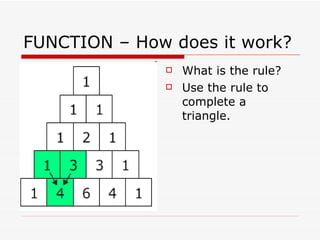
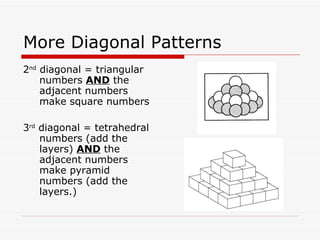
The document explores Pascal's Triangle, named after mathematician Blaise Pascal, highlighting its historical significance and its use in probability. It discusses rules for completing the triangle, patterns in row totals, and diagonal relationships such as triangular and tetrahedral numbers. Additionally, it examines the distribution of odd and even numbers, encouraging investigations into color patterns and ratios within the triangle.