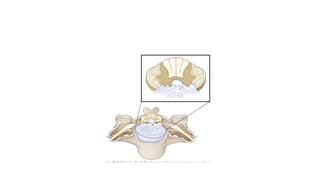
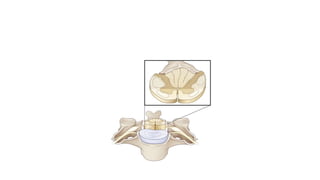
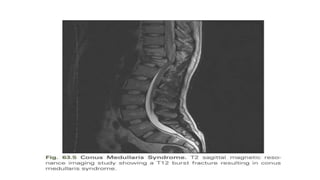
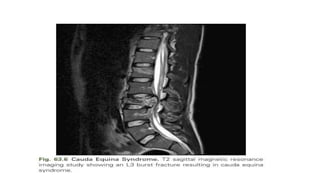
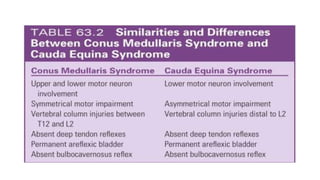
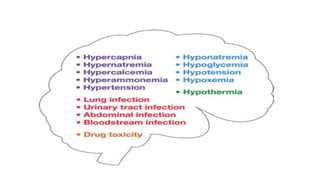
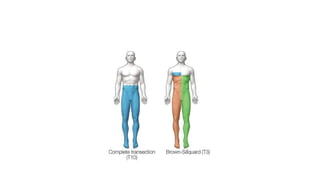
This document discusses cerebral swelling and edema that can occur after traumatic brain injury (TBI). It describes two main types of edema - vasogenic edema caused by blood-brain barrier disruption and cytotoxic edema caused by osmolar and cellular changes. Excitotoxicity from excessive glutamate release can also contribute to edema and neuronal injury through sodium and calcium-dependent mechanisms. Both necrosis and apoptosis can result from secondary injury processes. Animal studies show developing neurons are more susceptible to excitotoxic injury. Various spinal cord injury syndromes are also summarized.