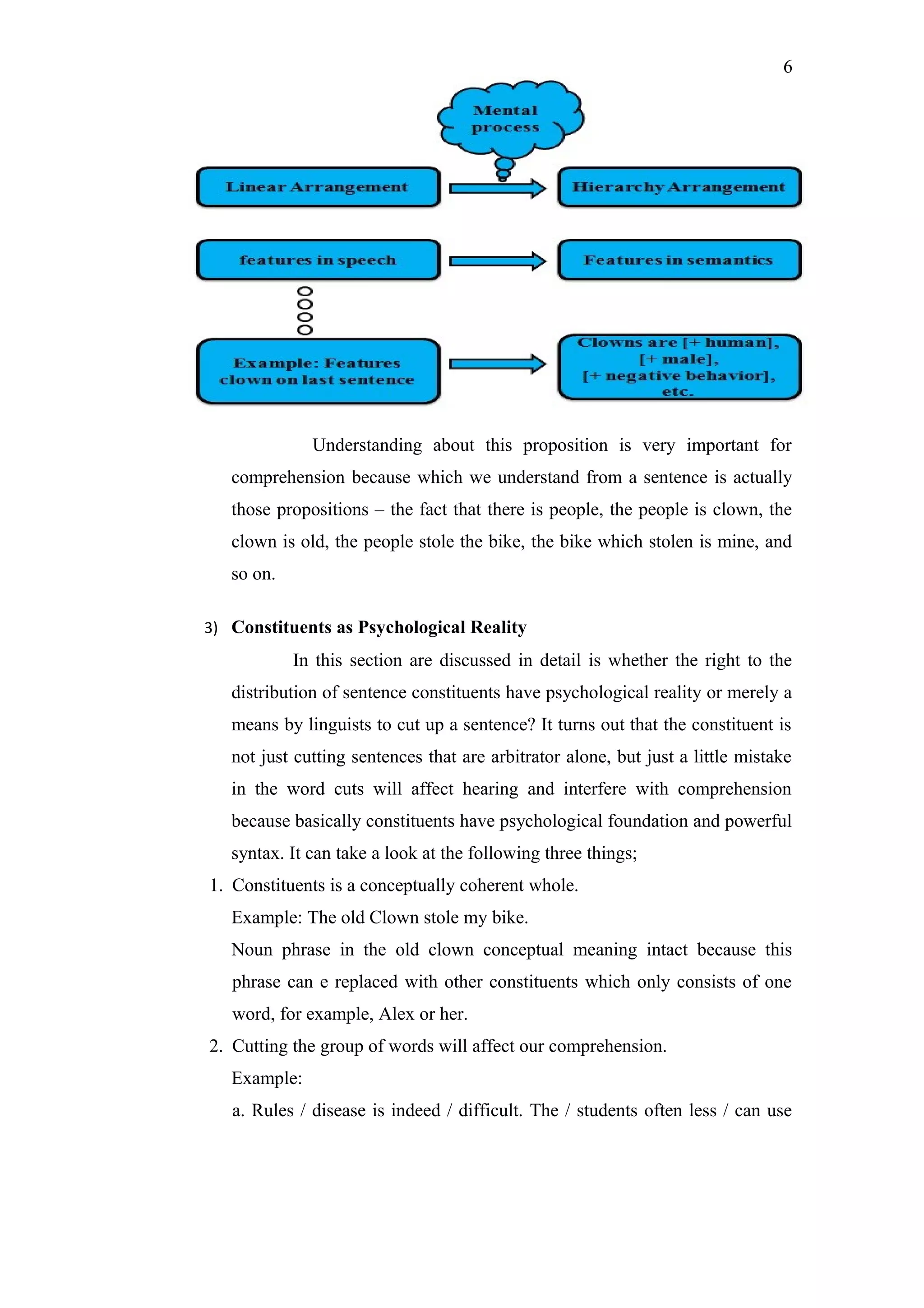
This paper explores the mental processes involved in speech comprehension, emphasizing theoretical foundations, inner structures, and cognitive strategies that listeners use to interpret spoken language. It highlights how comprehension goes beyond mere recognition of words to include deeper interpretation of meanings and underlying propositions. Additionally, it discusses the complexities of ambiguity and the strategic cognitive mechanisms listeners employ to make sense of speech.