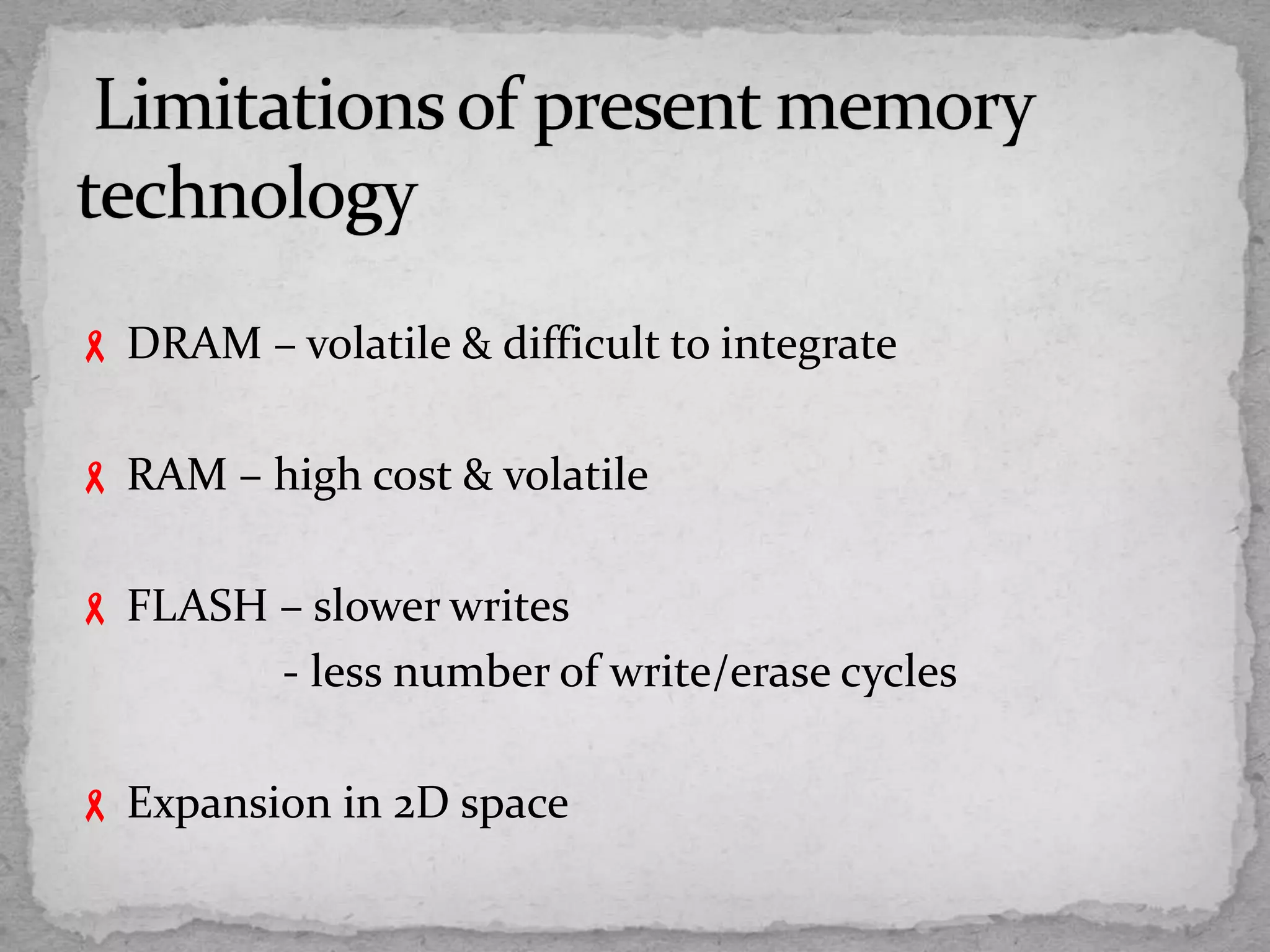
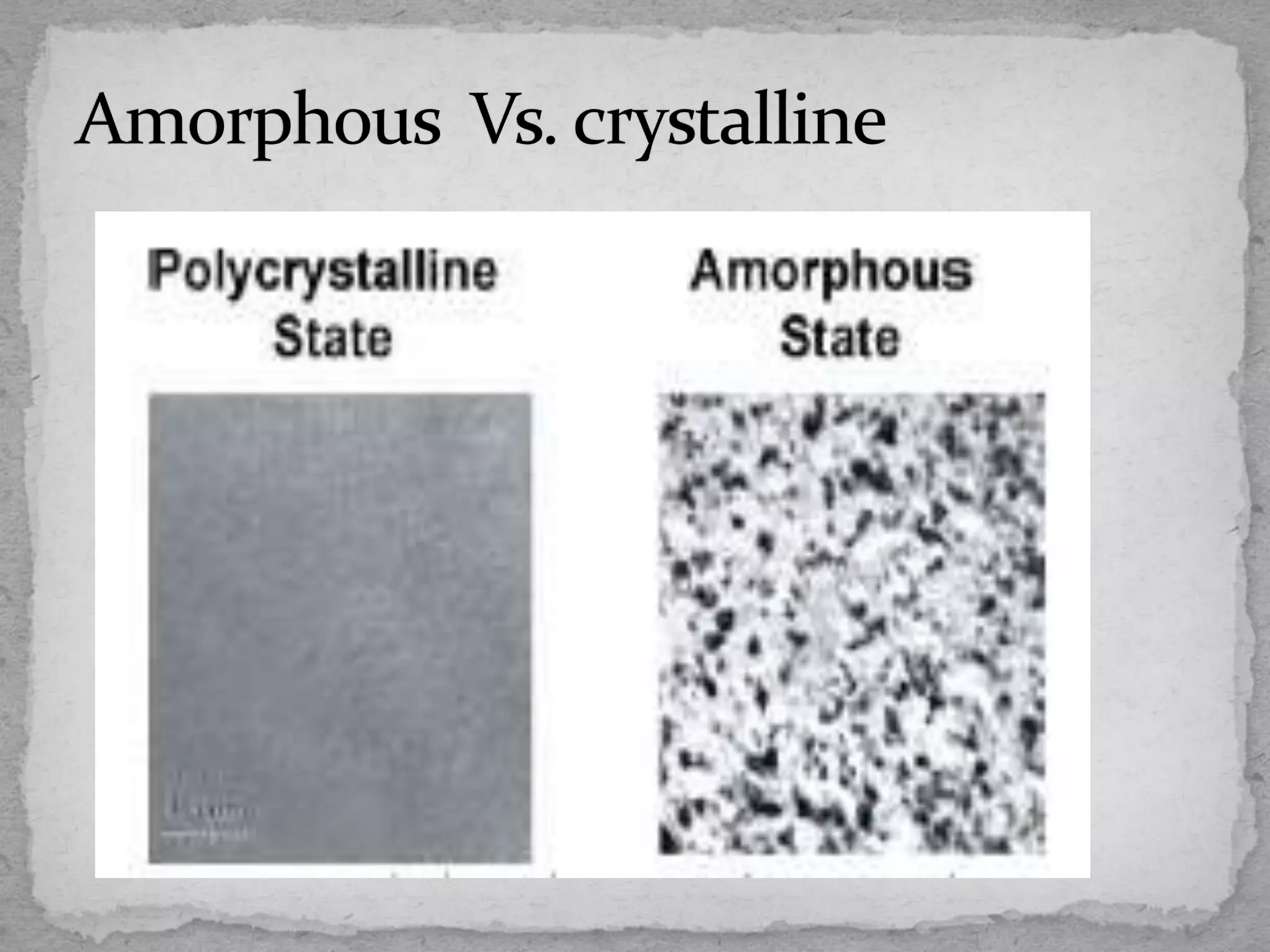
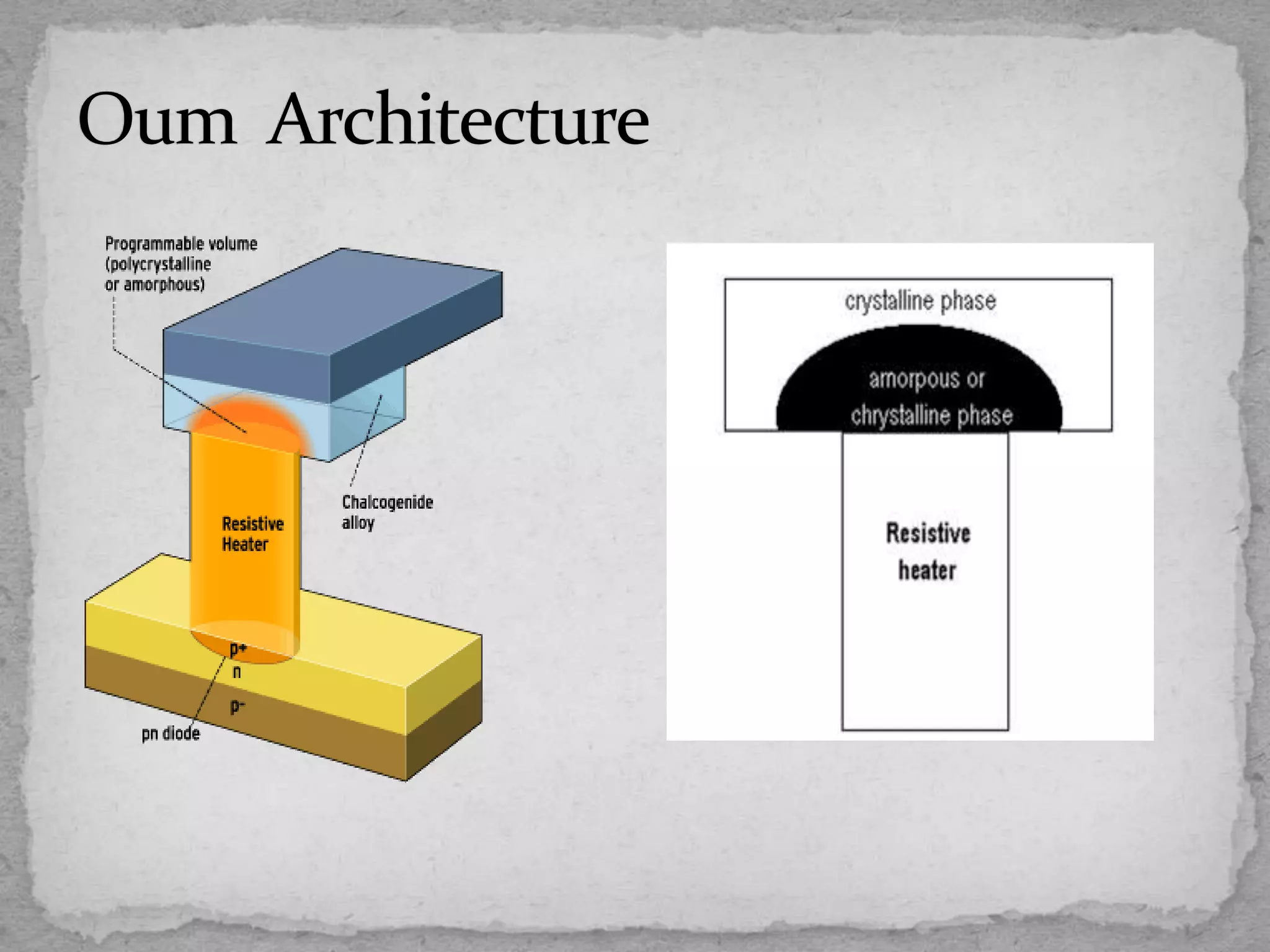
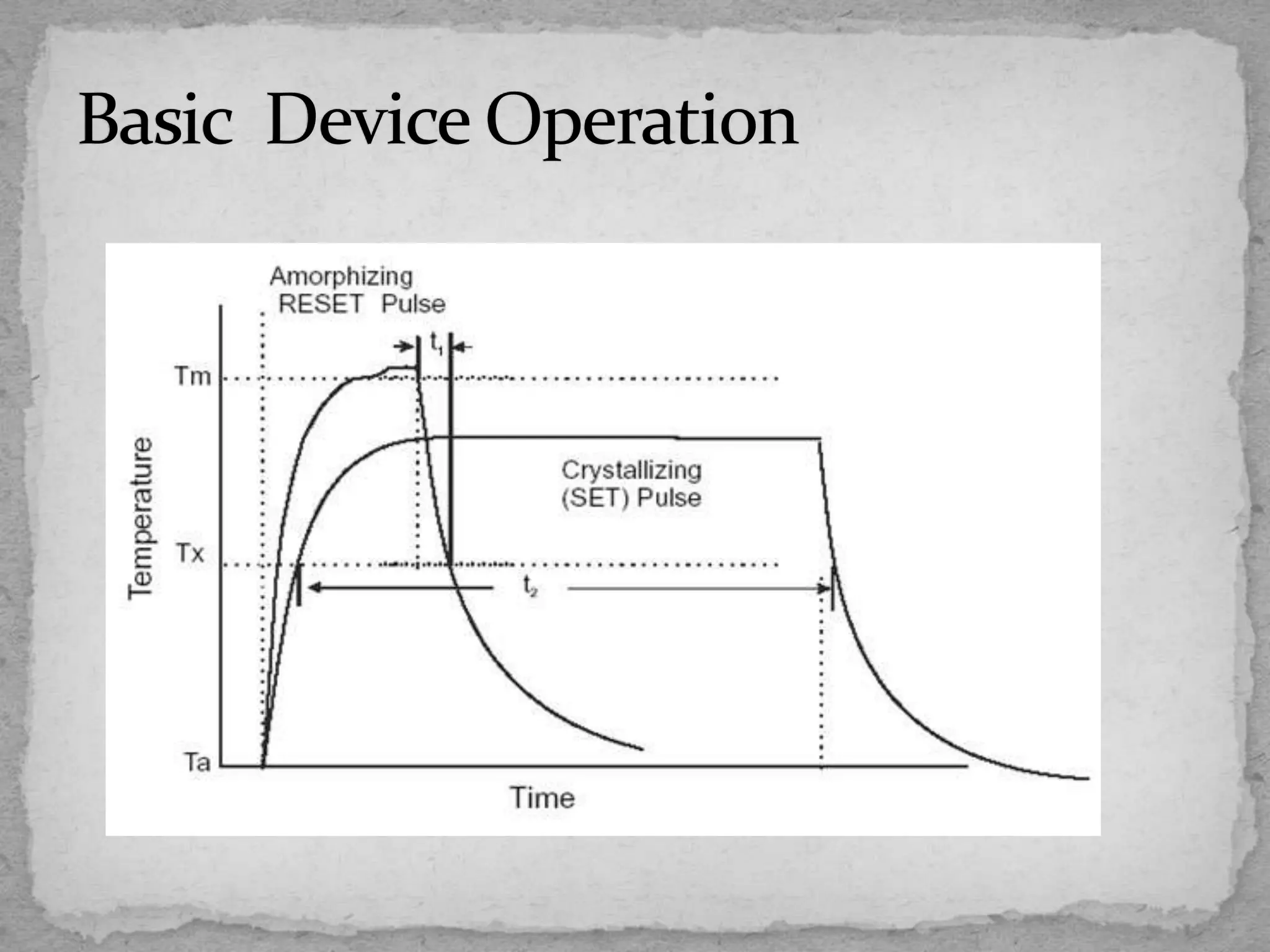
This document discusses emerging non-volatile memory technologies and focuses on Ovonic Unified Memory (OUM). It outlines the limitations of current memory technologies like DRAM, RAM, and FLASH. It then explains the fundamentals and operation of OUM, which uses a chalcogenide material that can be switched between amorphous and crystalline structural states by applying electric current to heat the material. The document notes several advantages of OUM, including its non-volatility, high density, simple structure, low cost and scalability. OUM offers improved memory that addresses many of the limitations of present technologies.