The document summarizes the pathoanatomy of clubfoot deformity. Key findings include:
1) Bones are smaller and angulated, with the talus facing down and medially. The calcaneum is small and concave.
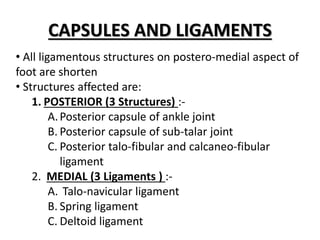
2) Joint deformities include equinus at the ankle, inversion primarily at the subtalar joint, and forefoot adduction and cavus at the midtarsal joints.
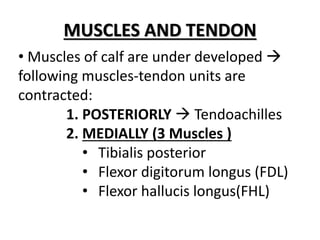
3) Muscles of the calf are underdeveloped and the posterior and medial muscle-tendon units are contracted, including the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus.