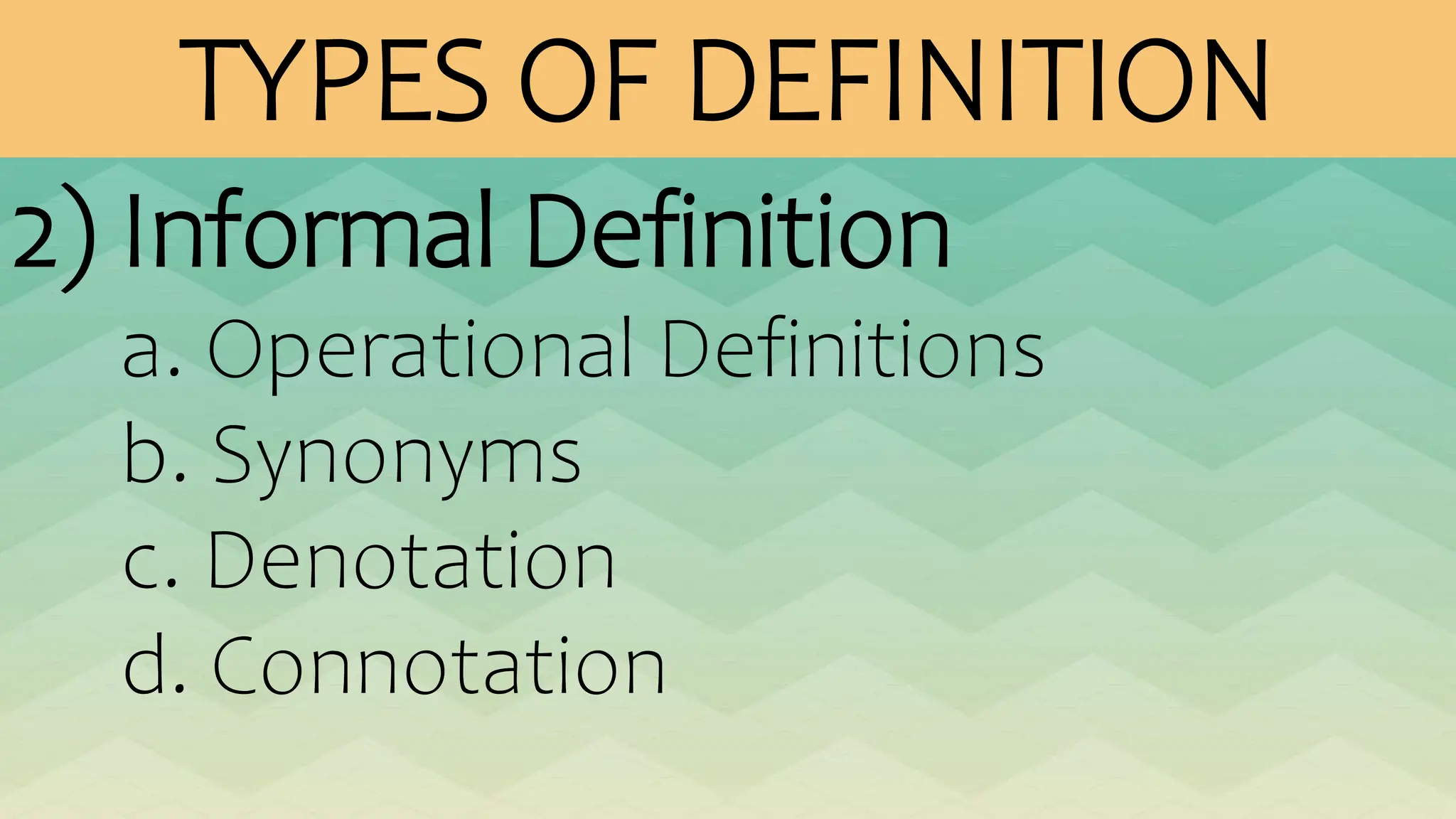
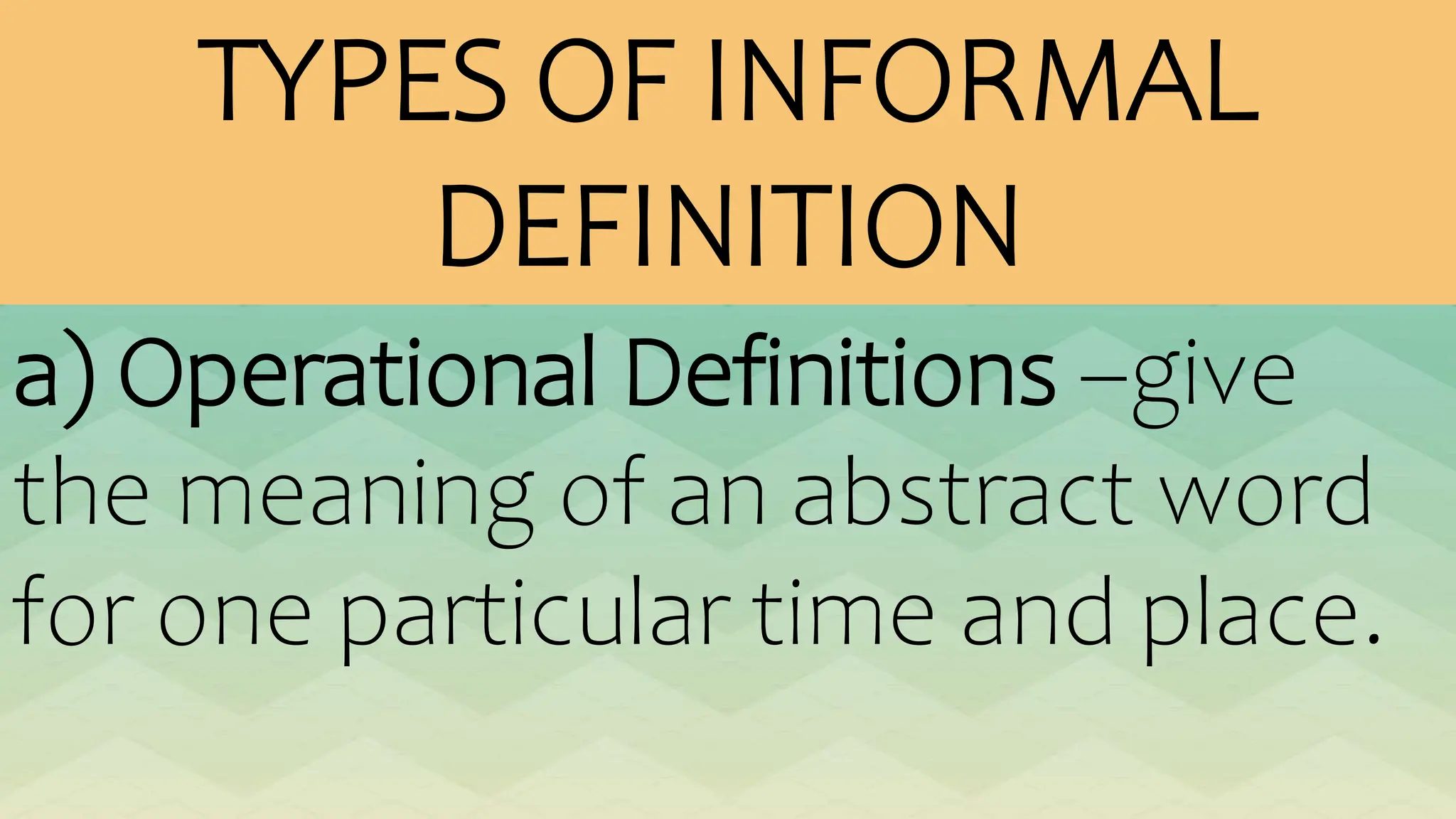
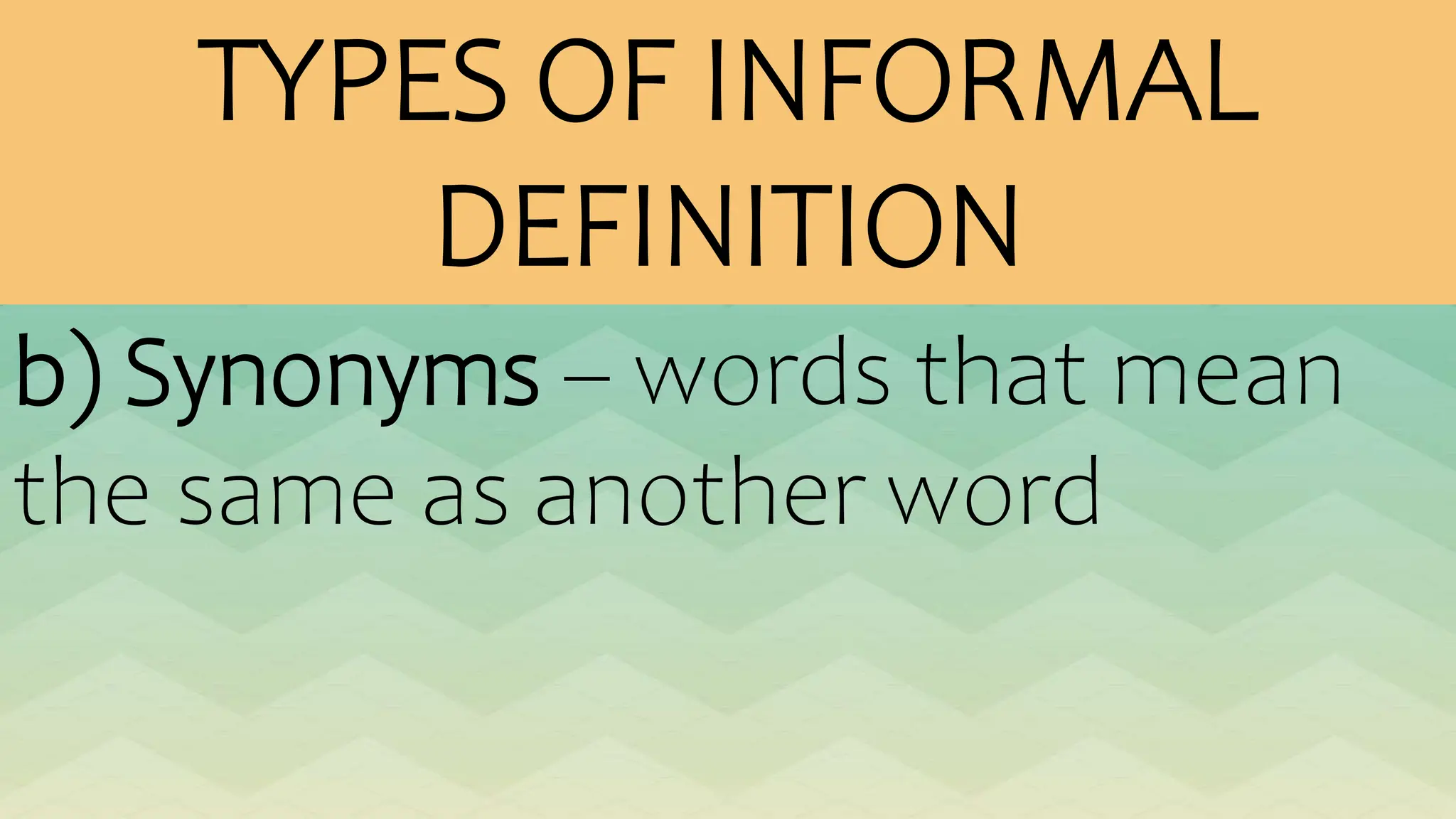
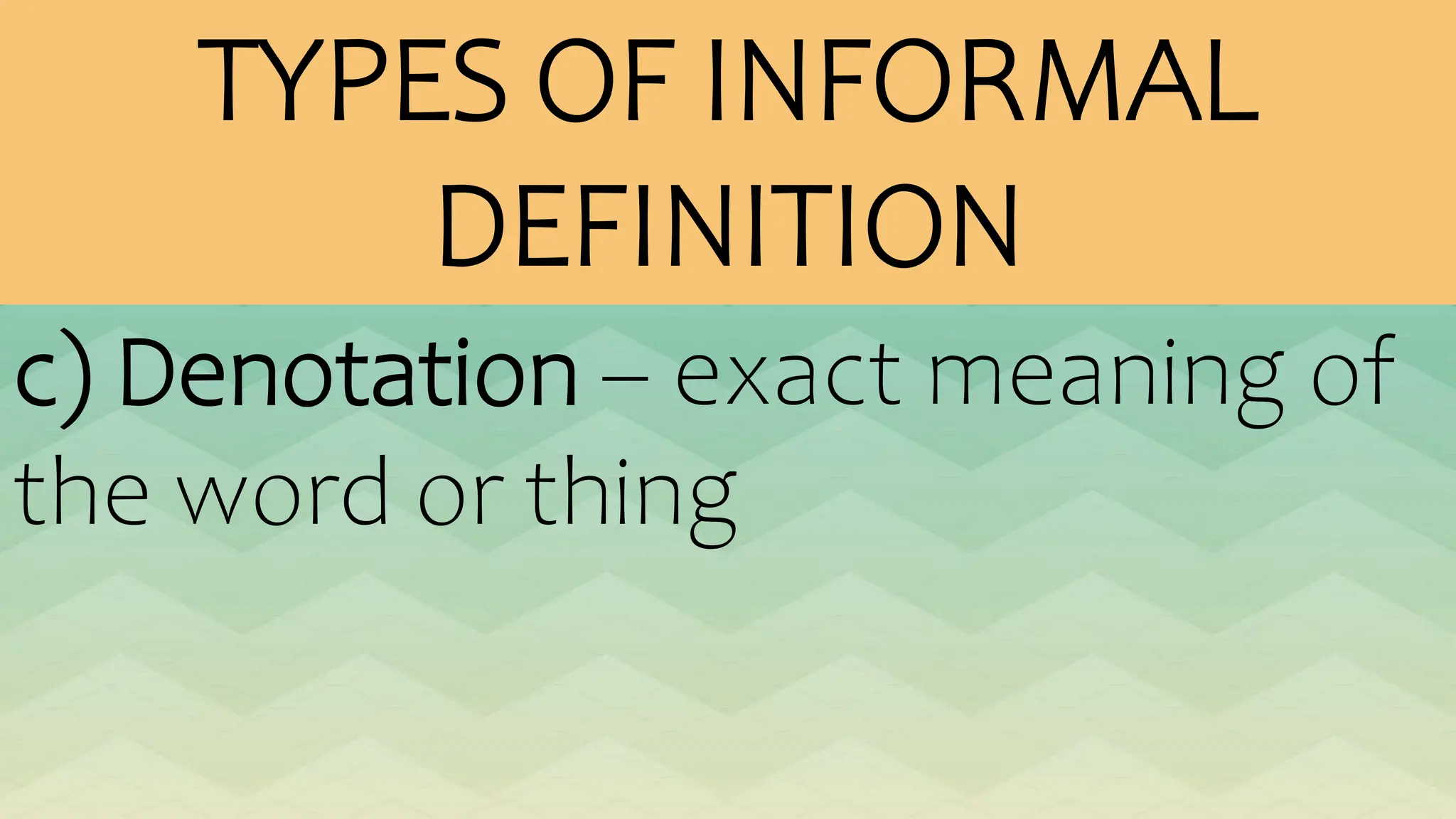
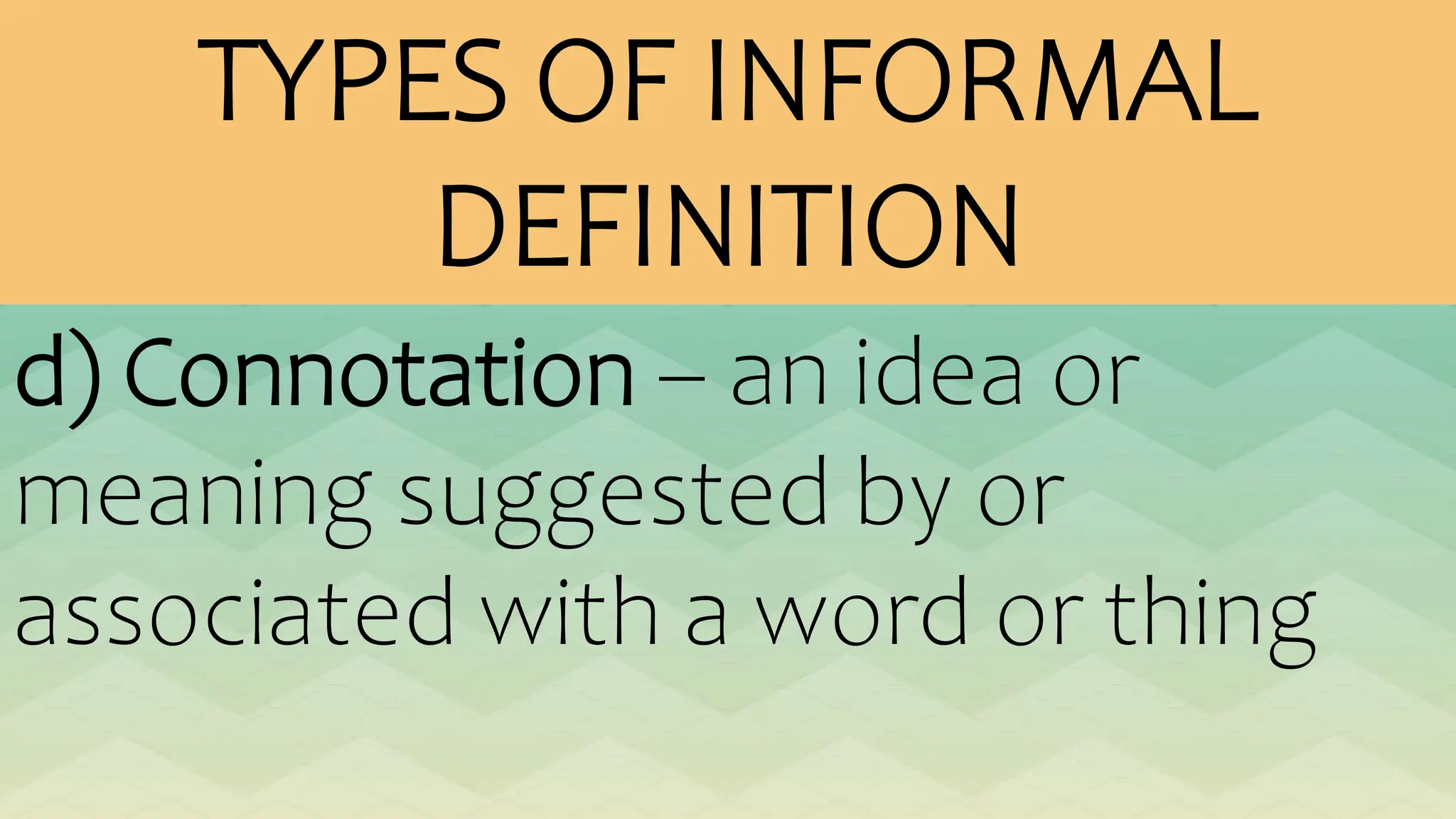
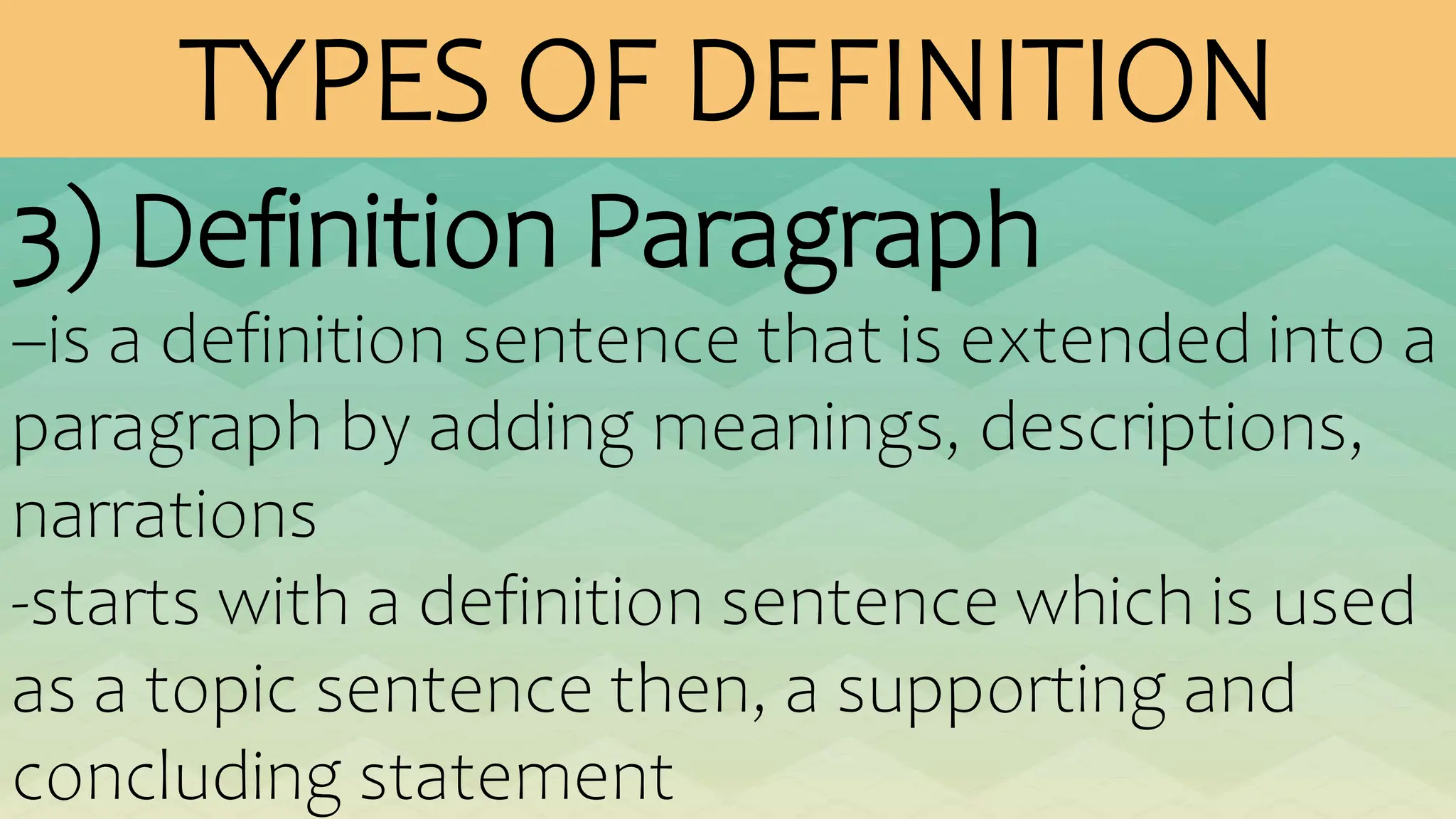
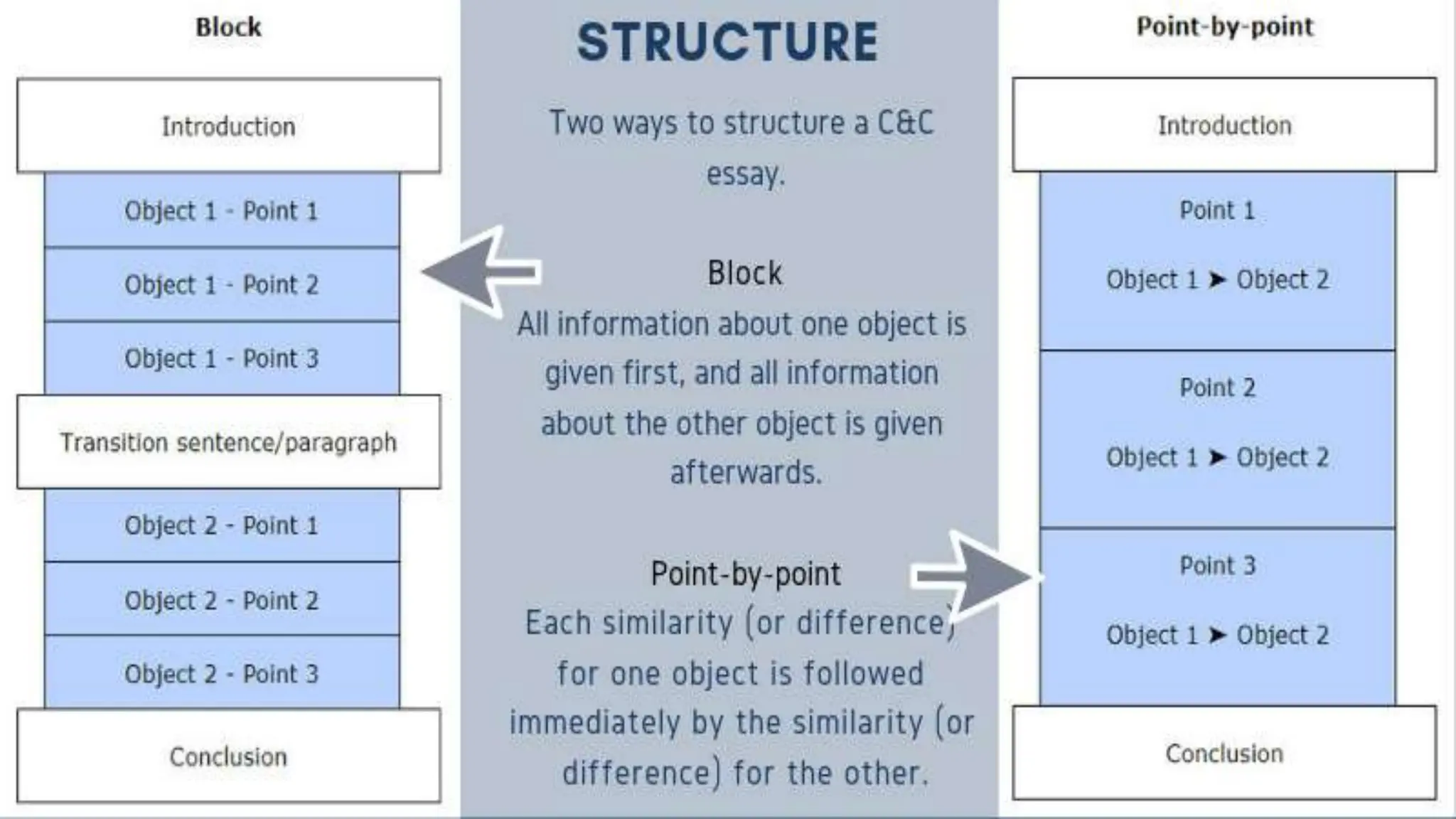
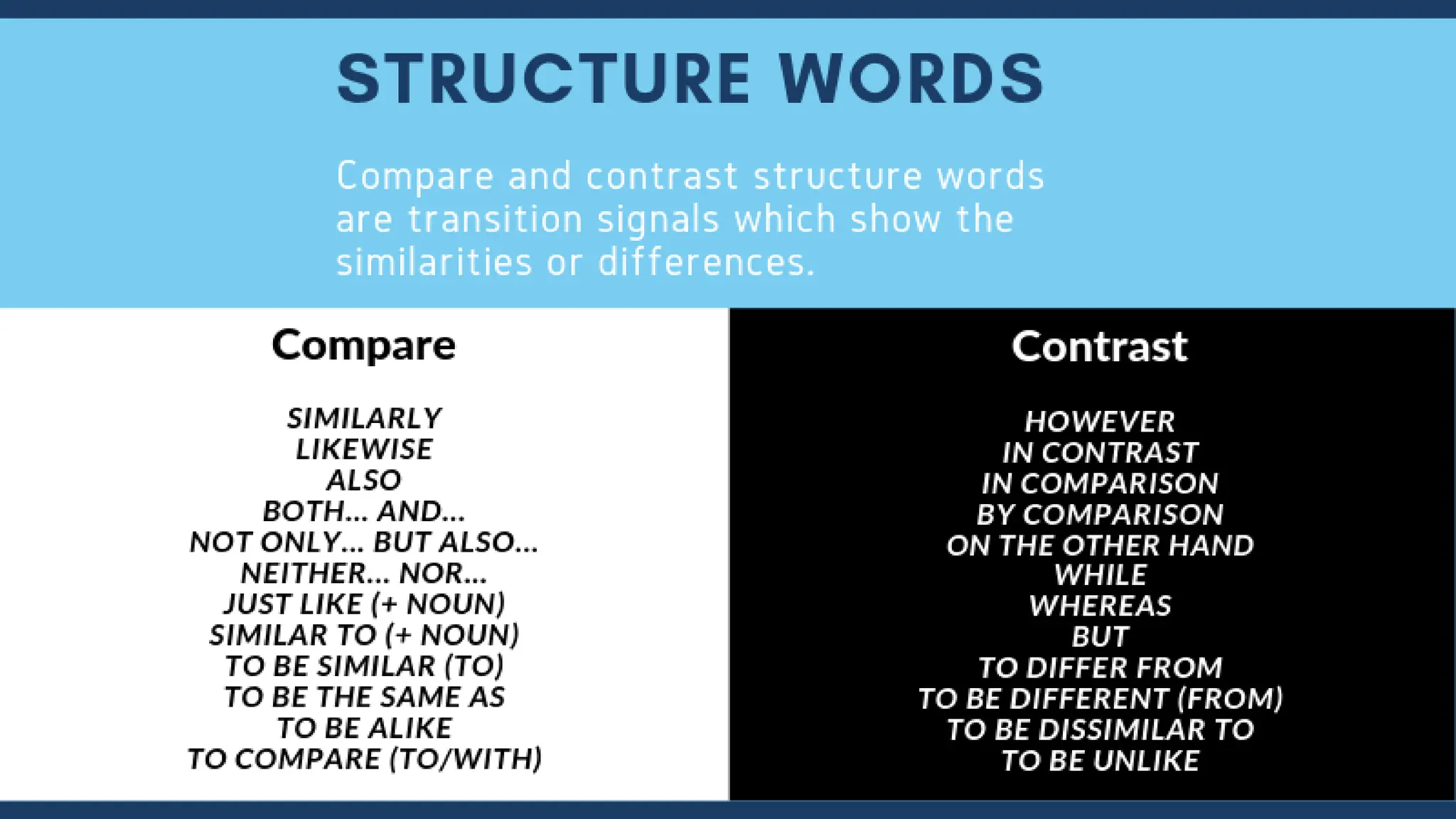
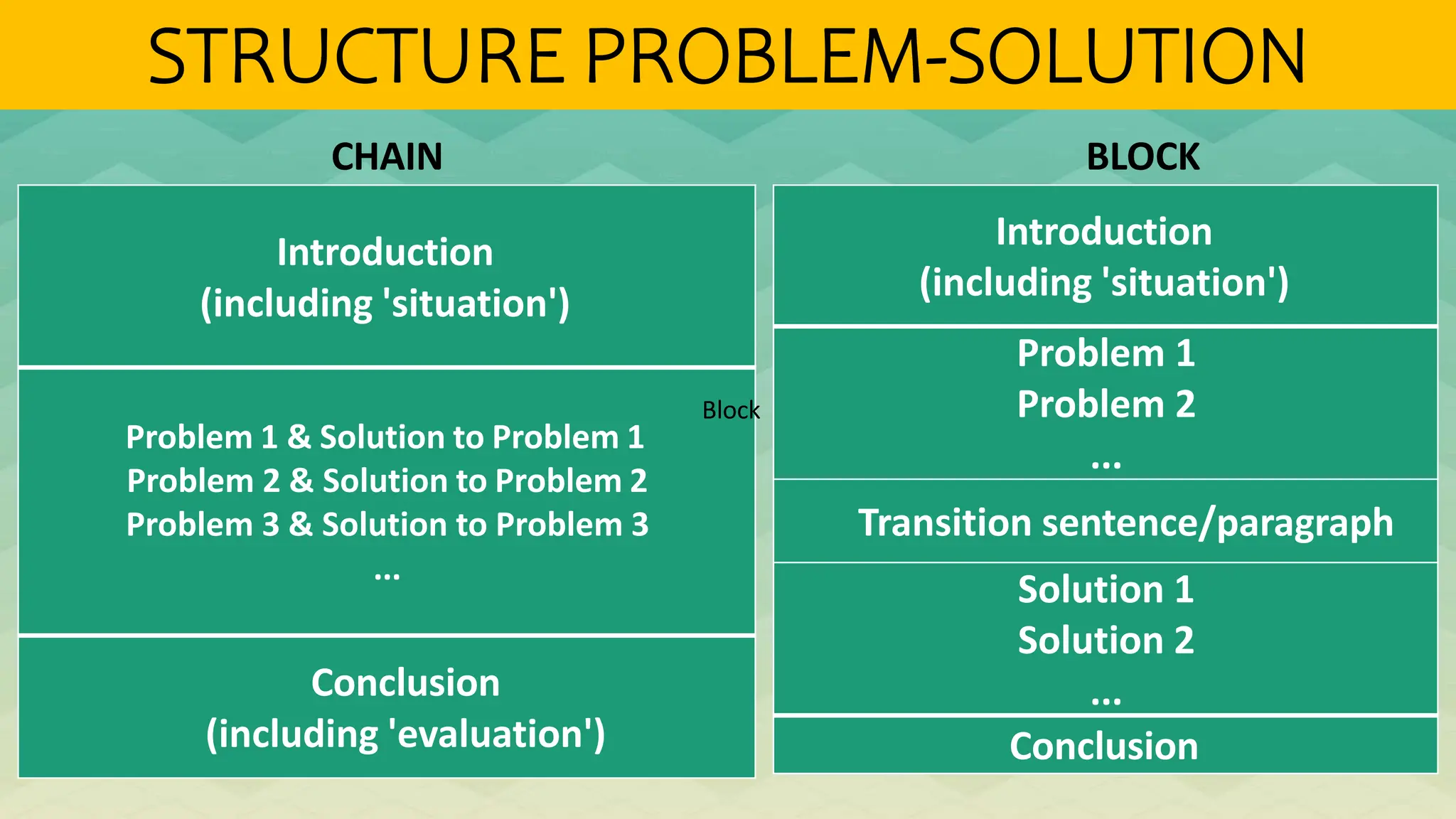
The document outlines various patterns of development that writers use to organize their ideas, including narration, description, definition, exemplification, comparison and contrast, cause and effect, problem-solution, and persuasion. Each pattern serves a distinct purpose and employs specific structures to enhance clarity and engagement in writing. Key elements of these patterns are detailed, including narrative components, types of descriptions, definitions, and methods of persuasion.