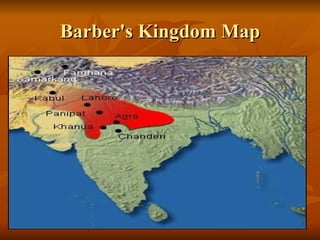
Babur founded the Mughal Empire in India after defeating Ibrahim Lodhi in the Battle of Panipat in 1526. As a young ruler, Babur fought many battles to control the kingdom of Farghana and later conquered Kabul in 1504. Babur invaded India five times to consolidate his rule and crossed the Indus River each time. In the fifth expedition, Babur encountered Ibrahim Lodhi at Panipat and was better equipped with guns while Lodhi relied on elephants. Babur's strategy and use of gunpowder, which had never been used in India before, gave him an advantage and led to his victory over Lodhi. This marked the beginning of

![Babur - The First Mughal Emperor [1526-30] Introduction Zahiruddin Muhammad Babur founded the Mughal Empire in India after defeating Ibrahim Lodhi in the Battle of Panipat in 1526](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakistanstudieslesson3babur-100304055817-phpapp02/85/Pakistan-Studies-Lesson-3-Babur-2-320.jpg)