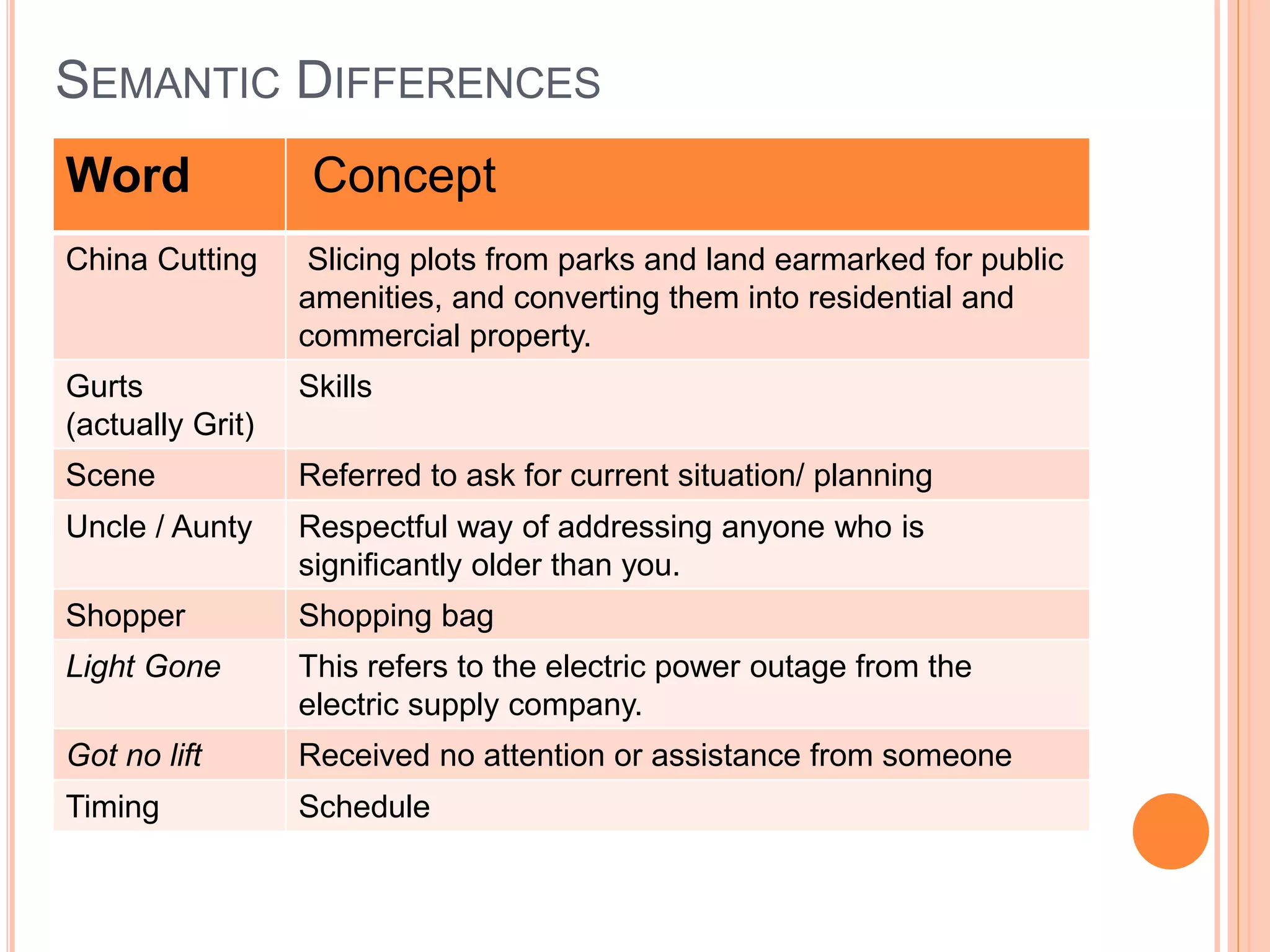
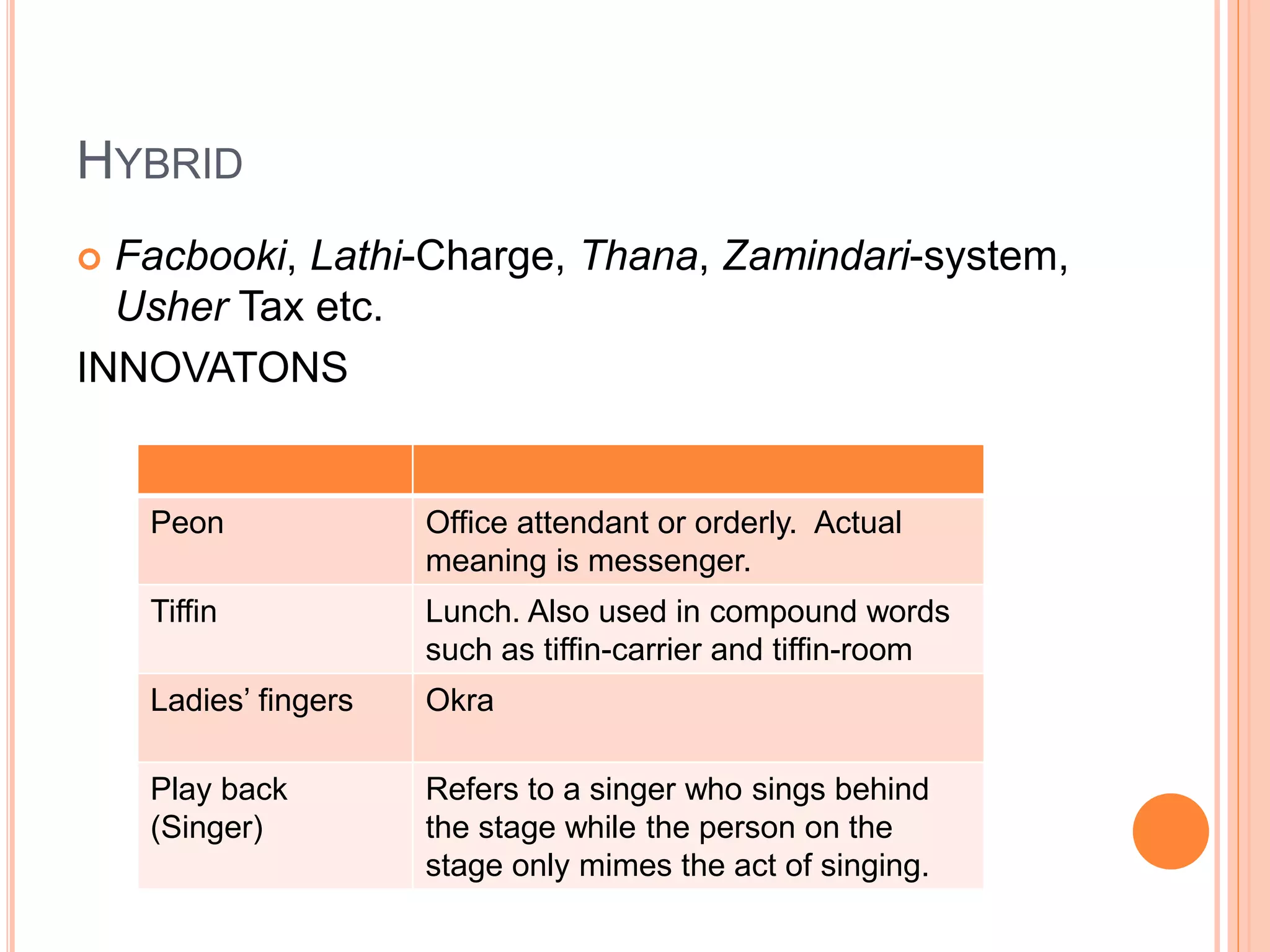
This document compares Pakistani English and British English. It outlines the background and history of how English came to be used in Pakistan through British colonization. It then describes some of the key phonological, semantic, and lexical differences between the two varieties. Phonologically, Pakistani English differs from British English in the pronunciation of words like "heart", "when", and "school". Semantically, words can have different meanings, like "China" referring to dividing up land plots. Lexically, Pakistani English incorporates words from Pakistani languages and culture, like "mujahiden" and "Sajan Sain", as well as innovations like "peon".