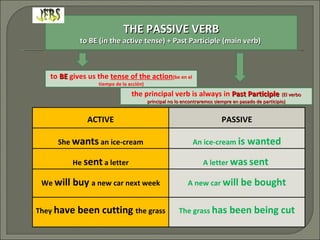
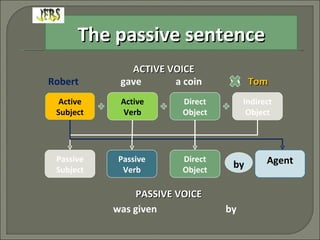
The document discusses the structure and use of passive sentences in English. It explains that a passive sentence highlights the action rather than the subject performing the action. The passive verb "to be" is used along with the past participle of the main verb. Various structures for the passive voice are covered, including those using verbs like "have" and "get" and introductory "it".