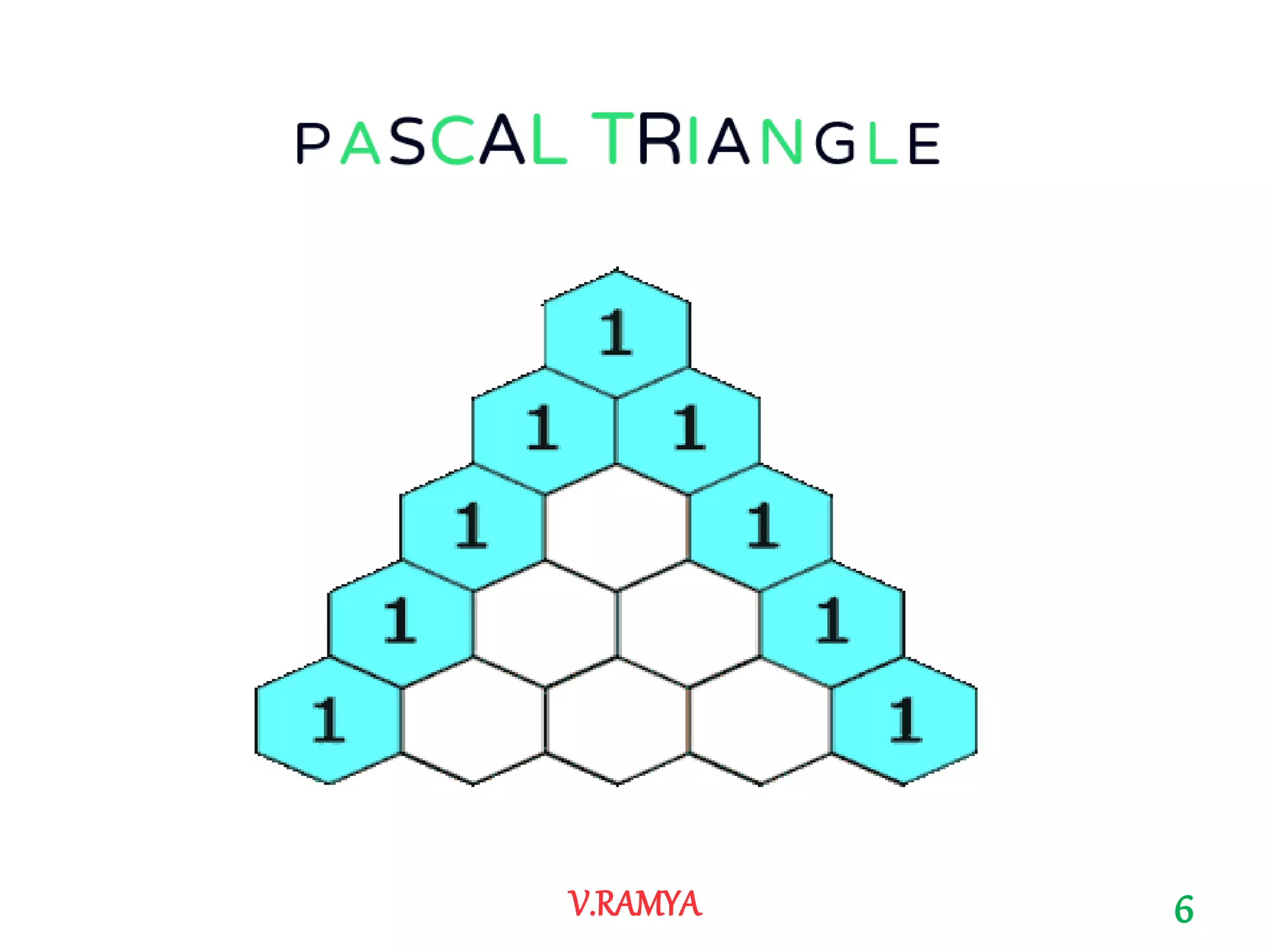
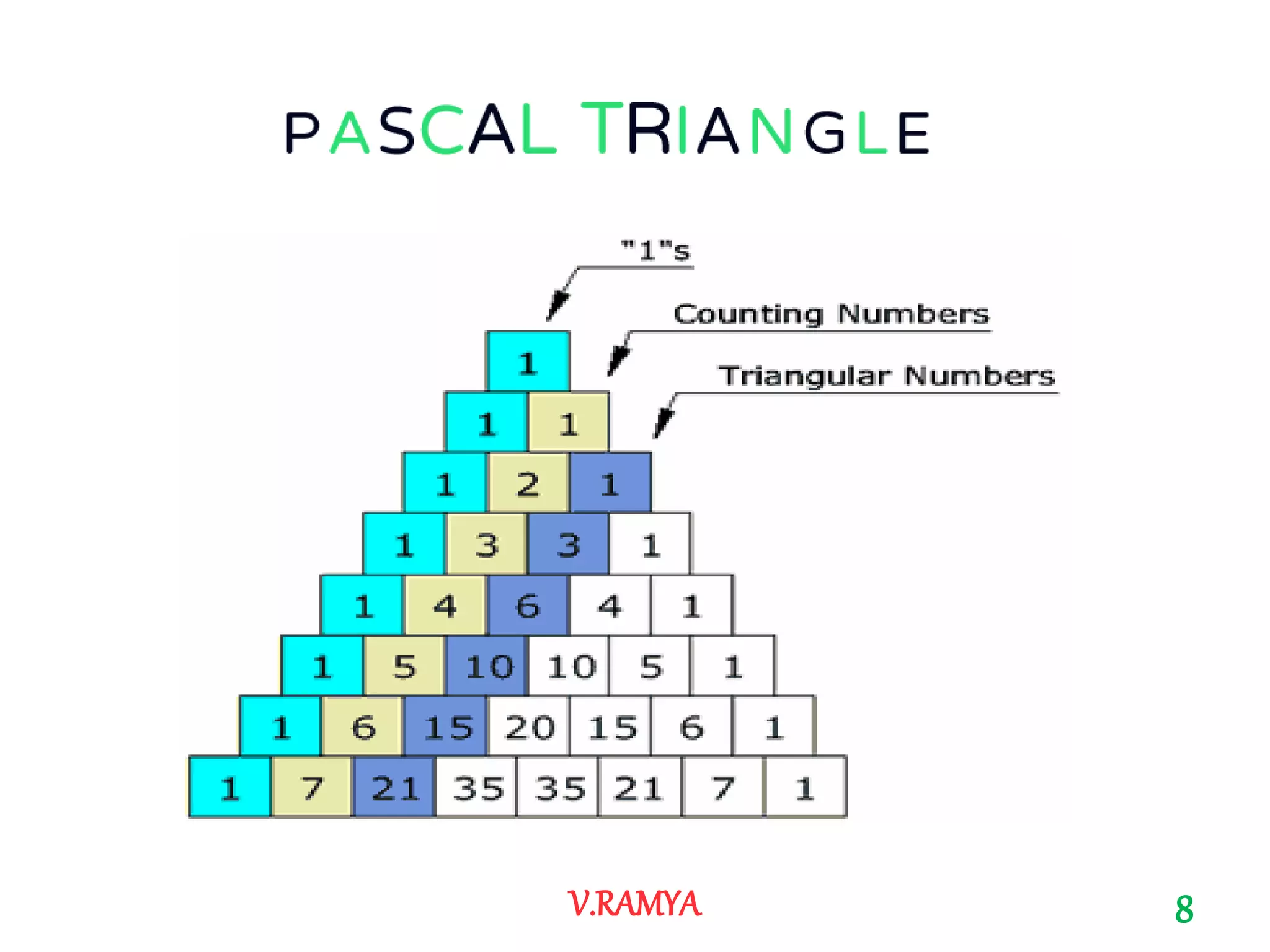
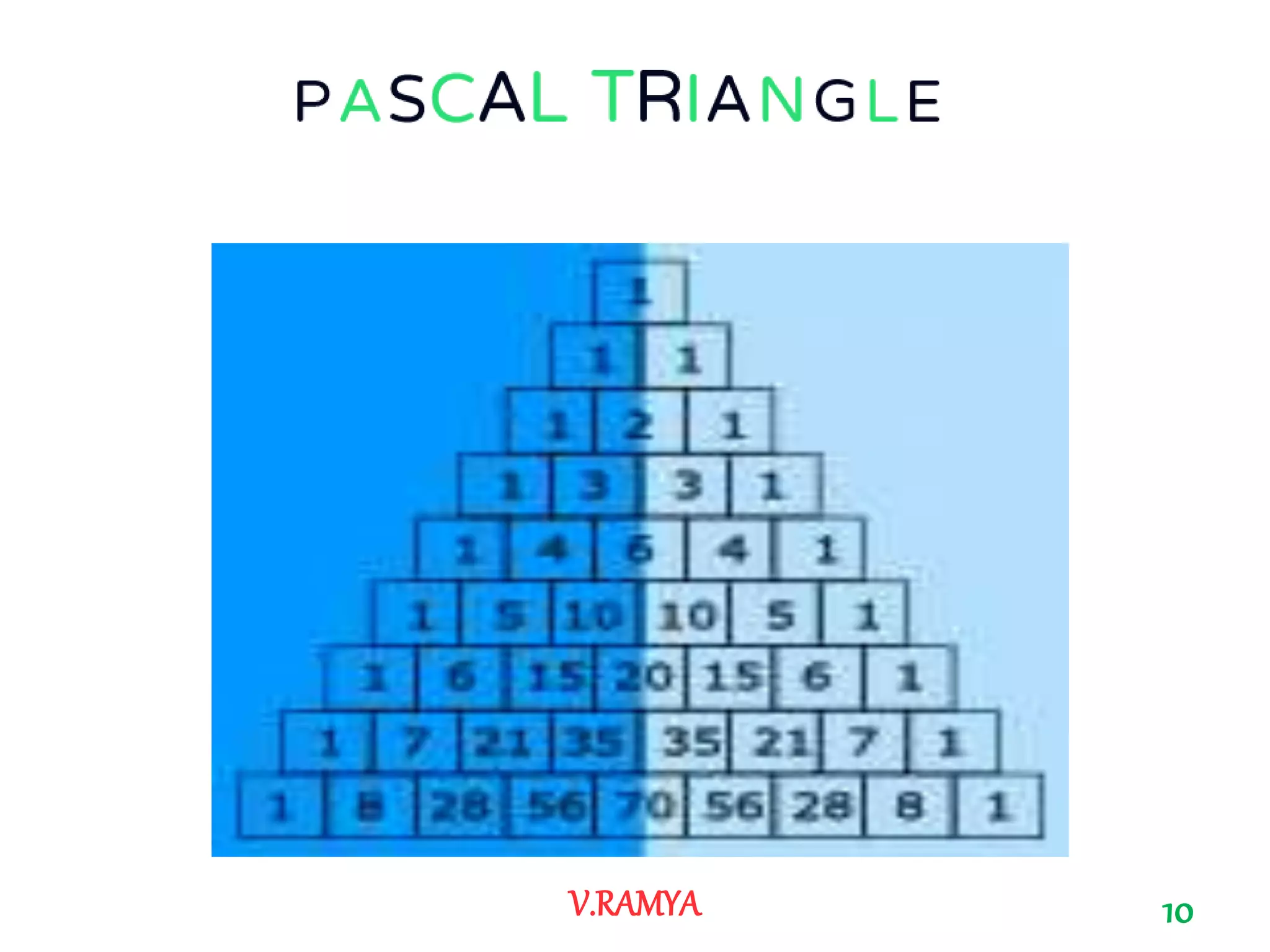
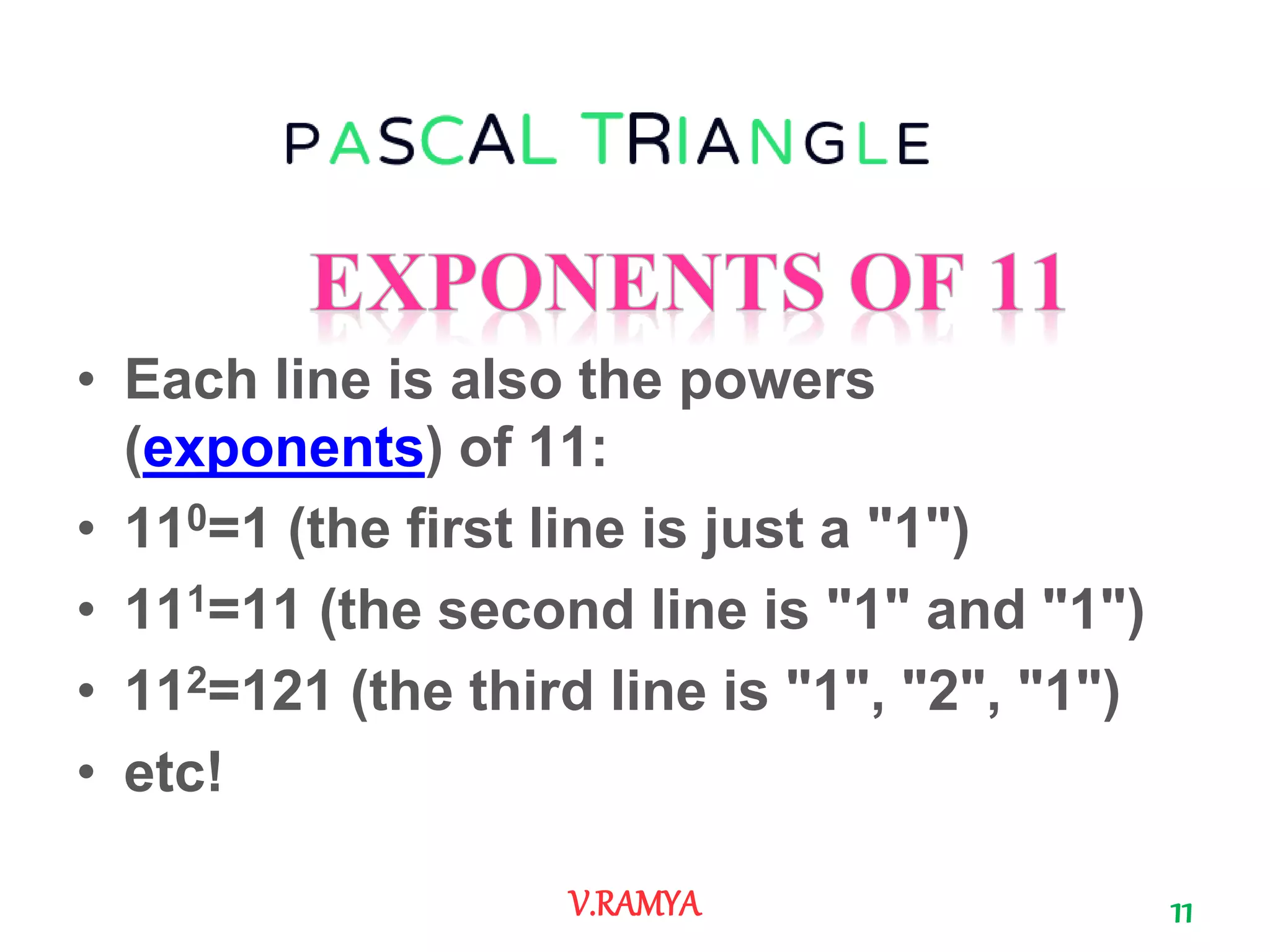
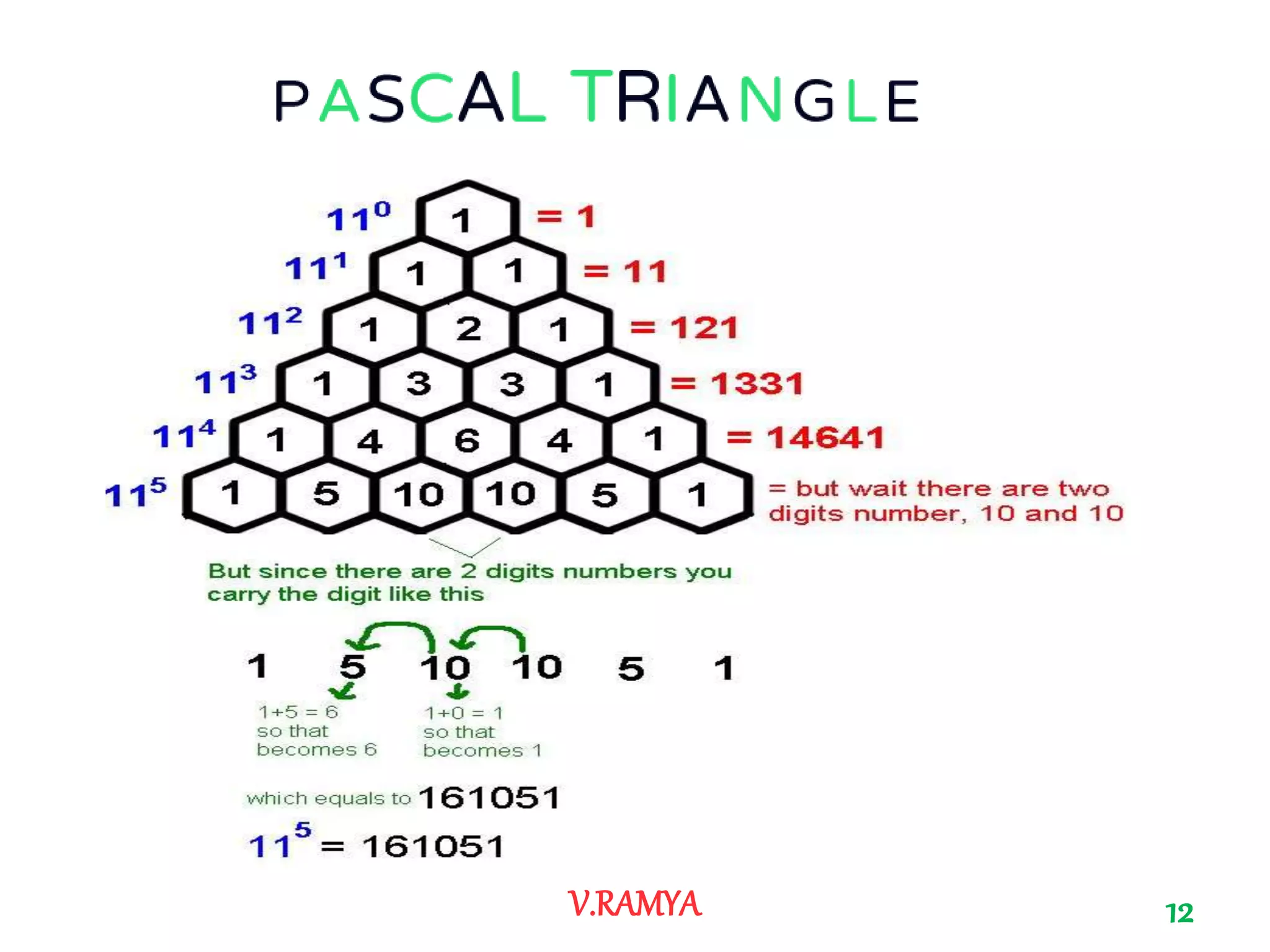
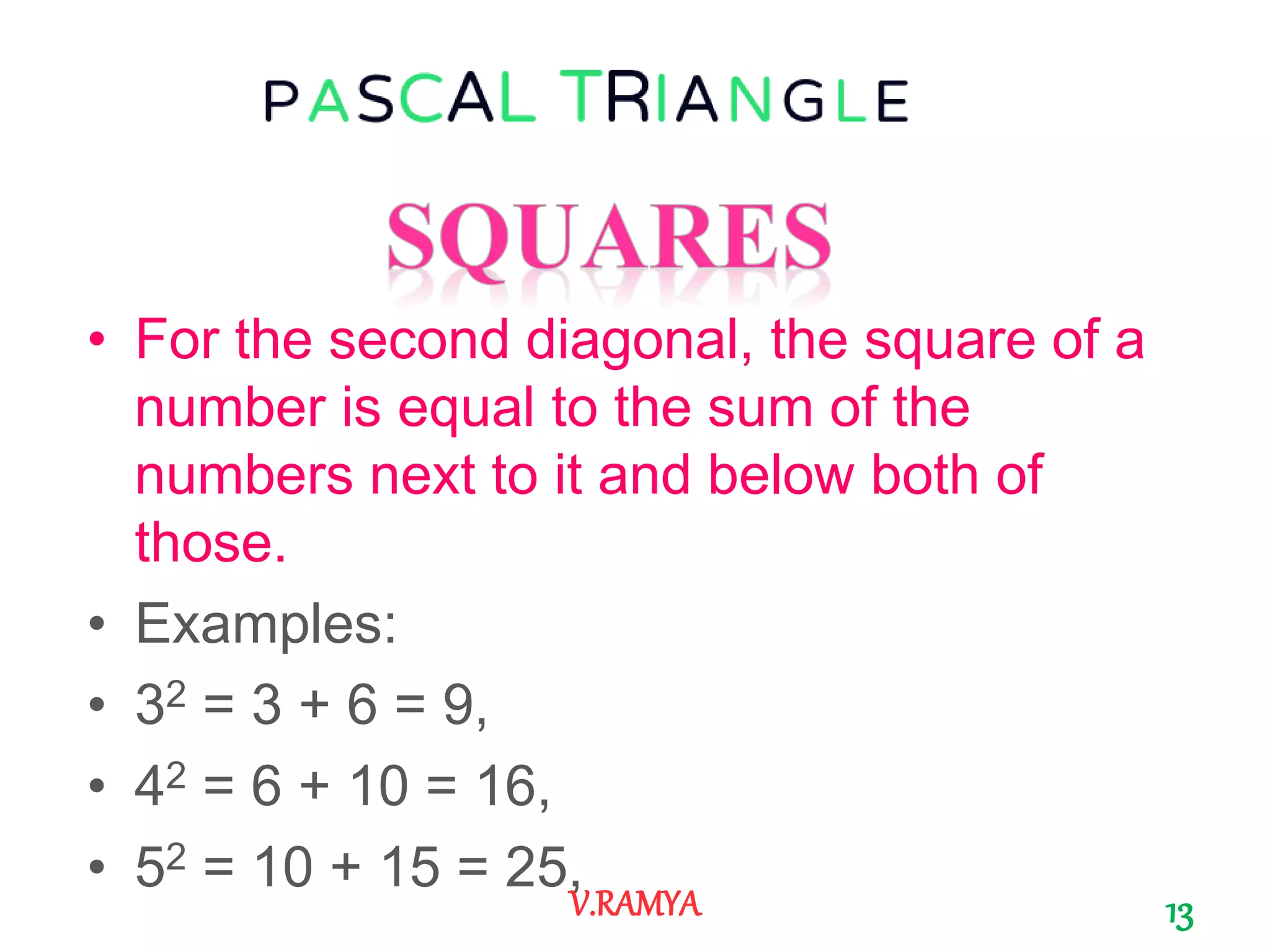
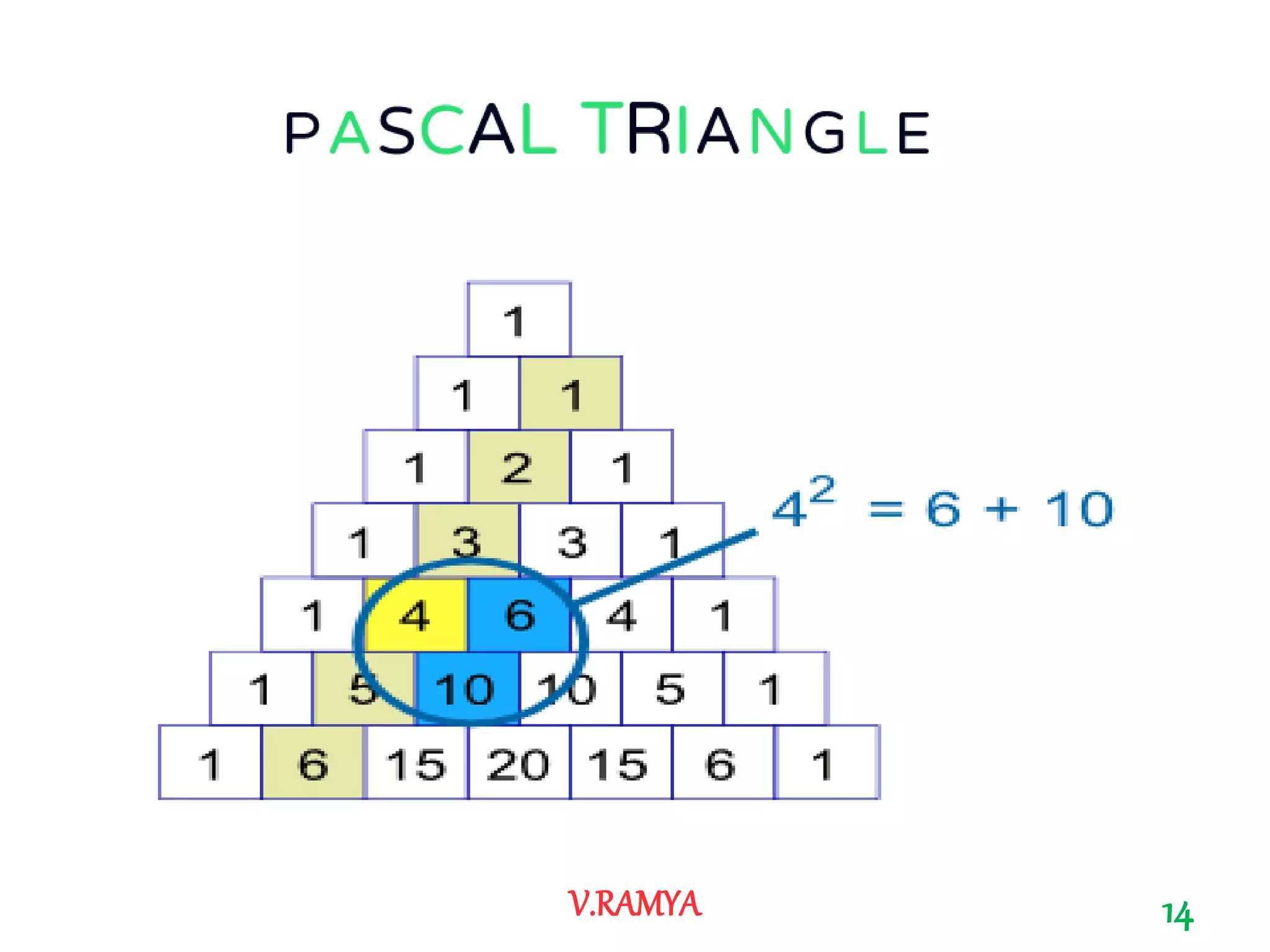
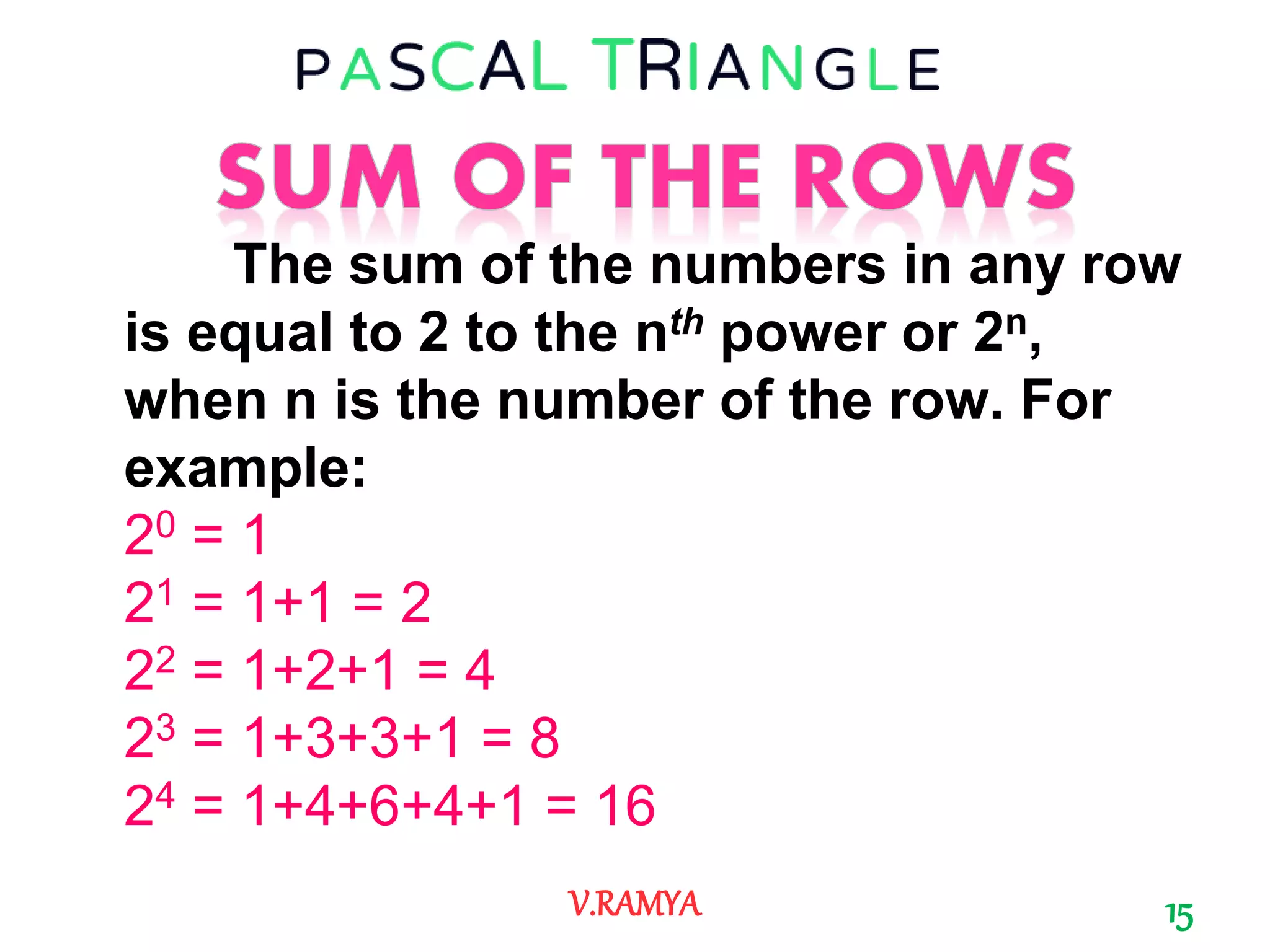
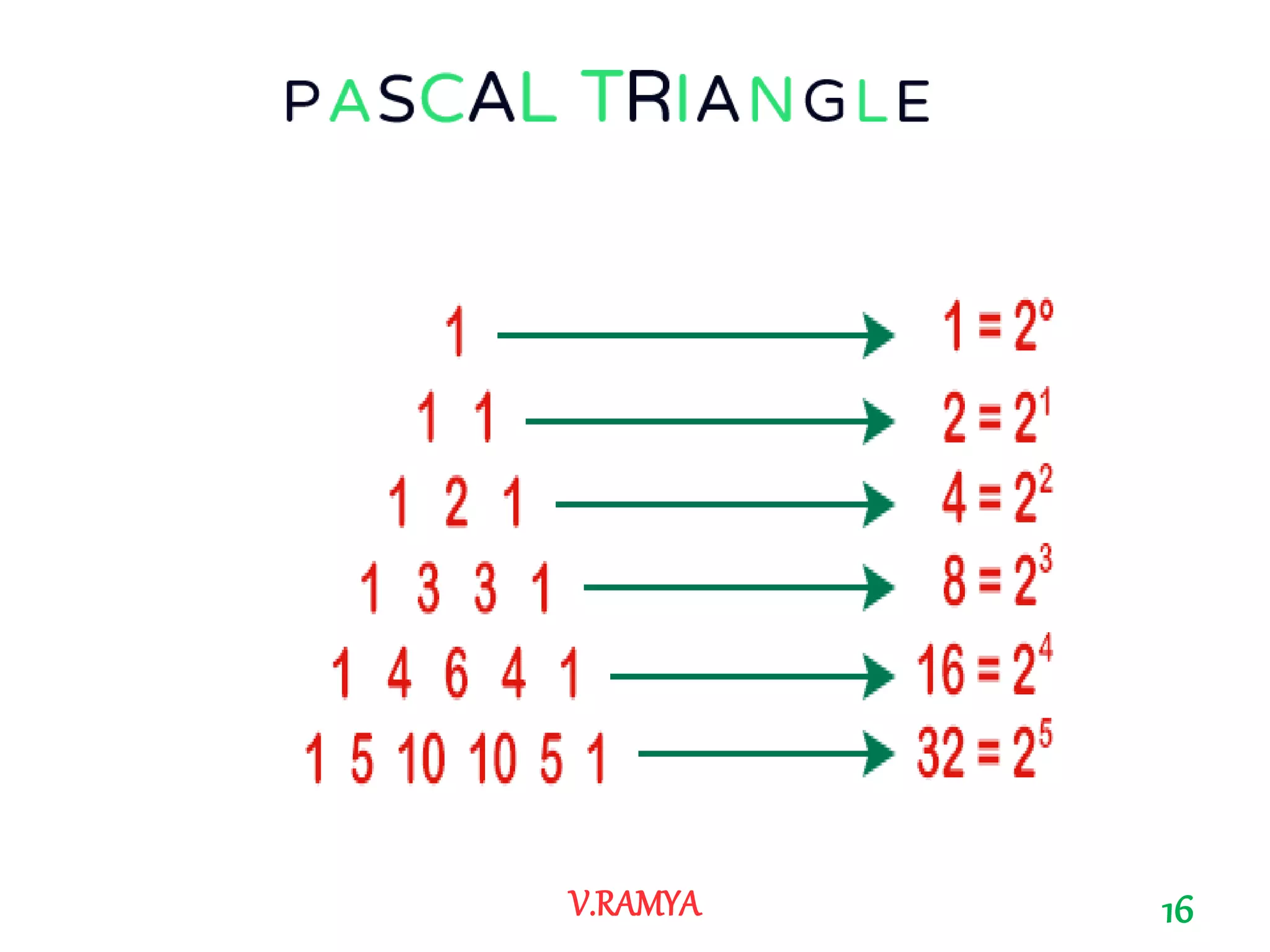
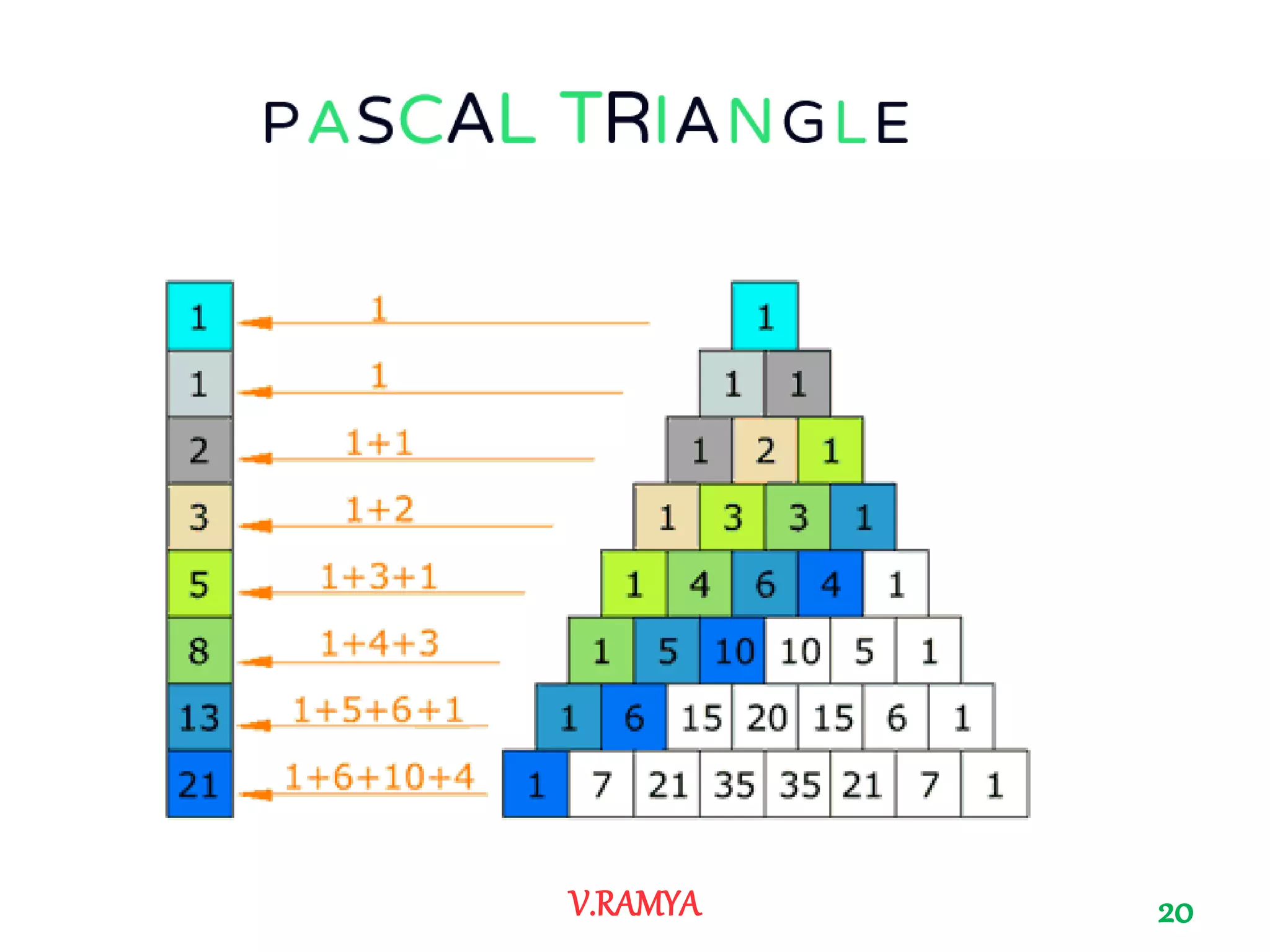
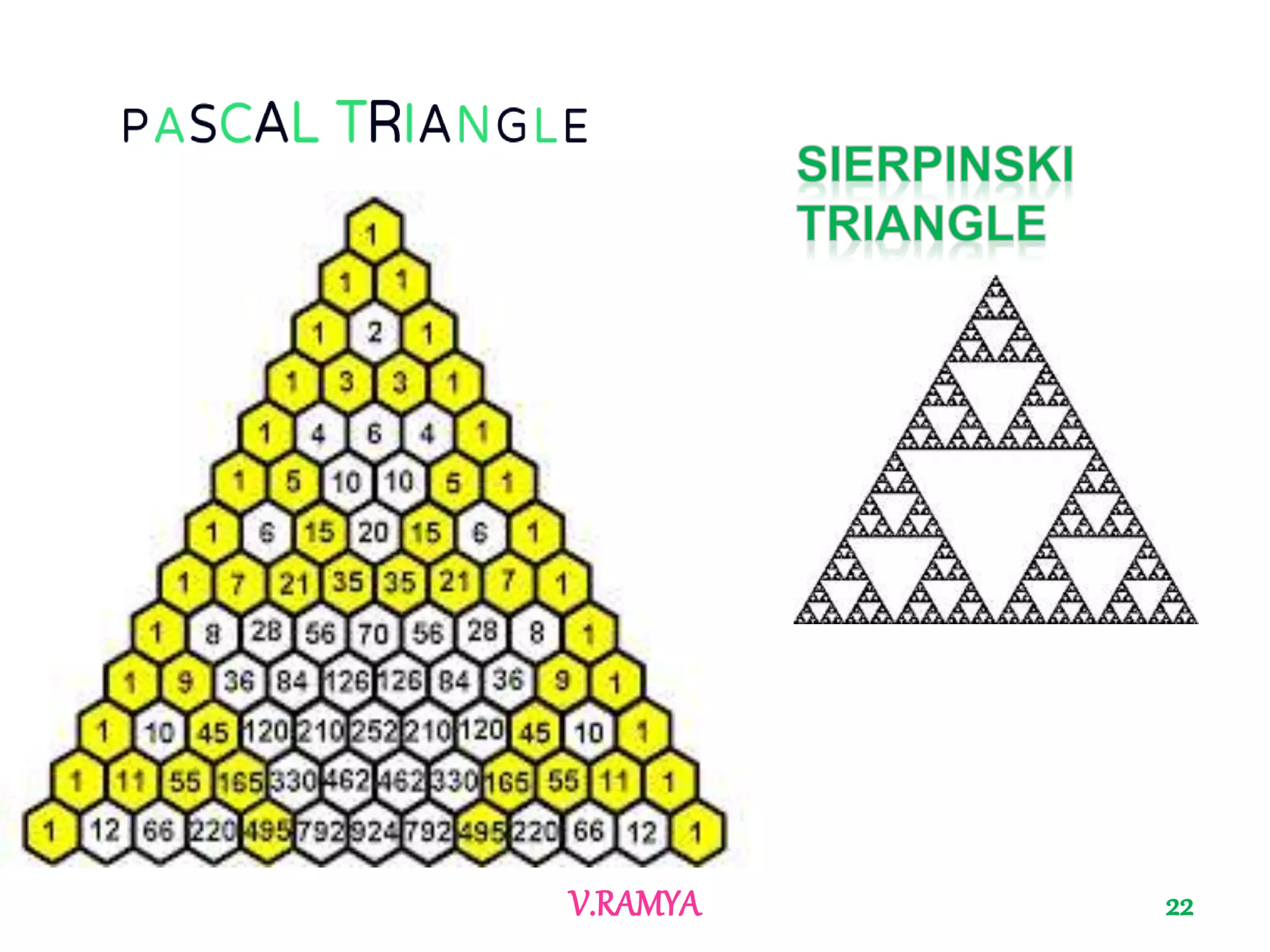
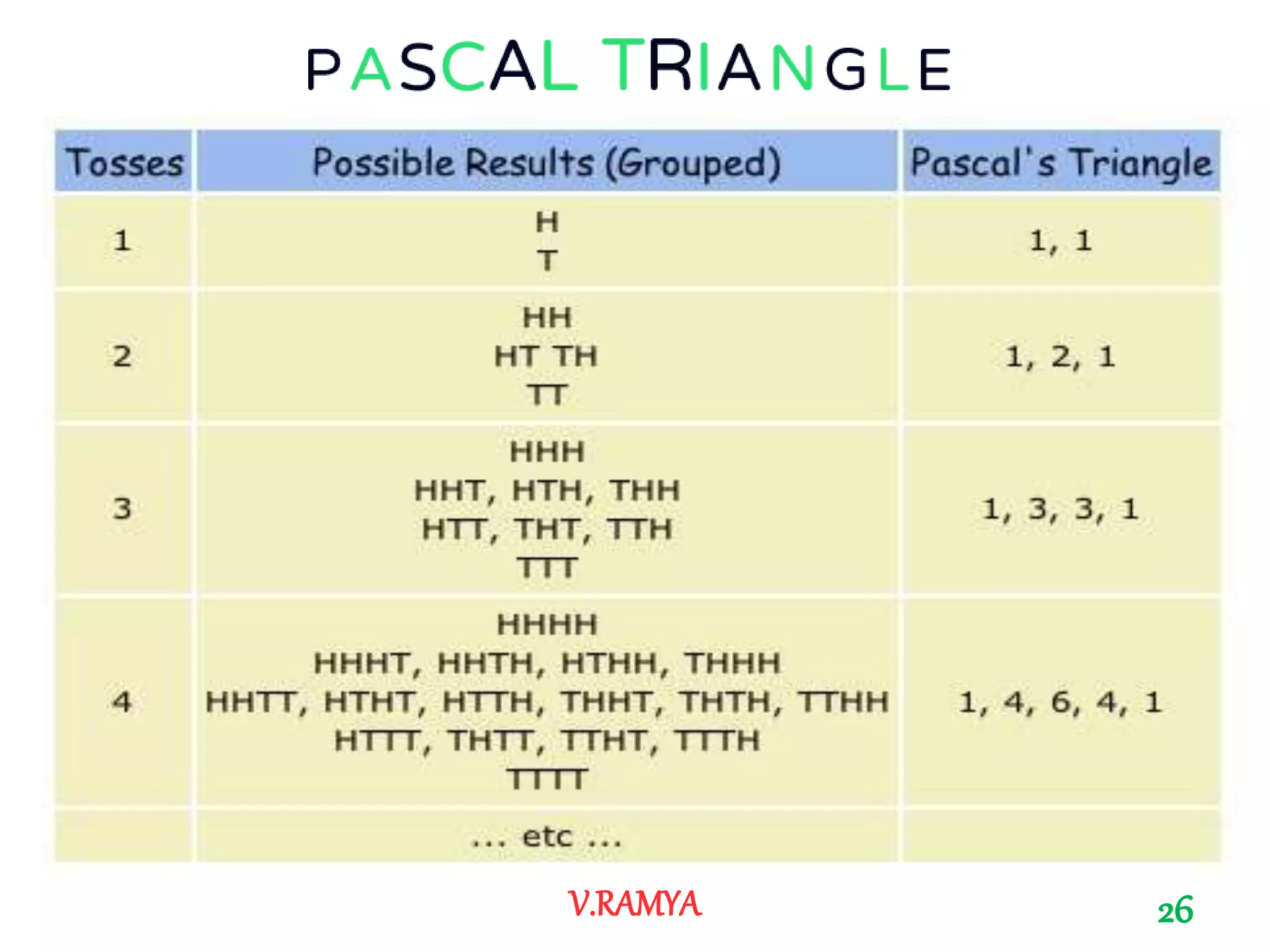
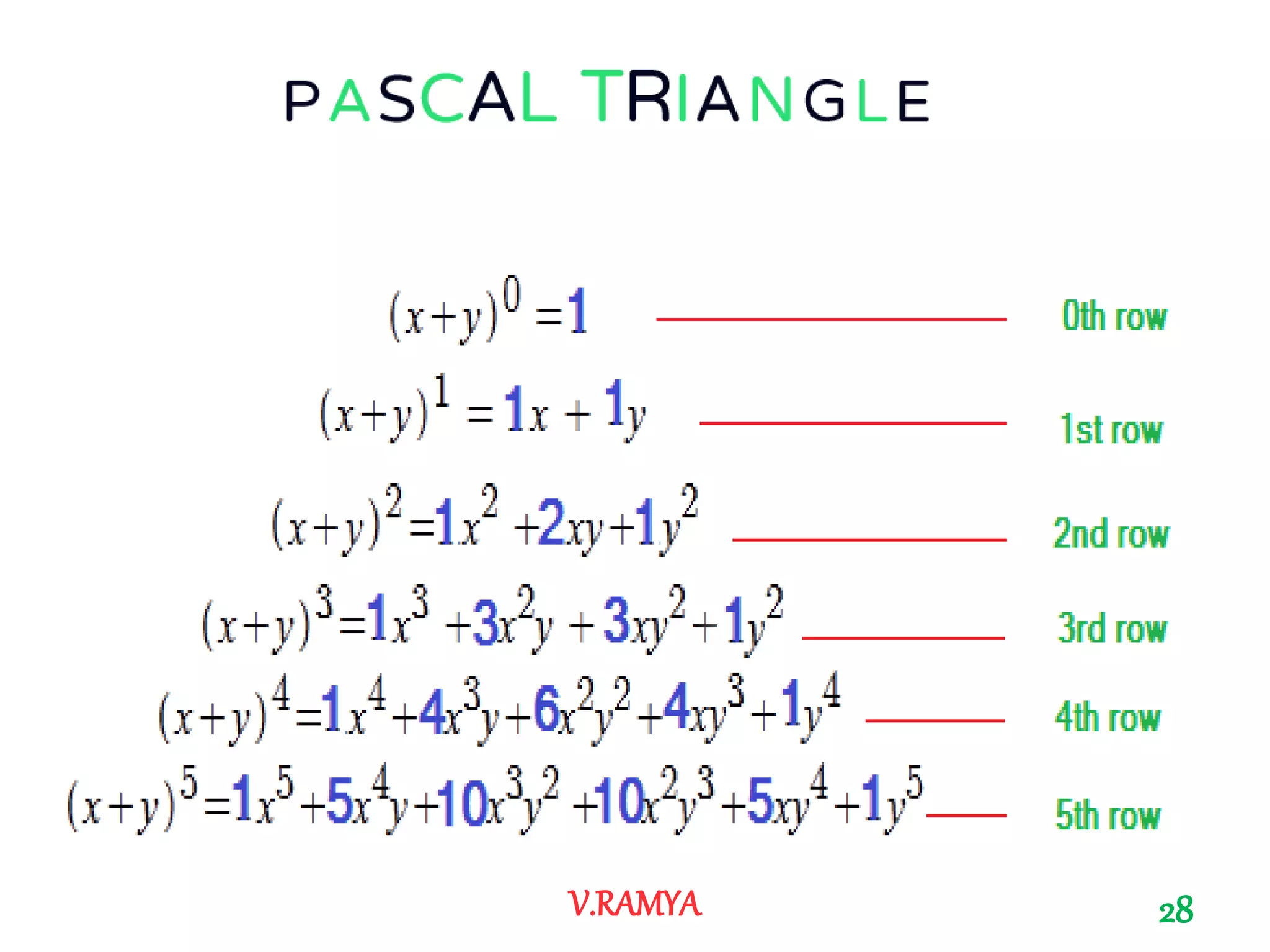
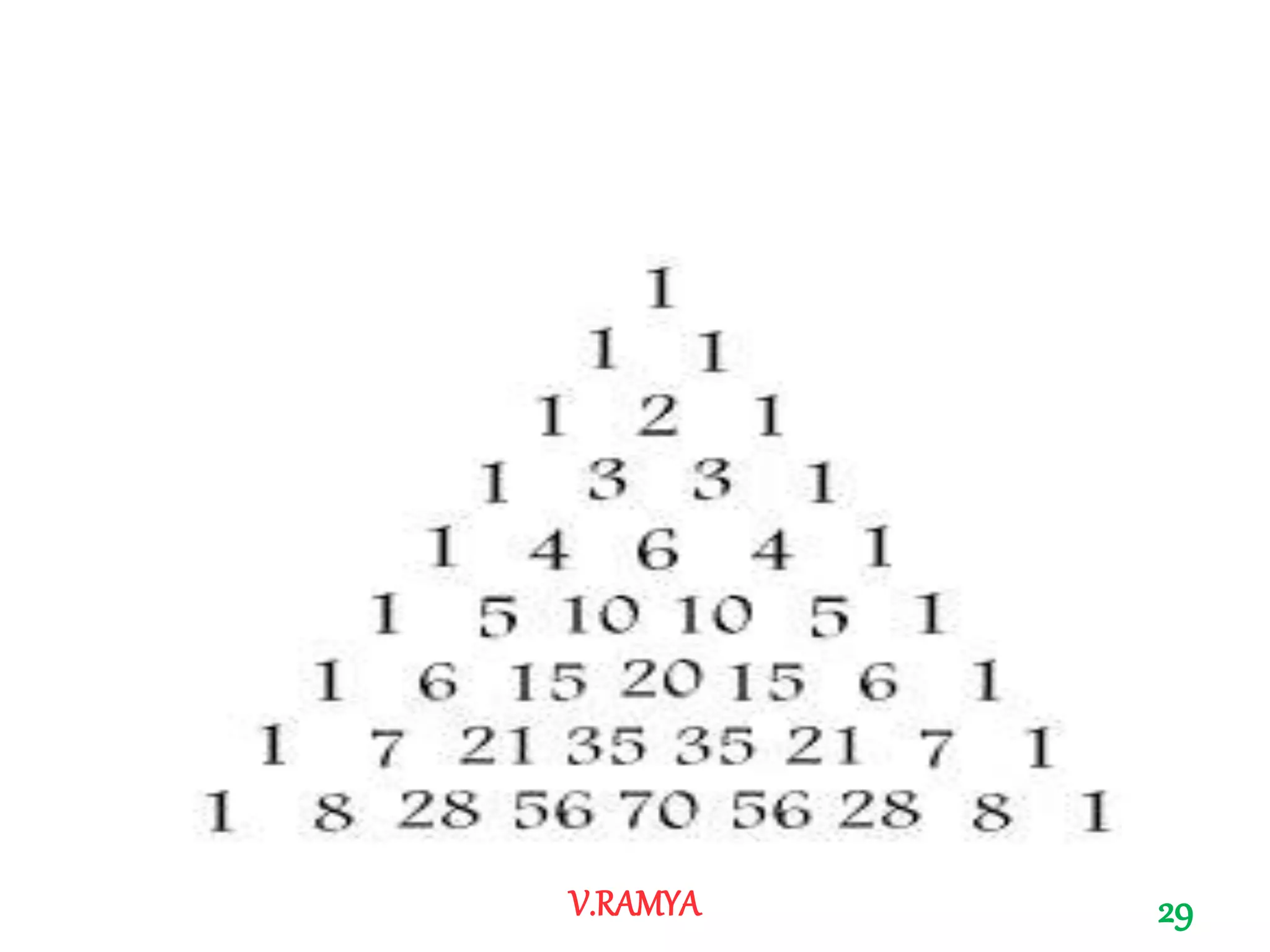
The document discusses Pascal's triangle, named after Blaise Pascal. It describes how to construct the triangle by placing numbers in a triangular pattern where each number is the sum of the two numbers above it. Some key properties mentioned include the triangle's symmetry, relationships between diagonals and powers of numbers, and how it can be used to show combinations and coefficients in binomial expansions.