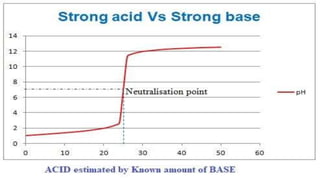
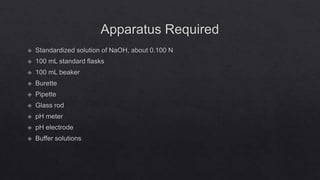
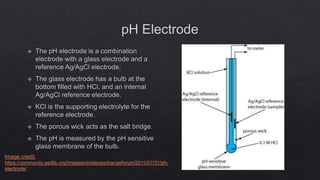
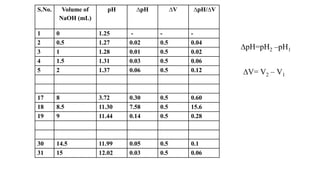
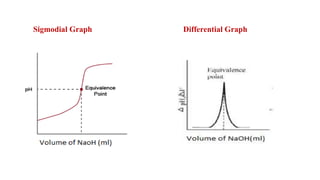
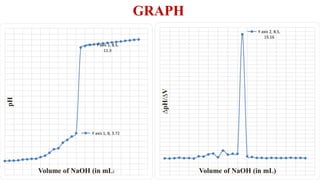
This document describes the procedure for determining the strength of a strong acid using pH-metric titration. The titration involves adding a strong base (NaOH) to a strong acid (HCl) until the equivalence point is reached. The pH is measured after each addition of base. By determining the volume of base required to reach the equivalence point and using the concentrations of the acid and base, the concentration of the original acid solution can be calculated. Calibrating the pH meter using buffer solutions ensures accurate pH measurements during the titration.


![• pH –
The negative logarithm of the H ion activity
pH = -log[H+]
• Strong Acid or Base :
– The acids or bases that completely dissociated into their ions
when the acids or bases that completely dissociated into their
ions when it is in aqueous solution.
• Weak Acid or Base :
– The acids or bases that partially dissociated into their ions when
it is in aqueous solution
PRINCIPLE AND THEORY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmetrictitration-210710042028/85/P-h-metric-titration-3-320.jpg)