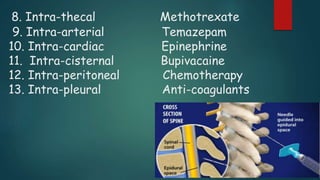
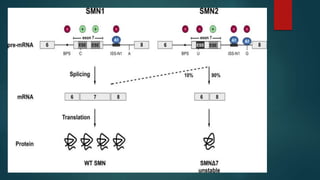
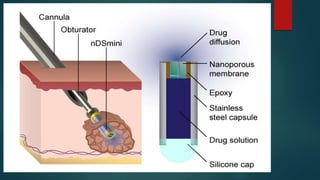
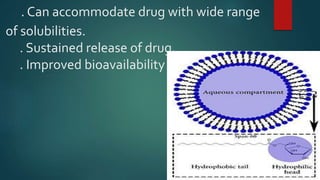
Parenterals are sterile preparations that are injected through the skin or mucous membranes into the body. They provide quick onset of action and accurate dosing but require aseptic technique. Common routes include intramuscular, intravenous, and subcutaneous. Advantages include rapid absorption but disadvantages include pain and risk of infection. The only approved treatment for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is the drug Spinraza, which works by binding to mRNA to make the SMN protein functional and treat SMA, an inherited neuromuscular disease. Future parenteral delivery systems aim to reduce injections and provide sustained drug release through methods like nanoparticles, in-situ forming depots, niosomes, and liposomes.