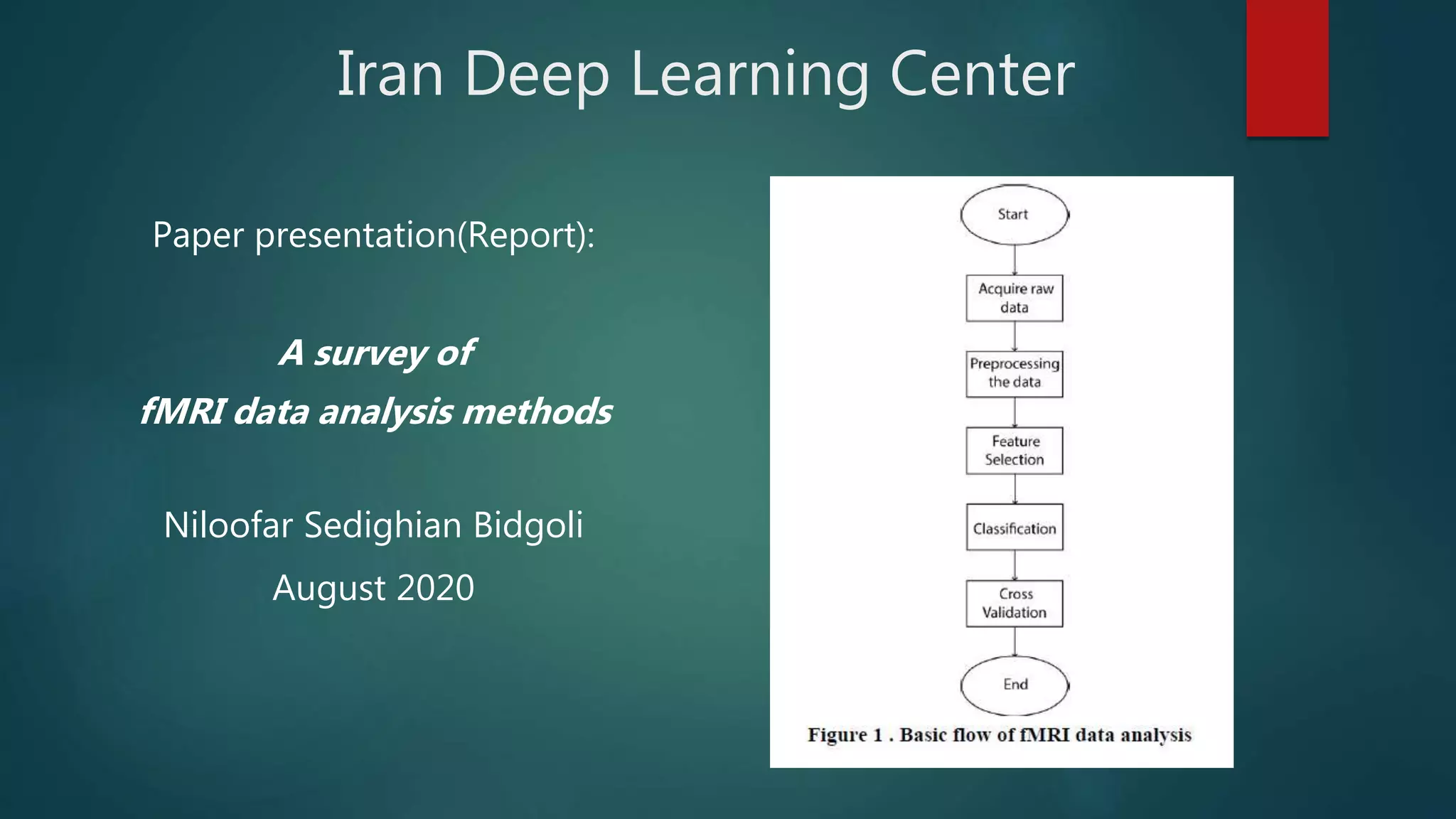
The document summarizes methods for analyzing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. It discusses preprocessing steps like realignment and normalization required for the raw fMRI image data. It also covers resting state fMRI, confirmatory and exploratory data analysis techniques, important experimental parameters, analysis tools like FSL and SPM, feature extraction methods including independent component analysis and principal component analysis, region of interest analysis, and Fisher transformation of correlation matrices between regions of interest.