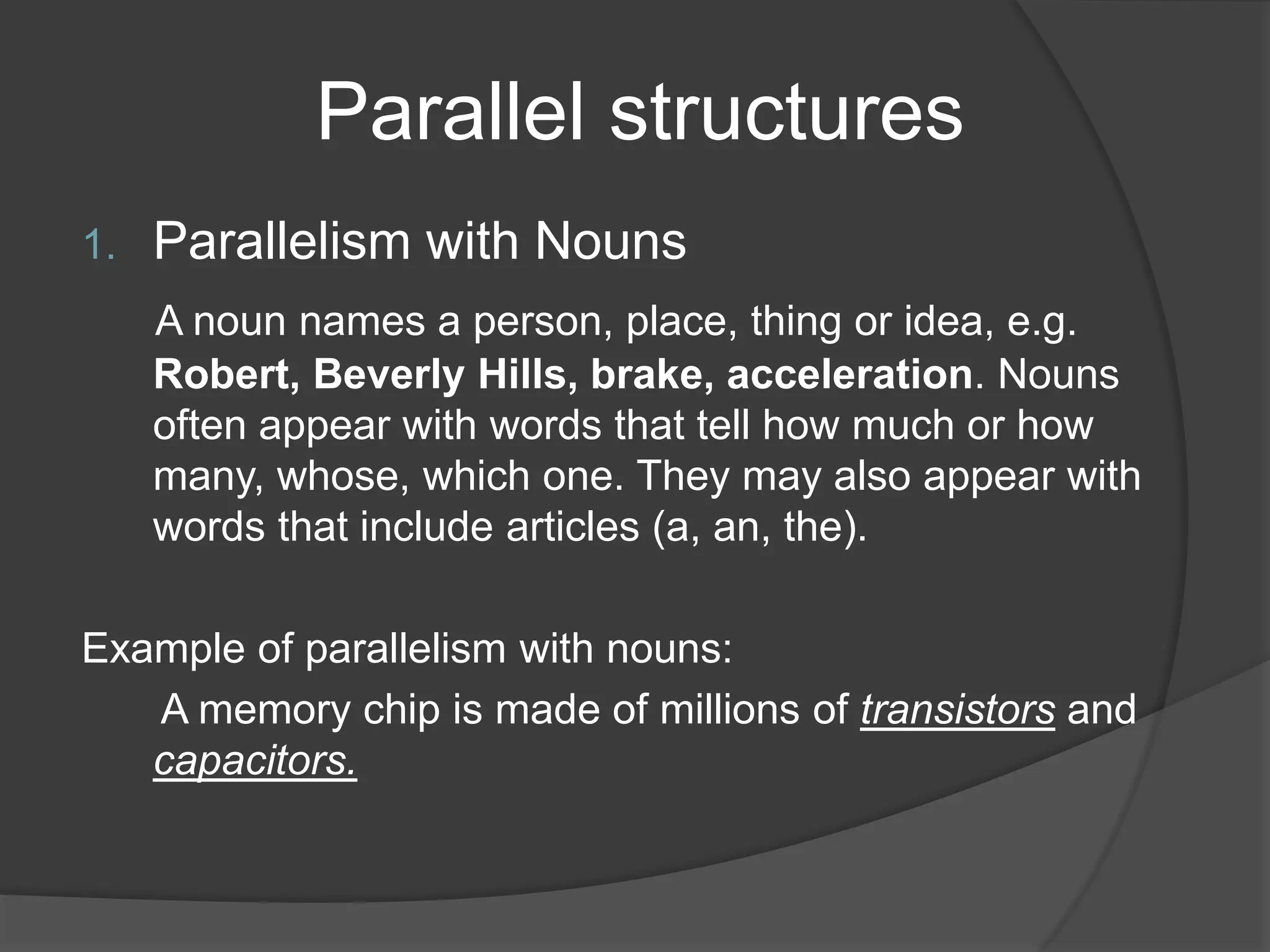
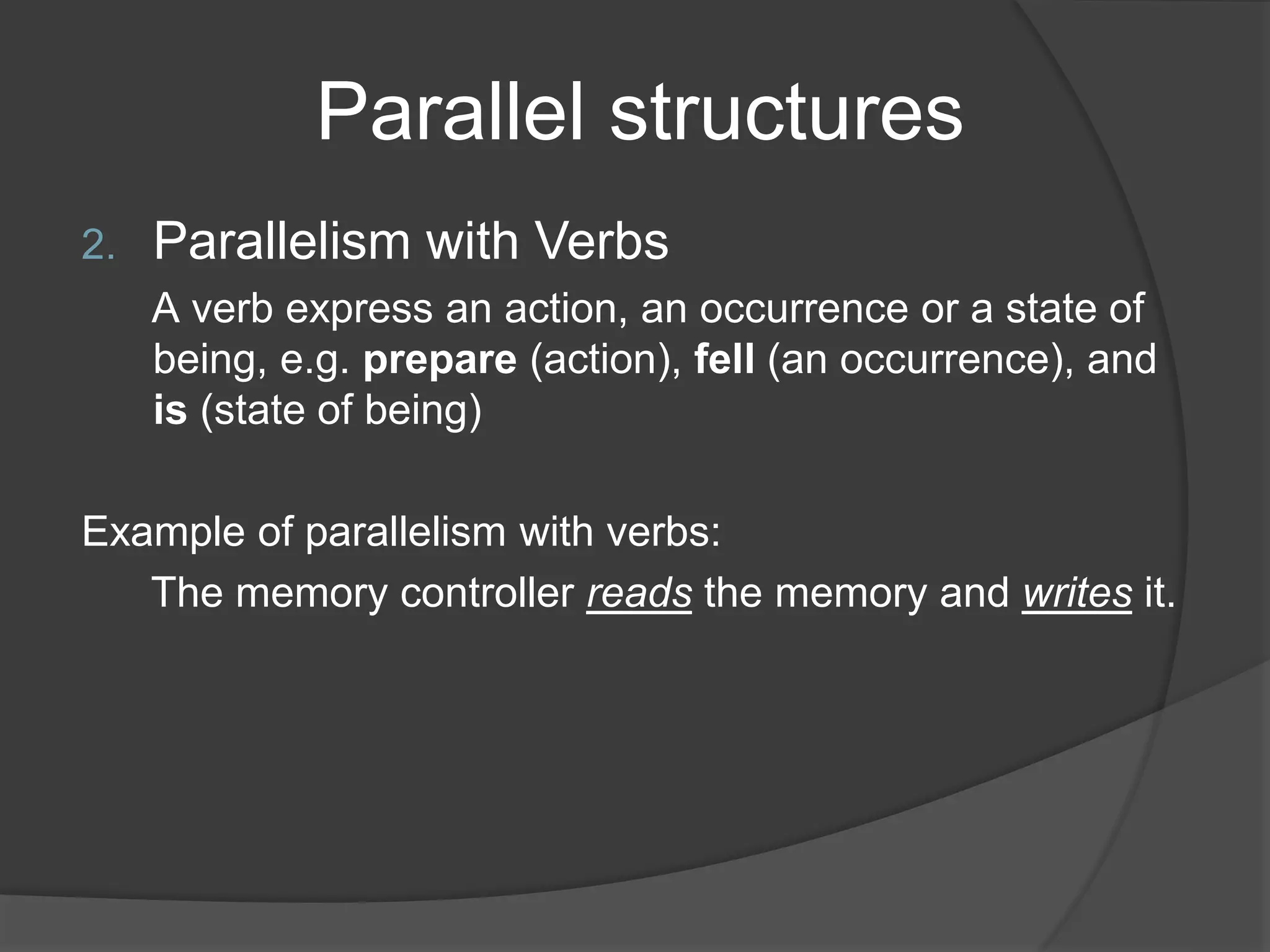
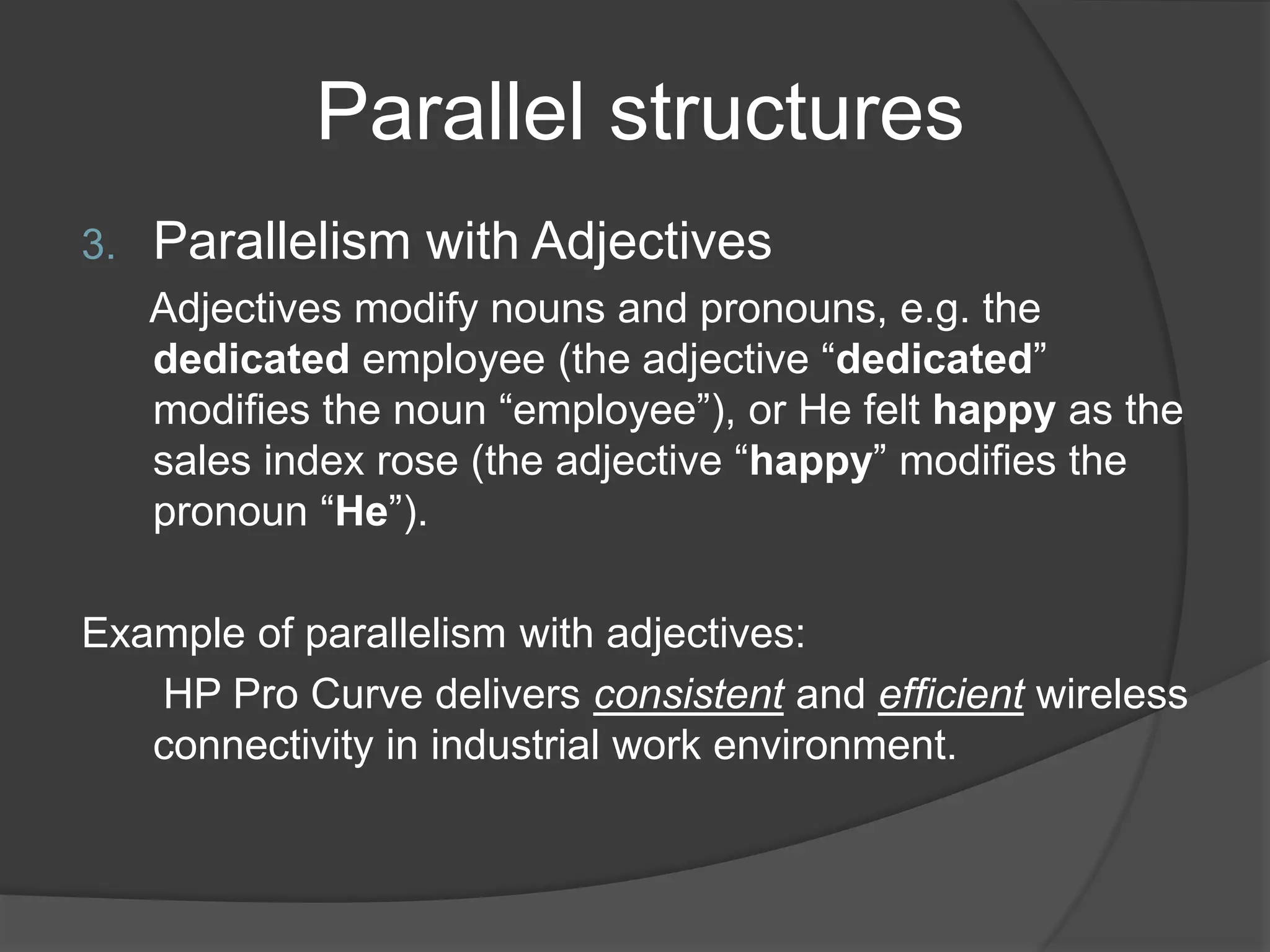
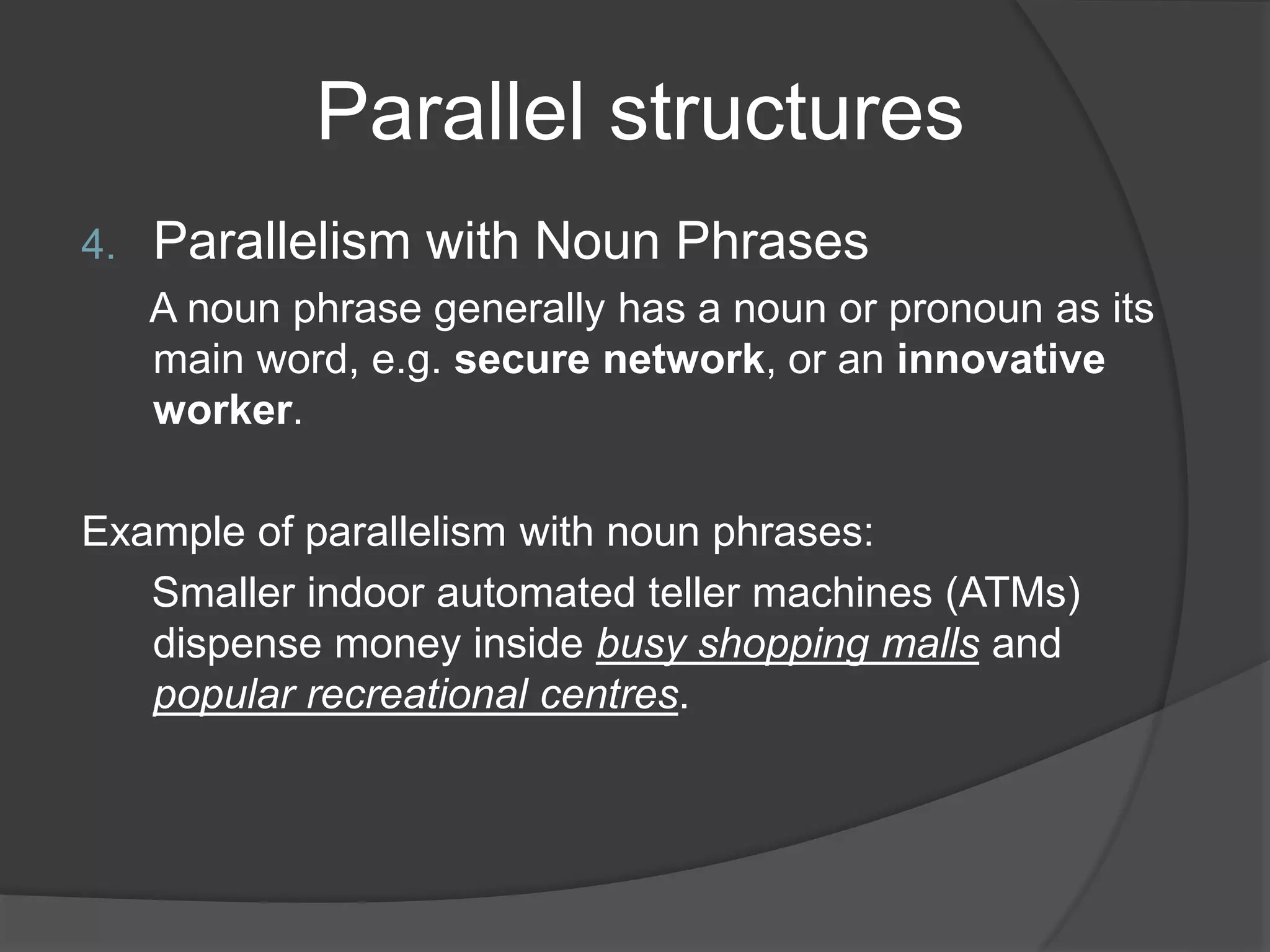
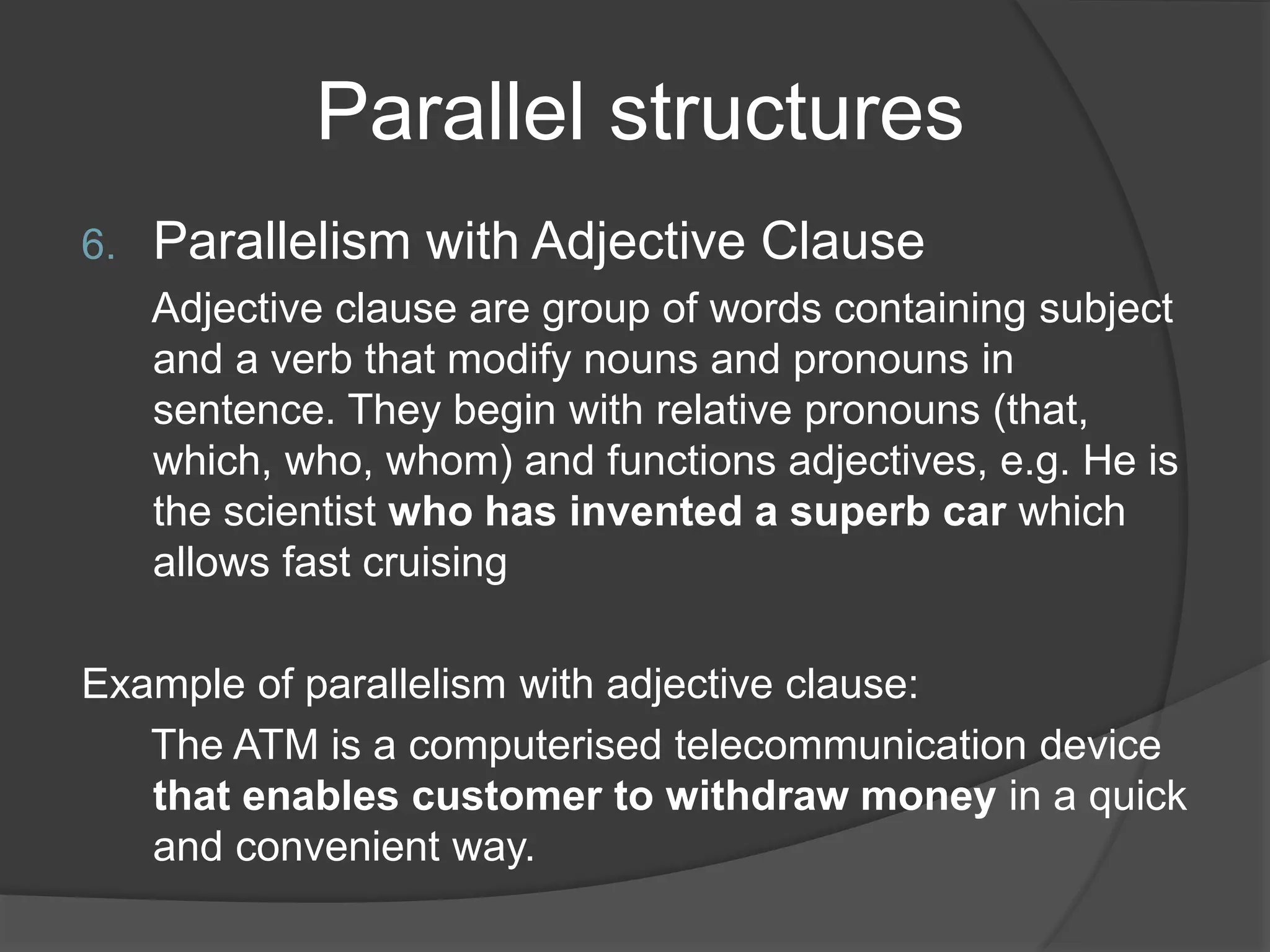
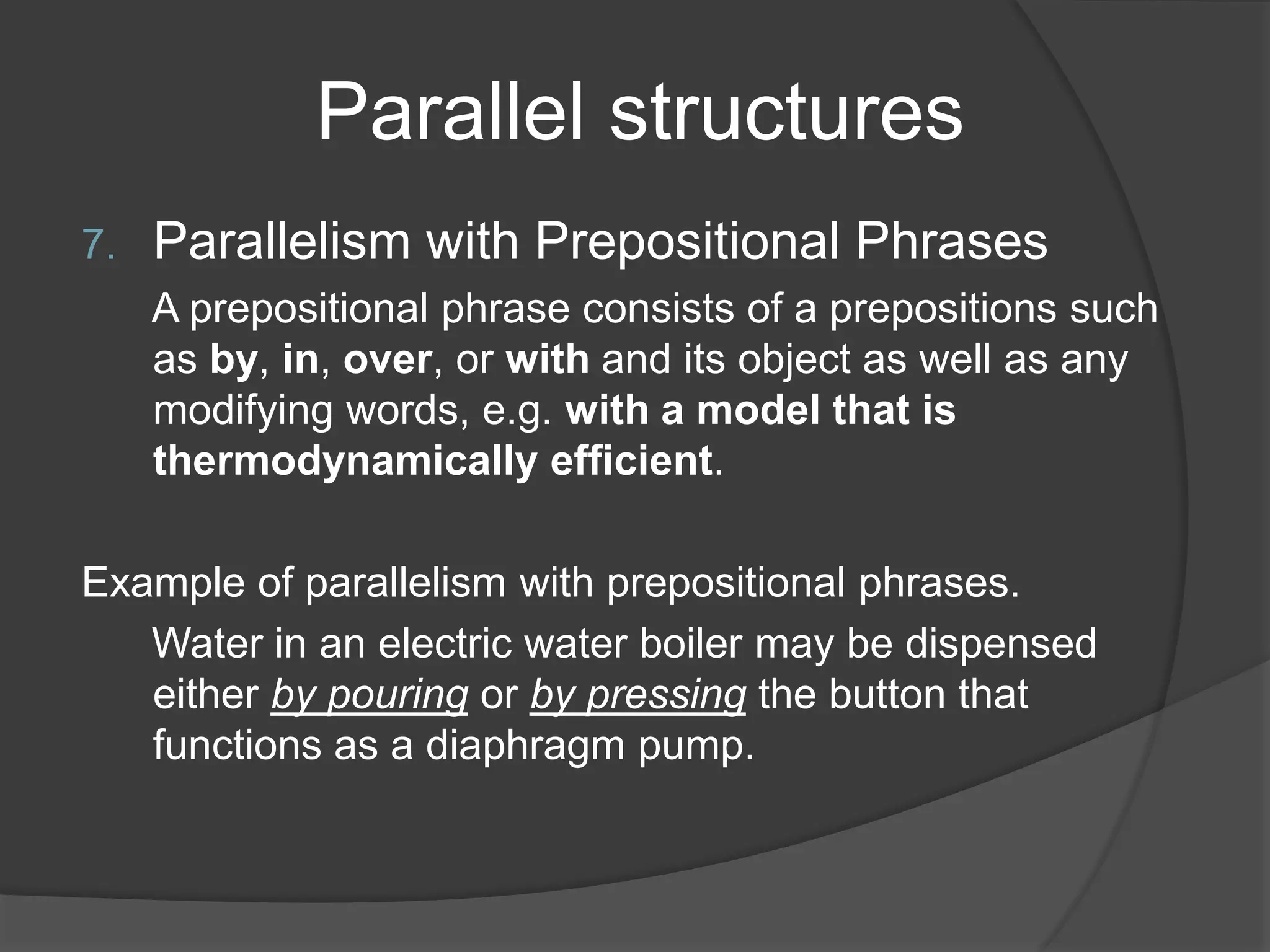
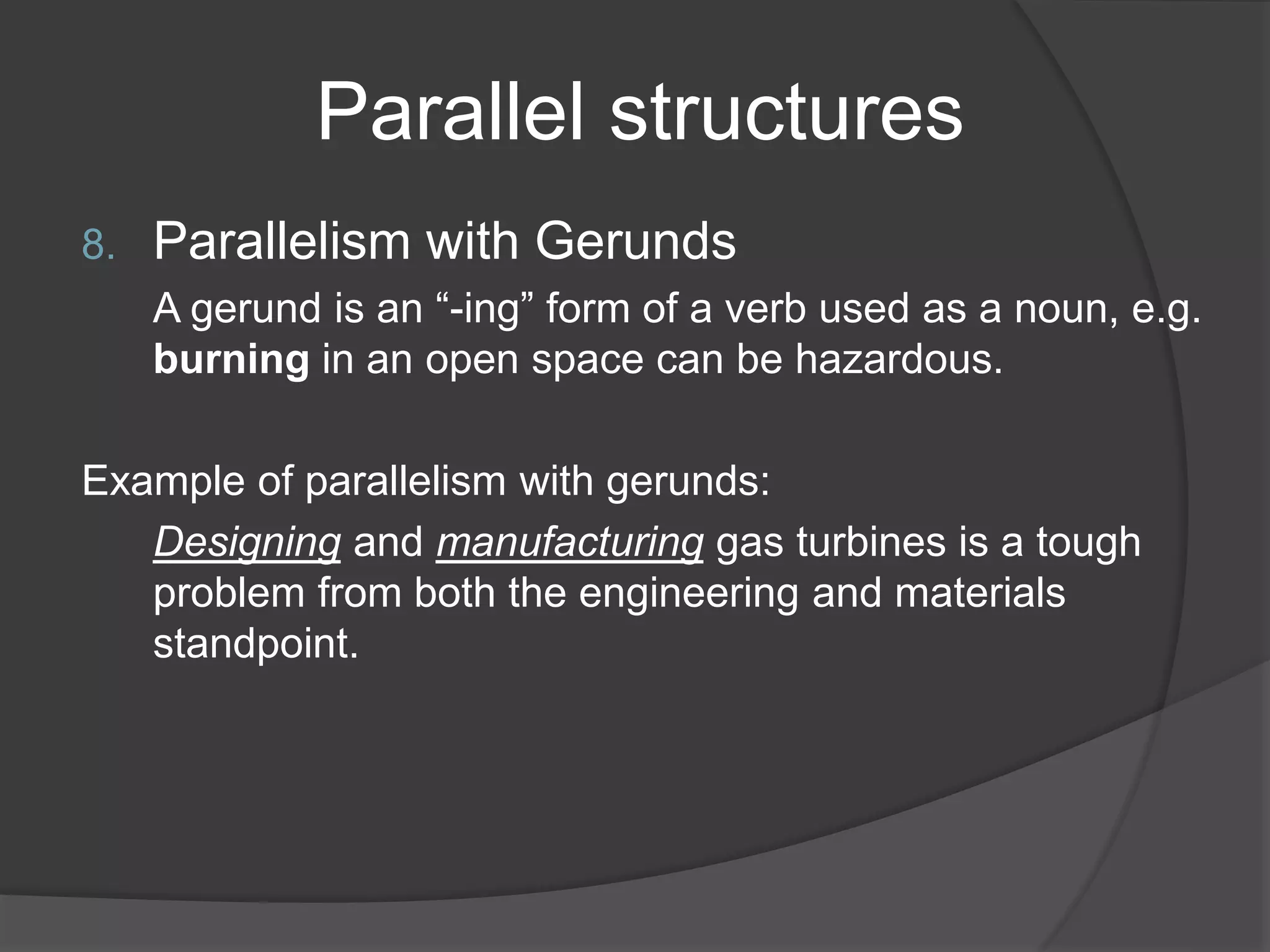
This document discusses different types of parallel structures that can be used in writing, including parallelism with nouns, verbs, adjectives, noun phrases, verb phrases, adjective clauses, prepositional phrases, gerunds, and infinitive phrases. Examples are provided for each type of parallel structure to illustrate its use. The purpose is to explain how to create parallelism through matching grammatical elements in a sentence or across sentences.