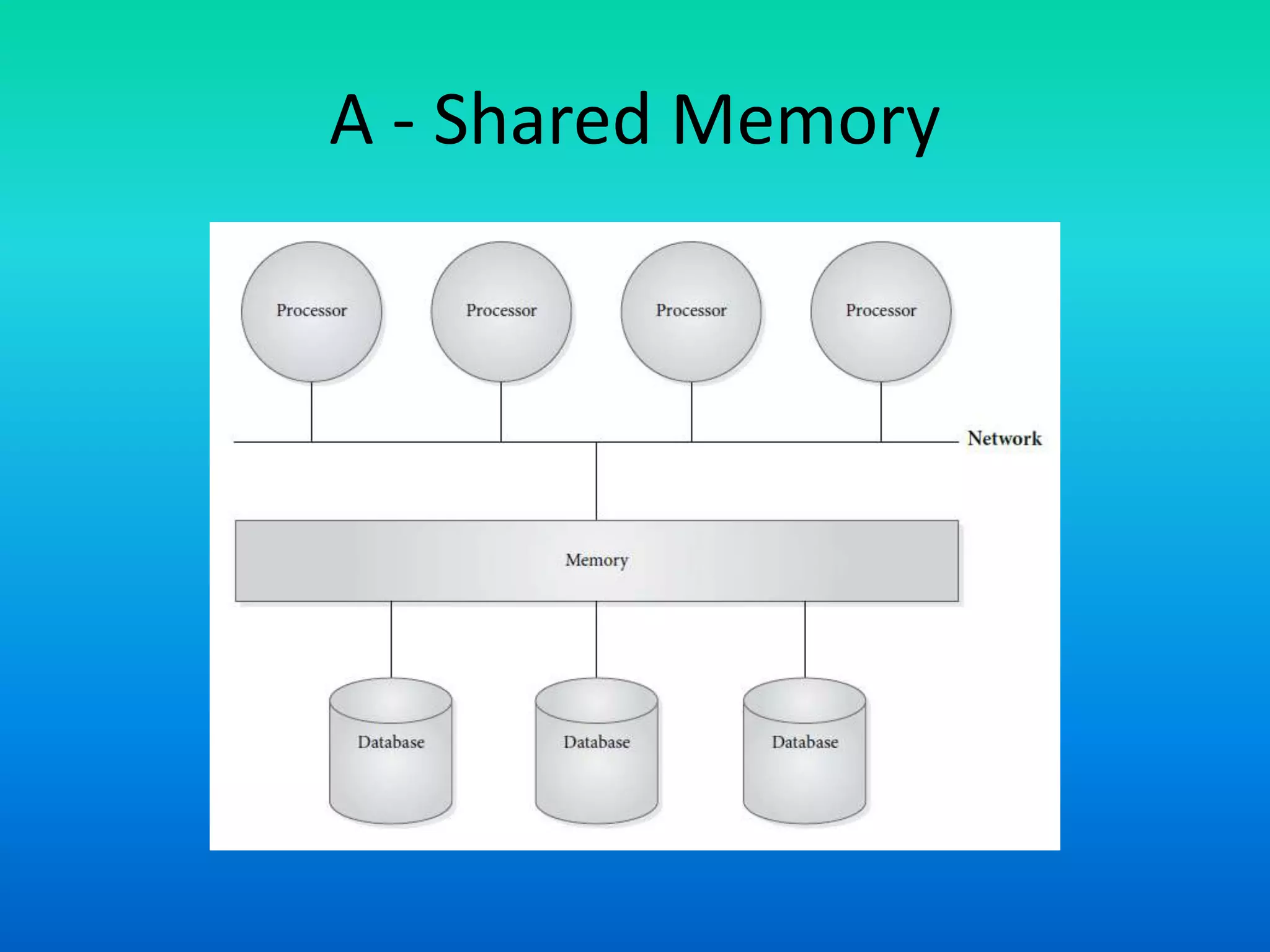
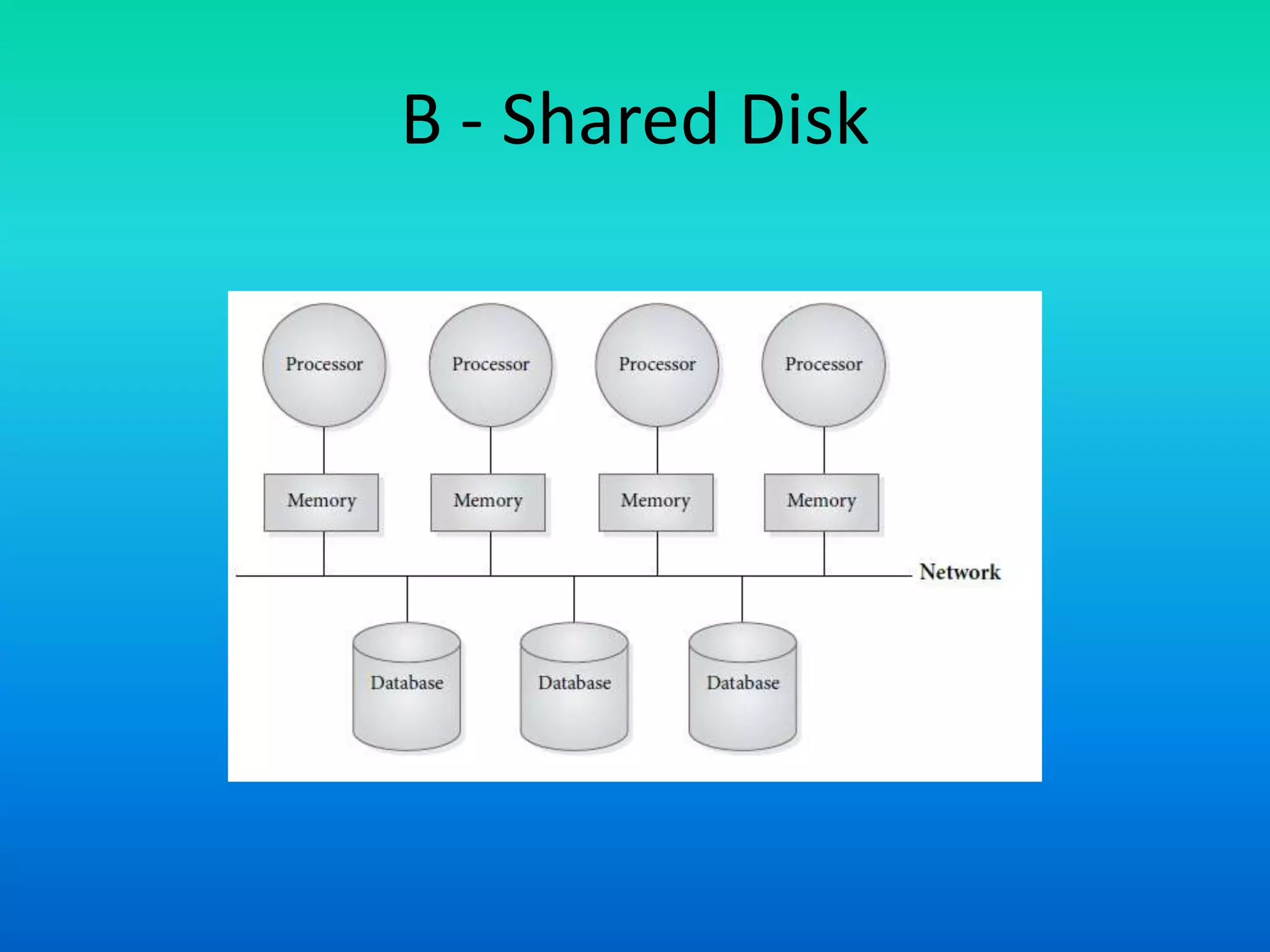
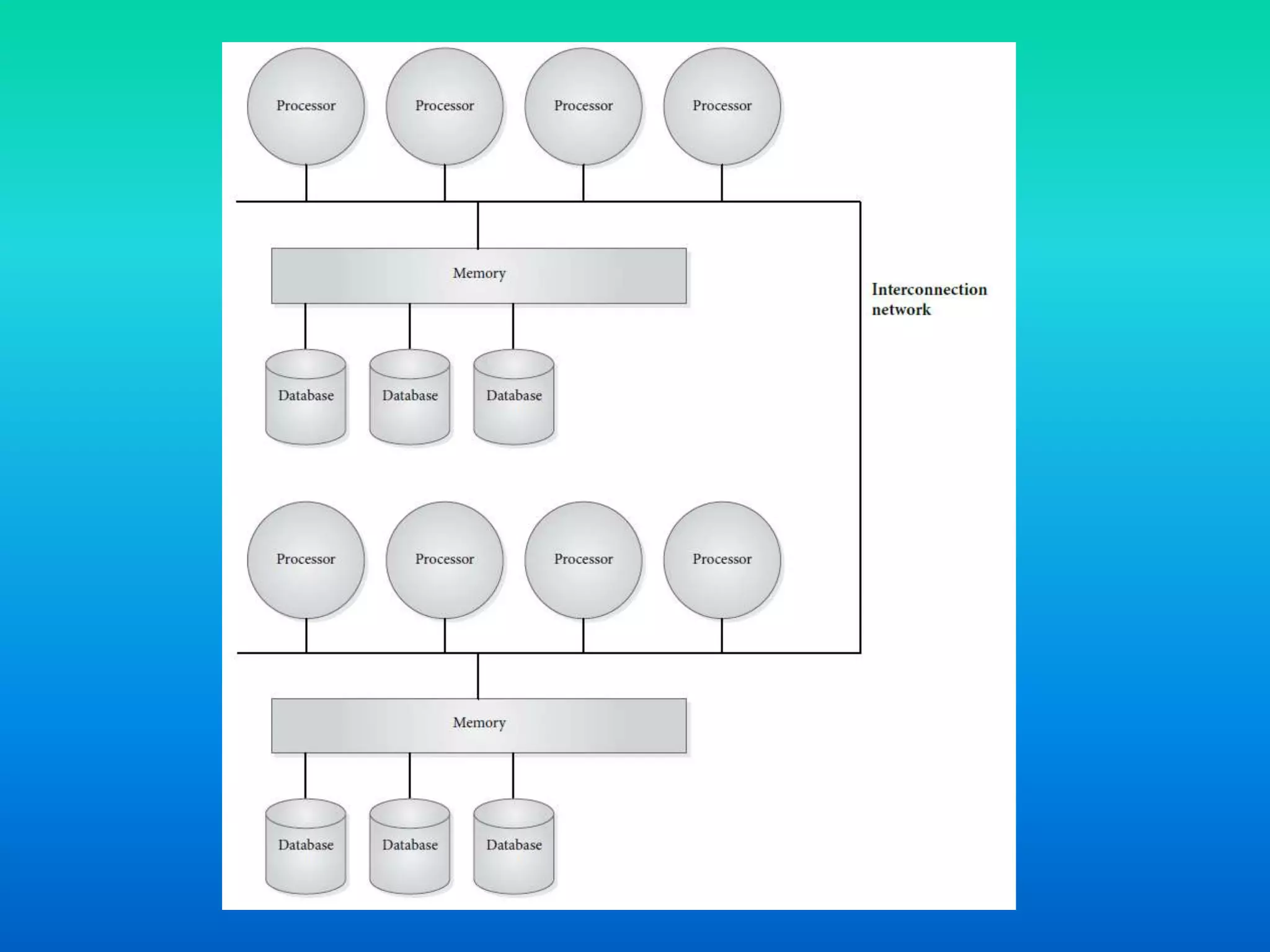
Parallel database architectures allow multiple processors to control multiple disk units containing partitions of a database. There are several types of architectures including shared memory, shared disk, and shared nothing. In shared memory, all processors access the same memory and disks. In shared disk, each processor has exclusive memory access but shared disks. In shared nothing, each processor has exclusive memory and disk control but can communicate. Careful data partitioning across disks is important to allow parallel query processing.