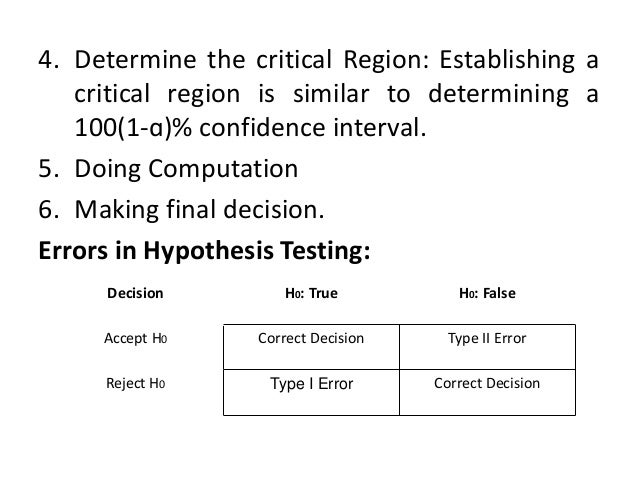
This document discusses hypothesis testing and different types of statistical tests. It explains that hypothesis testing involves setting a null and alternative hypothesis, determining a significance level, choosing a test statistic, establishing a critical region, doing computations, and making a final decision. Errors can occur by incorrectly accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis. Parametric tests like the t-test, z-test, and ANOVA assume the data comes from a normal distribution, while non-parametric tests like the chi-square test and Mann-Whitney test make no assumptions about the distribution. The t-test can be used for samples less than 30 and comes in one sample, two independent sample, and paired sample versions.