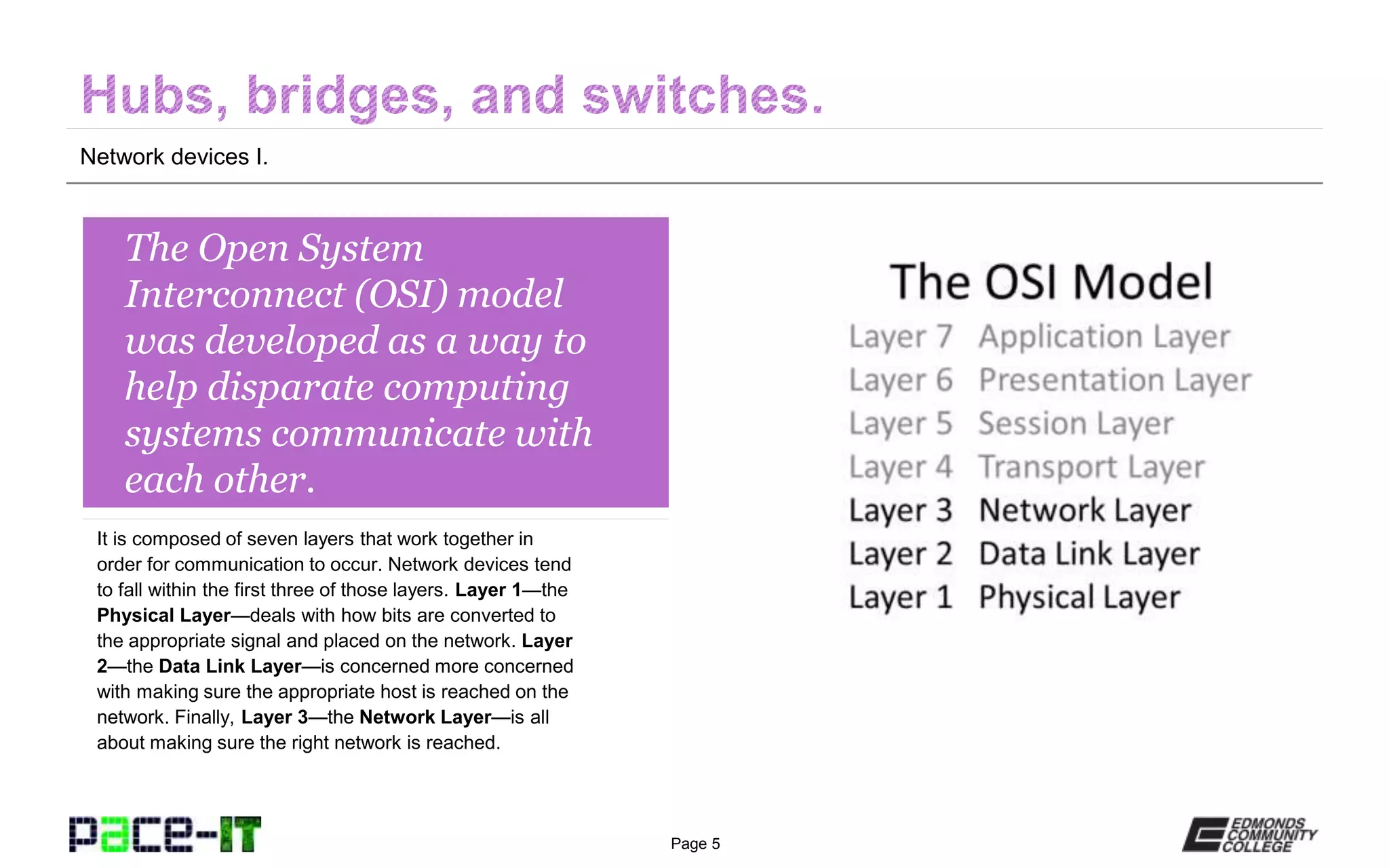
The document outlines various network devices functioning at different layers of the OSI model, including hubs, bridges, switches, modems, and routers. It provides detailed descriptions of how each device operates and the specific roles they play in connecting and managing network traffic. Additionally, it highlights the funding and equal opportunity provisions related to the Pace-IT program at Edmonds Community College.