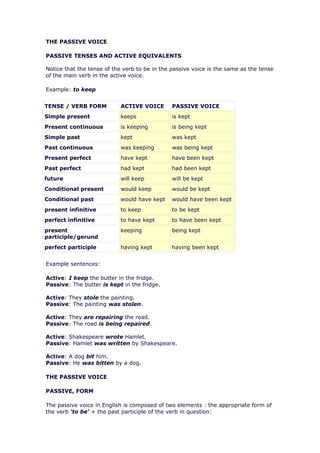
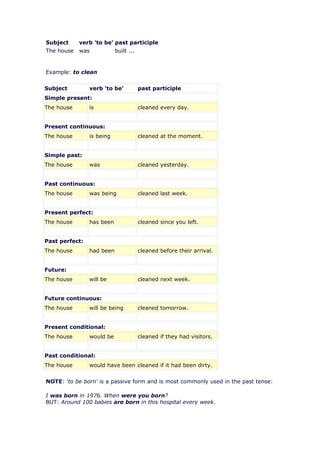
The document discusses the passive voice in English. It describes how the passive voice is formed using the appropriate form of the verb "to be" plus the past participle of the main verb. It provides examples of passive constructions in different tenses. It also explains the functions of the passive voice, such as when the subject experiences the action rather than performs it or when the agent is unknown.