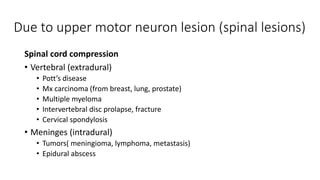
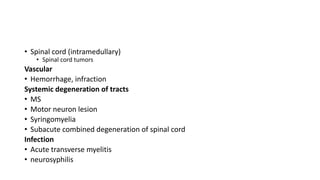
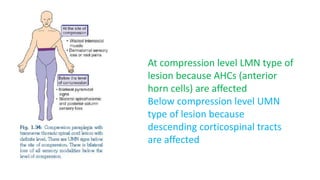
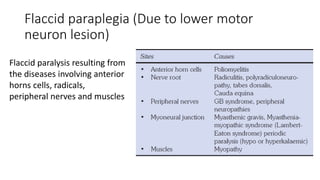
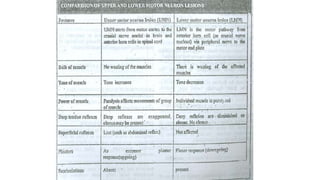
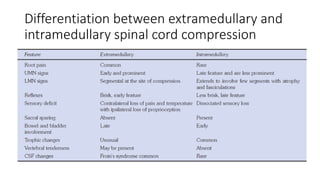
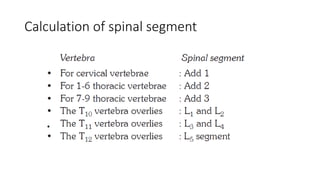
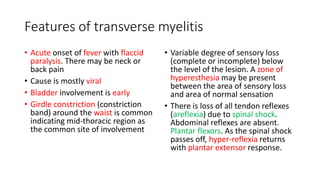
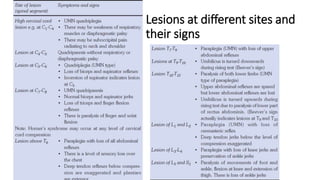
Paraplegia can be flaccid or spastic depending on whether it is caused by a lower motor neuron or upper motor neuron lesion. Cerebral paraplegia results from lesions in the paracentral lobule and presents with bladder retention and cortical sensory loss. Spinal cord paraplegia can be compressive or non-compressive. Compressive paraplegia often shows a sensory level and root pain while non-compressive lesions may cause asymmetrical sensory loss. Differentiating intramedullary from extramedullary lesions considers features like root pain and bladder involvement. Causes of paraplegia include spinal cord tumors, infections, vascular lesions, and traumatic injuries or compressions.