This project focuses on path planning for mobile robots, specifically evaluating two algorithms: the cell decomposition method and rapidly-exploring random trees (RRT). It highlights the importance of understanding the differences between these approaches to select the most suitable planner for navigation tasks, demonstrating a trade-off between computation time and path optimality. The study also suggests future improvements and possible extensions to include other algorithms in the evolving field of robotics.





![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
2. Introduction
Since the field of robotics was kick-started in 1956 with the first commercial robot from
Unimation [1,2], researchers have constantly been in pursuit of creating completely
autonomous robots. Autonomous robots are such that they can undertake high-level
tasks and processes and accomplish them without the need for any human intervention
[3,4]. In other words, they possess sufficient artificial intelligence to operate
independently so that the user only needs to specify a command and the robot will be
able to identify how to accomplish it using its own intelligence.
The mission to create autonomous robots stimulates several open-ended problems to be
solved in order to develop their artificial intelligence. One of these issues under
investigation is path planning for a mobile robot [3]. Most commercial robots used in
industry have to accomplish their tasks by either moving themselves or parts like
manipulator arms and actuators. For this, the robot needs to have the ability to plan what
motions it needs to undertake to achieve its goal position(s) without colliding with any
obstacles in the workspace [3,5].
Previous research in the field of path planning has led to the development of various
algorithms using different approaches to tackle this problem [6]. It is therefore natural
that one may wonder which of these would be the best to implement in their robot. The
answer lies in the subtle fact that obtaining a perfectly efficient path planning algorithm
has little chance of success given that numerous constraints and properties vary between
different workspace environments [7]. Therefore, it is crucial to identify which of the
approaches is most suitable for the conditions the user intends to operate the robot in.
However, the last comparative study on the different path planning algorithms was
written a few years ago in 1992 [6]. Considering that the research landscape has further
developed since then, especially with the introduction of the new RRT method [7],
present users would need more information to identify a suitable path planner for
implementing an autonomous navigation robot. Therefore, the current need of the day
would be for a comparative study investigating the properties of the current industry-
standard algorithms. This project aims to take a step towards this direction by studying
the performance of 2 different approaches.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-6-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
The algorithms chosen in this study incorporate the cell decomposition method and
rapidly-exploring random trees. Since we are only concerned with the study of the path
planner’s performance, it will be assumed that a map of the environment and the robot’s
position are already known to the robot from other mapping systems. Under these
constraints, the chosen algorithms will be simulated in a MATLAB environment and their
performance will be investigated and compared.
In the following sections of the report, a literature review will be presented to summarise
the previous research in this field and then the technical details of the study will be
discussed. In each chapter covering the particular algorithm in focus, a short theoretical
background will be provided before the implementation details and experimentation
results are discussed.
3. Literature Review
The concept of path planning is very closely related to the mathematical problem of
finding the shortest route between two points in a network which has been studied by
mathematicians from a much earlier time in the form of the popular ‘Piano Mover’s
Problem’ [8]. The computationally most efficient procedure for the shortest path between
a specified pair of nodes in a network was first described by Dijkstra in 1956 who used the
principle of successive approximation to solve it [9]. Due to the algorithm’s fast running
time, it gained popularity amidst different fields and is now generally formalised as
Dijkstra’s algorithm.
The problem of path planning in relevance to robotics (which is encapsulated under the
subject of motion planning) was first formally encountered by a team of researchers from
the Stanford Research Institute as they worked on developing a robot called Shakey for
navigating a room with obstacles [10]. In 1968, they first suggested a heuristic approach
to determine the minimum cost paths for the robot to navigate [11]. Applying this new
approach to Dijkstra’s algorithm which was currently in use, they suggested some
significant improvements to develop the A* algorithm which could run faster to obtain the
optimal solution [12]. This algorithm marked a significant step to this field such that it is
still the most popular algorithm in use [3].
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-7-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
In an attempt to further develop the grid-based approach of the A* algorithm, Udupa
pioneered the concept of shrinking the robot to a point representation on the grid in 1977
[13]. This proved to be a major development as it finally led to the formulation of the
geometrical theory behind motion planning and boosted future study and research in this
subject [3]. This idea was almost immediately exploited in a systematic fashion as it led to
the development of the first path planning algorithm for polyhedral robots and obstacles
by Lozano-Perez and Wesley [14]. Their work is widely considered to be the first
contribution to the exact study of motion planning as it had not been identified as a
unique field prior to this development [3].
The ability to represent robots and obstacles as points or polygons in grid coordinates led
to the birth of the notion of configuration space. A configuration of a robot is a
specification of its position and orientation in its workspace and its configuration space is
the mathematical space of all such possible configurations [5]. The development of this
formal mathematical basis for the robot and environment specification has made it easier
for researchers to apply the knowledge of linear algebra and geometry to the study of
path planning.
Using the above geometrical basis, Lozano-Perez proceeded to introduce the principle of
the approximate cell decomposition approach [15] which is the first of the 4 different path
planning approaches identified currently. The basic idea behind this method is to sub-
divide the free space of the robot’s configuration into smaller polygonal cells [15]. The
unique feature however lies in the fact that each cell will continue to be recursively
subdivided till it is found that every cell in the space is known to be either completely full
(with an obstacle) or empty [16]. While the polygonal cells can introduce inaccuracies in
the exact shape of the obstacle, the advantage is that we can gain a finer resolution only
in spaces where needed which saves computational complexity. After this decomposition,
a connectivity graph is established to identify the adjacency relationships between the
cells [15]. Using this graph, a channel and path can subsequently be obtained by linking
adjacent cells in the goal direction.
Though the above method feels intuitive to a person given the geometric data, it is not
necessarily the only way to interpret the information. While Lozano-Perez constructed the
cell decomposition approach, Khatib explored a radically different approach in parallel
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-8-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
which led to the pioneering of potential field methods [17]. This approach treats the
robot’s point representation in the configuration space as a particle under the influence of
a potential field generated by the structure of its surroundings [17]. Obstacles in the free
space will generate a repulsive potential force on the robot while the goal position has
attractive potential. Therefore, the motion of the robot at any given time is guided by the
potential field at its present location [16].
Though the localised nature of this method affects the actual success rate of the planner
to find a path even when available, its real-time efficiency in saving computation time
makes it a viable approach to study and develop further [18]. This motivated Barraquand
and Latombe to develop a planner integrating both the cell decomposition and potential
field approaches discussed above [18]. They applied a Monte Carlo technique which
escaped the local minima by executing randomised Brownian motions [18]. This resulted
in an improvement of the original algorithm’s performance in terms of speed and
handling multiple Degrees of Freedom [18].
The geometrical concepts of the configuration space and polyhedral obstacles have also
motivated further research into exploiting them and a further approach developed to
tackle the path planning problem is the probabilistic roadmap (PRM) method. This
approach pioneered by Kavraki uses the principles of configuration space and a
continuous path by connecting all the vertices of the polyhedral obstacles with each other
using line segments [19]. This set of paths is called the roadmap and the program searches
for a continuous path between the initial and goal positions in this free space. If more
than one continuous path is identified in this search, Dijkstra’s algorithm is used to select
the optimal one [16].
Though the above mentioned approaches have led to the development of successful
algorithms, they cannot be easily extended to path planning problems with non-
holonomic constraints [7] which involve the dynamics of the robot and environment. In a
search to address this issue, LaValle was led to the pioneering of the Rapidly-Exploring
Random Tree (RRT) approach which is relatively new in this field [7].
Random trees are a data structure is computer science which grow and connect different
vertices with line segments using randomised variables [20]. Therefore, they essentially
represent an exploration of unknown area starting from a single point and branching out
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-9-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
in random directions. However, a problem with most trees is that their growth pattern
tends to be heavily biased in the direction of spaces already explored [7]. In LaValle’s
words, this can be practically understood using the analogy of a random walk a human
takes which will also bias towards familiar places already visited. Therefore, the final
outcome would reflect that the tree is not actually randomly exploring new spaces.
LaValle addressed this issue in his development of RRTs by using a Monte Carlo technique
to bias the tree’s search into the largest Voronoi regions (undecomposed spaces) [7]. This
alteration results in a tree which is more effective in filling the spaces of the area to be
explored. Therefore, these trees perform very efficiently in searching high-dimensional
spaces for robot path planning [21]. Hence, the promising properties of this approach
motivates further research into it as the method is still relatively new in use.
4. Cell Decomposition Method
4.1. Theoretical Background
This approach uses geometrical and algebraic techniques to process the workspace
information and since this tends to be highly intuitive to most people, it is one of the most
popular approaches to the path planning problem [3]. The basic principle behind the cell
decomposition method is, as described by its name, to decompose or sub-divide the
configuration space of the robot into polygonal cells [15]. Once the workspace has been
divided into cells, each cell can be classified as either being a non-traversable obstacle or a
free space with specific traversal costs through it.
Once such an occupancy grid has been created, a graph or node searching algorithm can
be used to find a path within this free space. In this project, the A* algorithm is used for
this purpose since it is currently the most widely-used in the industry [3, 22]. The A*
algorithm is a pathfinding and graph traversal algorithm which was first described by
Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson and Bertram Raphael in 1972 [12]. It extends the principles of
Dijkstra’s path searching algorithm by using heuristic functions.
The path finding problem is basically one where a robot is required to navigate between
specified starting and goal coordinates in an environment which may be filled with
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-10-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
obstacles. Therefore, the robot needs to acquire knowledge of the positions of the
obstacles to plan a path which traverses completely through the free space.
The A* algorithm uses a one-step look-ahead function to identify such obstacles and plan
the robot’s movements [12]. The first step in the implementation of the algorithm is to
identify a cost function to be used in the grid-based map environment. This cost function
which measures the expenditure in moving the robot from one point to the next could be
a function of distance, traversal time or combinations of both if known. Further a heuristic
cost function is also chosen which estimates the cost of traversing between the next
possible point in the path to the goal coordinate [23]. Therefore, the total cost of the path
will be the lowest possible sum of the cost of travelling to the next point and the heuristic
cost.
By calculating the lowest possible costs at each point of the robot’s position, the
algorithm is finally able to identify the path of lowest cost for the robot to travel between
the two initially specified coordinates. Therefore, it is quite obvious to see that the
definitions of the traversal costs and heuristic costs play an imperative role in the A*
algorithm.
4.2. Pseudocode
The pseudocode used to implement the A* algorithm is shown below.
OPEN = Ø
PARENTS = sstart
while (min sopen ≠ sgoal)
add neighbours of last PARENT to OPEN
for each of these neighbours
if current neighbour = any PARENT
total_cost = ∞
elseif current neighbour = obstacle
total_cost = ∞
else traversal_cost = cost of moving from last PARENT
to current neighbour
heurisitic_cost = estimated cost of moving from
current neighbour to sgoal
total_cost = traversal_cost + heuristic_cost
next_node = min (total_cost of current neighbours)
add next_node to PARENTS
return PARENTS list as shortest found path
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-11-320.jpg)

![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
Figure 1: Environment designed for testing of path planning algorithms
The above environment was constructed as a grid-based environment of 12x12 cells
initially and then 120x120 cells so that the independent variable of resolution could be
varied. Though the environment can theoretically be decomposed into cells of any
polygonal shape such as rectangles or hexagons [15], I chose to work with squares due to
their relative simplicity. Once the workspace was ready, a starting coordinate as well as a
goal coordinate could be specified in the program and the algorithm would compute and
return a path between those 2 points.
In order to vary the number of obstacles in the path, different starting and goal
coordinates in corresponding regions were specified in the experiments. For example,
obstacle-free paths were specified in the free space in the left-most side of the
environment. When multiple obstacles were required, the goal coordinate was placed in
the top-right corner to increase the complexity.
In order to quantify the performance of the algorithm, its computation time was
measured and the optimality of the path was also verified. In cases where the lengths of
the paths were able to be manually verified, the percentage optimality of the computed
paths was also measured.
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-13-320.jpg)

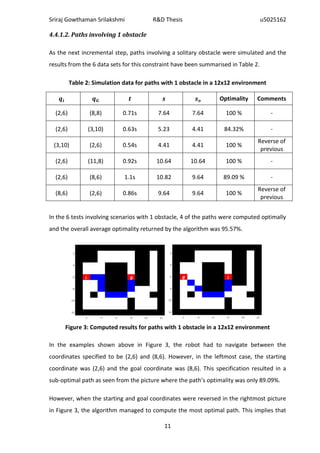




![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
4.4.3. Discussion of observations
Despite the several varying trials and results discussed in the experiments above, there
were a few common threads found between all of the results which will be discussed in
detail in the following sections.
4.4.3.1. Probabilistic Completeness
From all of the completed trials in the experimentation, the algorithm managed to find a
path (optimal or sub-optimal) whenever one existed in the environment. This property of
path planners is known as probabilistic completeness [3] and the therefore, it can be
concluded that the implemented algorithm is probabilistically complete. Therefore, if a
possible path exists, it will surely be found by the planner and if such a path does not
exist, failure will be reported.
4.4.3.2. Optimality in obstacle-free environments
Further, another observation from both the 12x12 and 120x120 grid resolutions was that
when given obstacle-free environments, the algorithm always computed the shortest and
most optimal path between the specified coordinates. Therefore, in simple environments,
there is no issue in using the above method to achieve perfect path optimality.
4.4.3.3. Sub-optimality in complex environments
However, when the complexity involving the obstacles in the environment increases, the
performance of the algorithm suffers and path optimality is affected. While the results of
the computed paths were reasonable in the 12x12 grid environment, as the resolution of
the grid was made finer, the degree of optimality worsened as the number of obstacles
were increased.
On analysis of the visual results of the computed paths obtained, it can be inferred that
the reason behind this sub-optimality is the fact that the heuristic function did not take
the presence of obstacles in the environment into account. The Euclidean heuristic
function implemented in the algorithm estimates the shortest possible distance between
a specified coordinate and the goal coordinate by computing the virtual straight-line
length between them [23]. However, this definition completely neglects the possibility
that the straight-line distance between the 2 points may have an obstacle between them.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-20-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
This implementation meant that the algorithm behaved like what is commonly referred to
as a greedy best-first planner [3, 23]. That is, the algorithm always tried to use the
straightest possible path to the goal without realising an obstacle may be impeding its
way. It does not realise the presence of the obstacle until it is right next to it as the A*
algorithm uses a 1-step look-ahead. Therefore, the robot would have traversed an extra
unnecessary distance before reaching an obstacle and having to redirect itself.
4.5. Future improvements to be considered
In order to correct this issue of sub-optimality, there are a few options that could be
considered. The first possibility looked at was considering the reverse-path between the 2
specified coordinates. During the experimental trials, it was observed that the complexity
between the original and reverse paths can be different in most cases and even though
reversing the path cannot guarantee perfect optimality, it can improve the optimality in
most cases. Therefore, a viable option could be to ask the user to specify 2 coordinates
and compute paths for both the directions between them, compare the 2 paths and
finally return the most optimal of them. Though the computation time of the algorithm
will be more than doubled by this modification, it ensures that the output of the method
is maximised to the best of its ability.
Another option could be to use multiple-step look-aheads instead of the 1-step currently
implemented. This can help the robot identify an obstacle before-hand instead of only
finding it only when right next to it. However, a key question which arises here is how
many steps forward do we need to look? While a small number like 3 steps is enough in
small environments like the 12x12 grid, we would need to look ahead more than 10 times
that number in larger and finer grid environments. Therefore, the computation time of
the algorithm would increase by an extremely large amount and hence this option is not
viable.
However, the key problem was with the heuristic function not taking the obstacles into
account and both of the above options do not solve that particular issue. Therefore, the
best possible option is to develop a new heuristic function which can account for the
presence of obstacles in the environment. As of current research from the literature
review, there is no current heuristic function which accomplishes this.
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-21-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
Therefore, it is likely that a new algorithm would need to be developed for this purpose.
The rough background of this algorithm would be to first calculate the straight-line path
and check if it passes through an obstacle. If an obstacle is detected, a secondary path
could be constructed traversing around the boundary of the obstacle. However, this
secondary path will not be optimal yet.
Once this path is obtained, periodic samples from it can be extracted such as 1 in every 3
or 1 in 5 of the total points (See Figure 8b) depending on the length of the path and the
desired computational complexity. Finally, these sampled points can be used to construct
the final path by drawing straight-lines between each of them. Therefore, this method will
use the current heuristic function but attempt to optimise it step-by-step using obstacle
detection. While the final results can be expected to be as shown in Figure 8c, this
algorithm will have to be implemented and tested before we can make any conclusive
statements about its performance.
Figure 8: Expected planning steps in optimising the algorithm
5. Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees
5.1. Theoretical Background
Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees (referred to as RRTs from here on) are basically a kind of
data structure in computer science [20]. Inspired by biological trees, these data structures
start from a single node and branch out to various sub-nodes recursively and hence are
named after the more commonly known trees [20]. In this context of path planning, they
are used as a tool to aid us in the exploration of the configuration space and environment
around the robot [7].
When developed in conjunction by Steven LaValle and James Kuffner while at the Iowa
State University, the key motivation behind the creation of a new approach was to
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-22-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
accommodate the kinodynamic constraints of the robot into path planning [7]. In other
words, this algorithm can also take account of the robot’s velocity, acceleration or jerk
properties (if known) to plan a more realistic and smoother path with no sharp turns.
The basic principle behind this algorithm is to create a tree node at the specified starting
coordinate and then randomly branch out in all the directions to create further nodes in
the free space [7]. By the positioning of these sub-nodes, we indirectly gain an idea of the
positions of the obstacles in the environment and we can sample the free space to varying
densities. So while the previous cell decomposition method evenly sampled the space
using equally sub-divided geometric cells, RRTs sample the space unevenly and randomly
which reduces the computational complexity associated with arranging the cells.
Therefore, despite being given the same environment and starting/goal coordinates, no
two RRTs can be expected to be the same each time.
The generation and growth of the above tree is stopped once the goal coordinate has
been sampled as a sub-node of tree within a specified proximity. Once the RRT for the
given environment is established, a graph-searching or node-searching algorithm can be
used to search the branches of the tree to find the shortest possible path between the
starting and goal coordinates [7]. The A* algorithm used previously in the cell
decomposition method fits this need and hence, it can be used with the RRTs as well.
5.2. Pseudocode
GENERATE_RRT(sstart, K, Δt)
tree.init(sstart)
for n = 1 to K, do
srand RANDOM_STATE();
snear NEAREST_NEIGHBOR(srand, tree);
u SELECT_INPUT(srand, snear);
snew NEW_STATE(snear, u, Δt);
tree.add_vertex(snew);
tree.add_edge(snear, snew, u);
return tree
The pseudocode above grows a RRT originating at the point sstart with K branches per node
for every time step Δt. In each iteration, K random points (srand) are generated and
connected to the nearest node on the tree (snear). These points (snew) are then connected
to the tree with a branch representing the kinodynamic state (u) pertaining to the robot.
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-23-320.jpg)

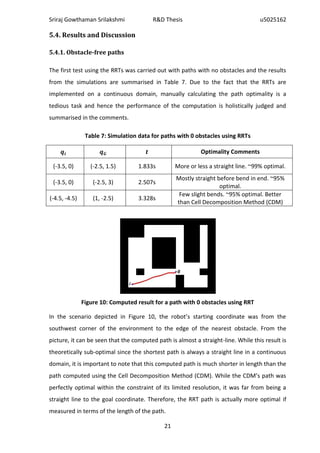


![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
observed in the original path but the reverse path did not run into the problem. In fact,
the reverse path is very close to being an optimal one.
5.4.4. Discussion of observations
In the following sections, the common characteristic properties of the RRTs observed will
be discussed in detail.
5.4.4.1. Probabilistic Completeness
Just like as observed with the Cell Decomposition Method, the algorithm incorporating
the Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees is also probabilistically complete. This means that if a
path between the 2 specified coordinates exists in the environment, it will certainly be
found given finite time [3].
This is because the RRT propagates from the starting coordinate and grows in continuous
iterations till it is confirmed that the goal coordinate has been sampled as one of its
nodes. Therefore, once a RRT has finished growing, it is definite that both starting and end
points are part of its node network and since all of its nodes are only part of the free
space, it follows that a path will always exist between the 2 coordinates and the A*
algorithm will find it even if the computation takes a practically long time.
5.4.4.2. Perceived Sub-optimality
The key distinction between the CDM and the RRT approaches is in the sampling of the
free space. While the CDM decomposes the space into polygons and samples it in regular
discretized fashion, the RRT treats the space as a uniformly continuous domain and
samples it randomly. Therefore, if a RRT is grown to sufficient iterations as shown in
Figure 9, the free space is practically similar to an infinite resolution grid.
On such a continuous domain of points, the theoretical shortest path between 2 points is
always the straightest possible line between them. However, this is not true in the case of
a grid which is constrained by its resolution. This means that while some paths computed
using the CDM which were not straight-lines were theoretically optimal under its
resolution constraint. However, none of the paths computed using the RRTs were
theoretically optimal because none of them were a perfect straight-line.
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-28-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
However, when both the paths computed by the 2 different methods are compared, it is
found most often than not that the paths computed using the RRTs were shorter in length
than those computed using the CDM. Since real-life applications intend to minimize the
length of the path as much as possible, this result implies that the paths computed by the
RRTs were more optimal in terms of path length despite being theoretically sub-optimal.
5.4.4.3. Randomness of the RRT Approach
As the name of the approach implies, the trees in this method grow in a randomised
nature with every node being selected using MATLAB’s in-built rand function. Therefore,
this randomness is subsequently reflected in the computed results of the algorithm as
well. No two RRTs have a practical probability of being the same. Therefore, even if the
same 2 coordinates are specified to the algorithm for a path to be computed, each
simulation will generate a different path and have different computation times as well.
For example, it was noted during the simulation testing that 1 particular problem took
nearly 11 minutes to compute a path but when it was re-simulated once more, it took
only 17 seconds to generate a slightly different path. This is because each time the
algorithm is run, the tree grown might have different sampling densities or sampling area
and this sampling pattern affects the path that can be chosen. If the particular iteration
had a high sampling density, it is likely that a more optimal path can be found but the
computation time can be longer due to the higher number of points to be considered.
Therefore, the simulation data discussed previously in the results are indicative of only 1
possible random scenario and these results cannot be replicated again. So, if the same
experiments and run again, we are likely to obtain different data which can be either
better or worse than before. However, in the case of the CDM, the environment is
sampled regularly and therefore, repeated simulations will always return the same results
and this forms a distinction between the 2 approaches. Hence, the results obtained from
RRTs carry uncertainty around them and it is recommended that the results obtained
using this approach be treated with caution.
5.4.4.4. Problems involving the heuristic function
It was previously discussed in the Section 4.4.3.3 that the heuristic function implemented
in the A* search algorithm did not take the presence of obstacles into account [23]. Just
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-29-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
like how this resulted in the problem of sub-optimality in the paths computed using the
CDM, the RRT paths were also similarly affected.
As highlighted most vividly in Figure 11, the robot immediately heads straight in the
direction of the goal coordinate like a greedy best-first planner without realising that an
obstacle impedes that path. Therefore, when the robot reaches the vicinity of the
obstacle, it gets confused as to which direction it should head next to cross the obstacle.
This results in a series of sharp left and right movements in order to find a way out and
the heuristic function is unable to provide a clear answer to the algorithm.
While the planner will eventually find a way past due to its property of being
probabilistically complete, a lot of computation time and traversal cost is wasted in the
robot moving this unnecessary distance around the obstacle. In a real-life application
where traversal costs have to be minimized, this is an undesirable effect and the issue
needs to be addressed.
5.5. Future improvements to be considered
While the best possible way to correct the traversal problem discussed above is to
formulate a new heuristic function which can take obstacles into account (as explained in
Section 4.5), there are other possibilities that can be considered as well.
One option that could help is inspired by the Tabu Search approach developed by
researches previously in tackling the reactive path planning problem [24]. In this method,
the robot is banned (or tabooed) against reversing its direction once it has chosen to
move ahead in a particular one [24]. For example, if the robot has chosen its initial
direction of navigation along the 0° direction, it can next head in any direction except the
region covered between 150° and 210° since the 180° direction is exactly opposite to it.
This constraint on the robot’s movement means that if it is confused by the heuristic
function, it is forced not to run into haphazard loops to try and get out. Instead, an
alternative median direction is chosen and adhered to so that a smoother path with lesser
waste of resources can be found even if it may be sub-optimal. If this constraint can be
adopted into the algorithm for the RRTs as well, the problem of the robot repeatedly
turning left and right in loops near the obstacle can be avoided. We will be able to
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-30-320.jpg)


![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
8. Bibliography
[1] S.Y. Nof, Handbook of Industrial Robotics, 2nd ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons,
1999, pp. 3 – 5.
[2] P. Mickle. (August, 2012). 1961: The first robot. Capital Century. [Online]. Available:
http://www.capitalcentury.com/1961.html
[3] J.C. Latombe, Robot Motion Planning. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1991, pp.
1 - 6.
[4] G.A. Bekey, Autonomous Robots: From Biological Inspiration to Implementation and
Control. Boston: MIT Press, 2005, pp. xiii – xiv.
[5] M.W. Spong, S. Hutchinson, M. Vidyasagar, Robot Modelling and Control. New Jersey:
John Wiley & Sons, 2006, pp. 5 – 6.
[6] Y.K. Hwang and N. Ahuja, “Gross Motion Planning: A Survey”, ACM Computing
Surveys, vol. 24, (3), pp. 219 – 291, 1992.
[7] S.M. LaValle, “Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees: A New Tool for Path Planning”. TR 98-
11, Computer Science Department, Iowa State University, USA, 1998.
[8] J.T. Schwartz and M. Sharir, “On the Piano Mover’s Problem I: The Case of a Two-
Dimensional Rigid Polygonal Body Moving Amidst Polygonal Barriers”, dissertation,
Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, NY, USA, 1982.
[9] E.W. Dijkstra, “A note on two problems with connexion with graphs”, Numerische
Mathematik, vol. 1, (1) , pp. 269 – 271, 1959.
[10] Stanford Research Institute. (August, 2012). AI Center :: Shakey. SRI. [Online].
Available: http://www.ai.sri.com/shakey/
[11] P.E. Hart, N.J. Nilsson, B. Raphael, “ A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of
Minimum Cost Paths”, IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics, vol. 4,
(2), pp. 100 – 107, 1968.
[12] P.E. Hart, N.J. Nilsson, B. Raphael, “Correction to a Formal Basis for the Heuristic
Determination of Minimum Cost Paths”, SIGART Newsletter, (37), pp. 28 – 29, 1972.
[13] S.M. Udupa, “Collision Detection and Avoidance in Computer Controlled
Manipulators” in Proceedings of the 5th joint international conference on Artificial
Intelligence, 1977, pp. 737 – 748.
[14] T. Lozano-Perez and M.A. Wesley, “An Algorithm for Planning Collision-Free Paths
Among Polyhedral Obstacles”, Communications of the ACM, vol. 22, (10), pp. 560 –
570, 1979.
[15] T. Lozano-Perez, “Spatial Planning: A Configuration Space Approach”, IEEE
Transactions on Computers, vol. C-31, (2), pp. 108 – 120, 1983.
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-33-320.jpg)
![Sriraj Gowthaman Srilakshmi R&D Thesis u5025162
[16] Computer Science Faculty. (August, 2012). Robotics: Motion Planning. Stanford
University. [Online]. Available: http://www-cs-
faculty.stanford.edu/~eroberts/courses/soco/projects/robotics/basicmotion.html
[17] O. Khatib, “Real-Time Obstacle Avoidance for Manipulators and Mobile Robots”, The
International Journal of Robotics Research, vol.5, (1), pp. 90 – 98, 1986.
[18] J. Barraquand and J.C. Latombe, “Robot Motion Planning: A Distributed
Representation Approach”, The International Journal of Robotics Research, vol. 10,
(6), pp. 628 – 649, 1991.
[19] L.E. Kavraki, P. Svestka, J.C. Latombe, M.H. Overmars, “Probabilistic roadmaps for
path planning in higher-dimensional configuration spaces”, IEEE Transactions on
Robotics and Automation, vol. 12, (4), pp. 566 – 580, 1996.
[20] D.E. Knuth, The Art of Computer Programming: Fundamental Algorithms, 3rd ed.
Boston: Addison-Wesley, 1997, pp. 308 – 423.
[21] S.M. LaValle and J.J. Kuffner, “Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees: Progress and
Prospects”, Algorithmic and Computational Robotics: New Directions, pp. 293 – 308,
2001.
[22] B. Siciliano, O. Khatib, Spirnger Handbook of Robotics. Berlin: Springer
Science+Business Media, 2008, pp. 109 – 128, pp. 827 – 850.
[23] A. Patel. (October, 2012). Amit’s A* Pages. Stanford University. [Online]. Available:
http://theory.stanford.edu/~amitp/GameProgramming/
[24] E. Masehian and M.R. Amin-Naseri, “Sensor-Based Robot Motion Planning – A Tabu
Search Approach”, IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, vol. 15, (2), pp. 48 – 57,
2008.
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathplanningformobilerobots-130130024153-phpapp02/85/Path-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots-34-320.jpg)