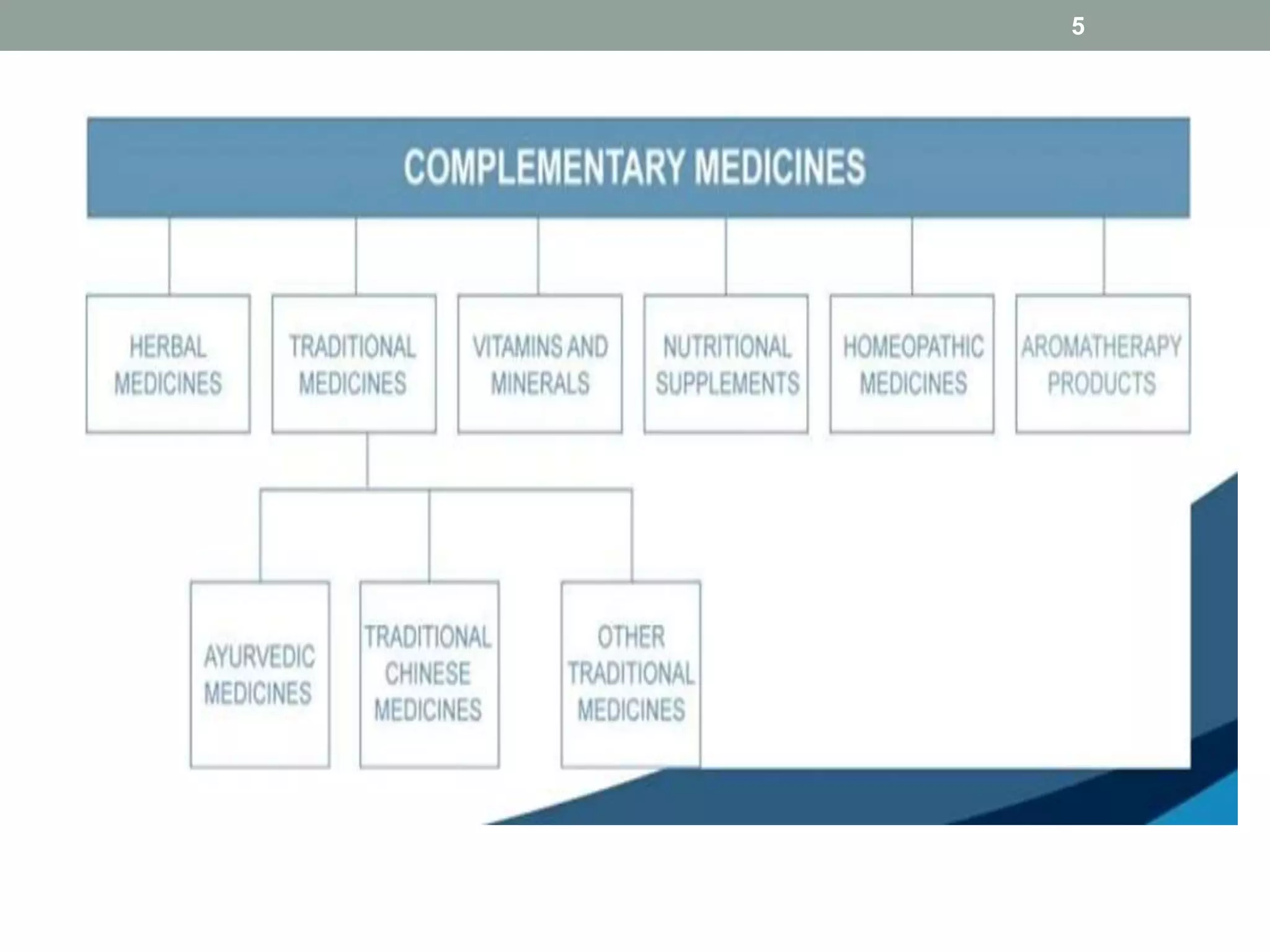
The document provides a comprehensive overview of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), distinguishing between complementary practices (used alongside standard treatment) and alternative approaches (used instead of it). It discusses various types of CAM such as mind-body therapies, biologically based practices, and whole medical systems, emphasizing the need for regulation and safety in their use. Additionally, it highlights WHO's strategies and guidelines for integrating and regulating traditional medicine globally, along with specific regulations in countries like India.