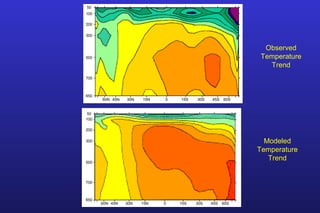
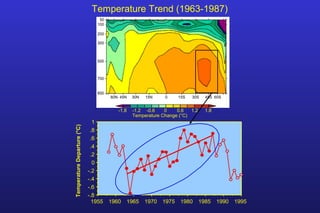
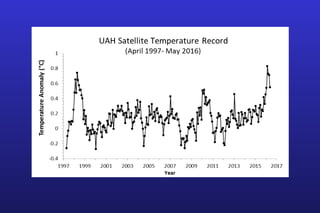
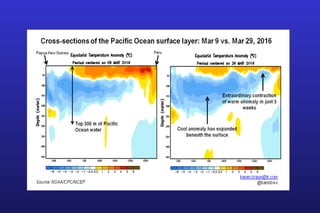
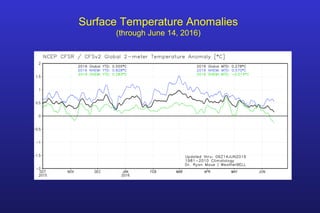
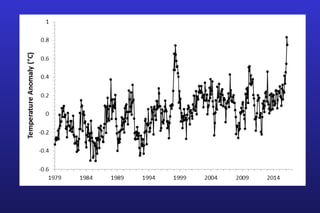
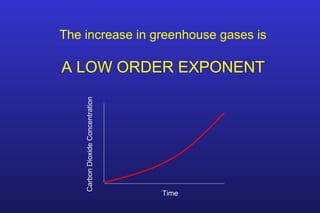
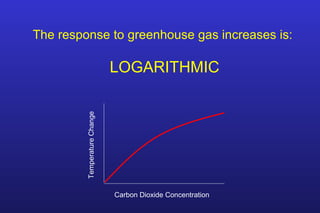
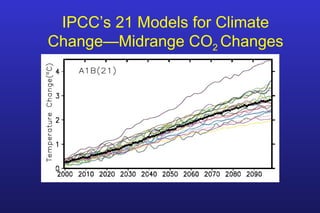
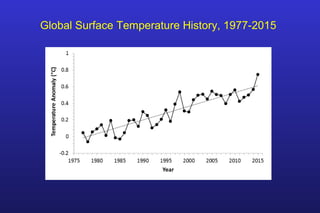
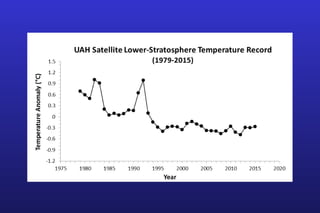
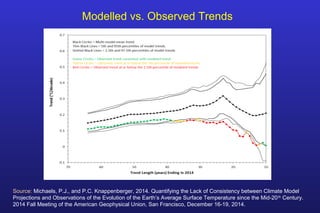
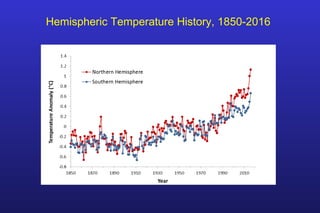
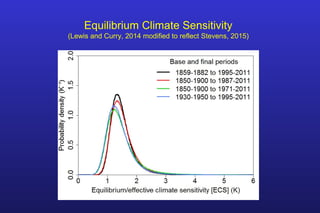
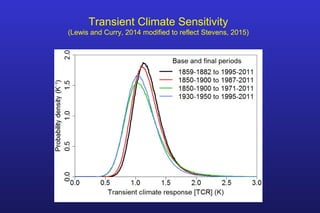
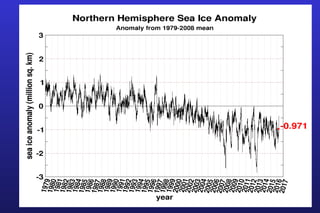
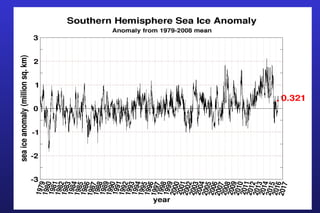
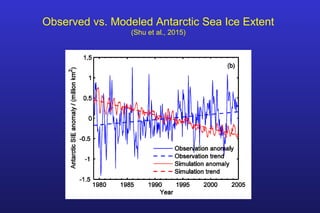
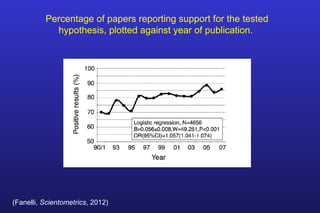
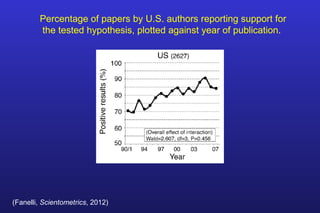
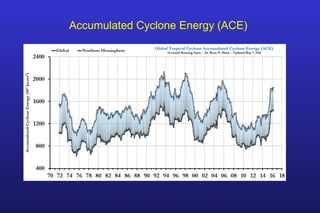
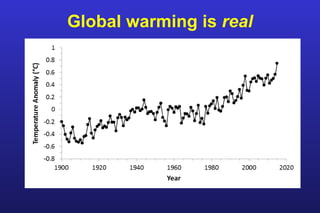
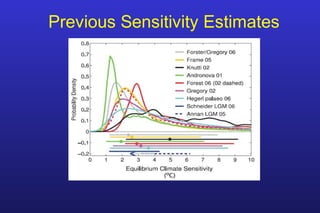
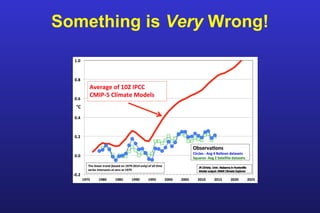
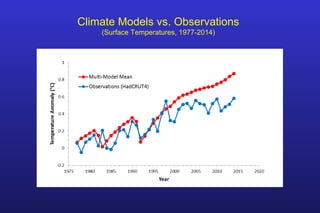
This document summarizes the key points of a presentation arguing that climate sensitivity to increased greenhouse gases is lower than estimated by previous climate models. It notes that climate models have overpredicted warming compared to actual temperature observations. It discusses the logarithmic relationship between carbon dioxide levels and temperature change, as well as evidence that climate sensitivity is on the lower end of estimates. The document concludes by arguing that concerns about extreme sea level rise are overblown based on comparisons to past interglacial periods when temperatures were higher than present.



![It’s not new
When increases in greenhouse gases only are taken
into account…most GCMs produce a greater mean
warming than has been observed, unless a lower
climate sensitivity is used…There is growing evidence
that increases in sulfate aerosols are partially
counteracting the [warming] due to increases in
greenhouse gases.
--Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1995](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bratislava2-160622095456/85/Patrick-Michaels-Lukewarming-The-New-Climate-Science-that-Changes-Everything-8-320.jpg)