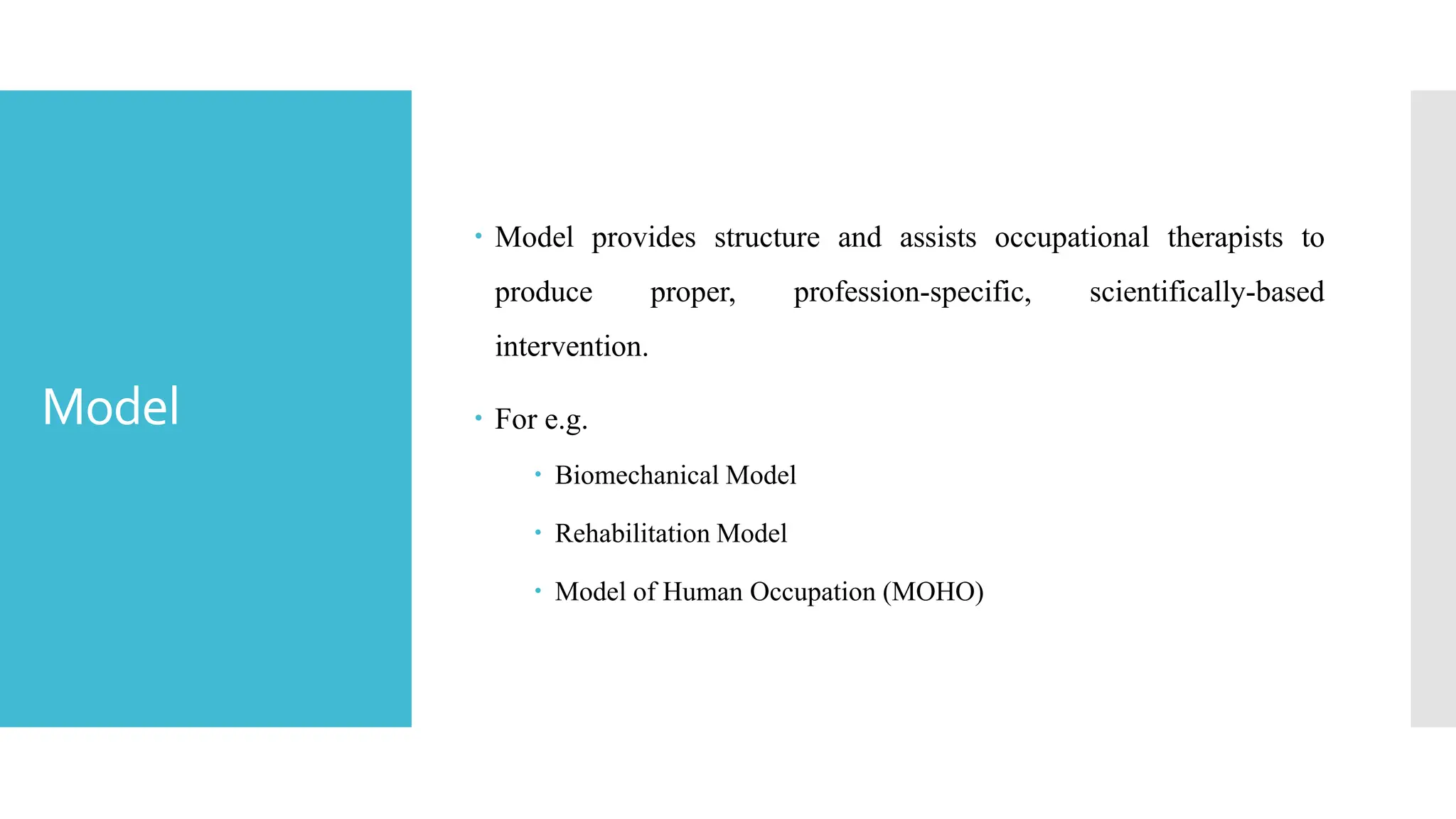
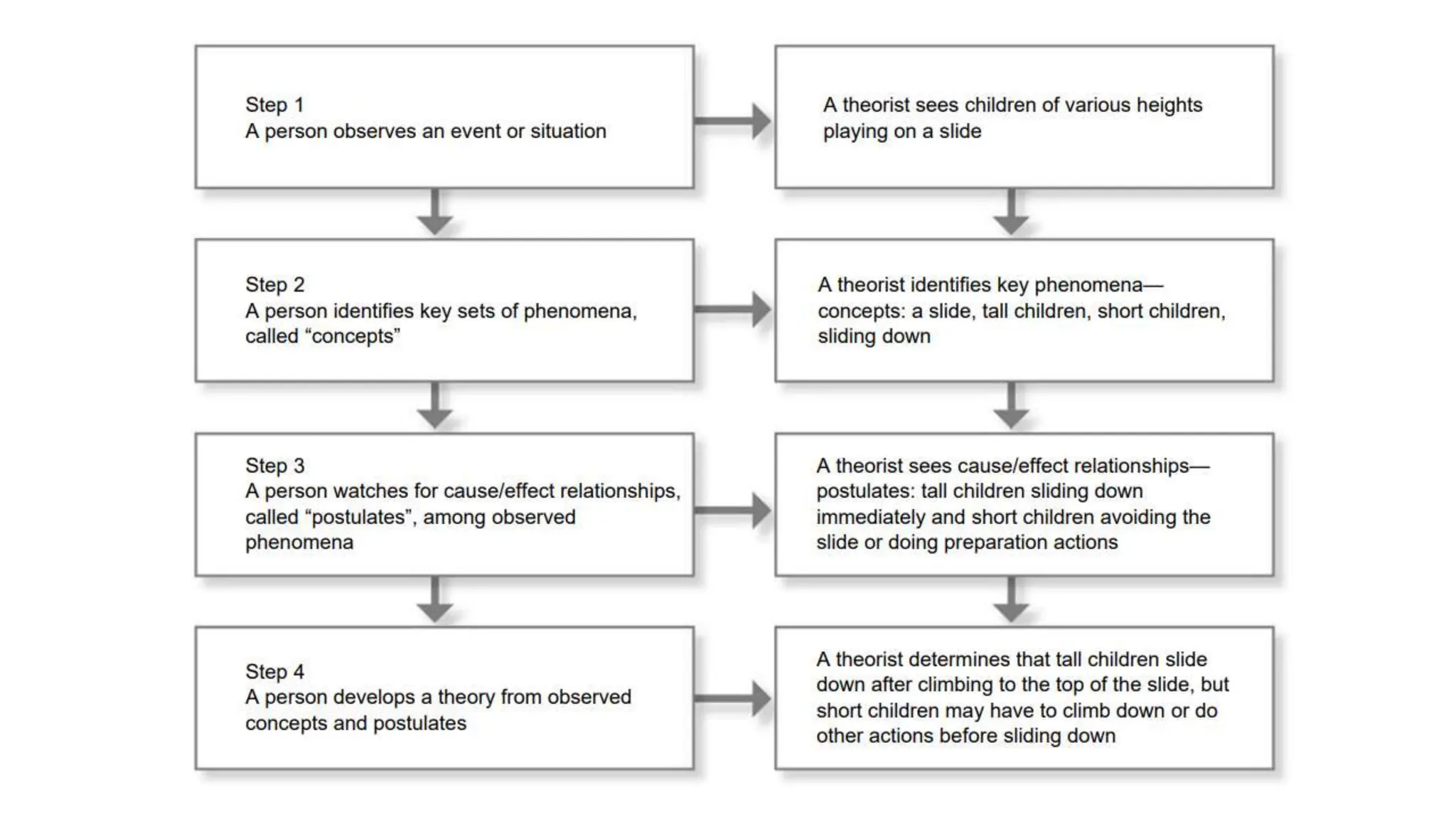
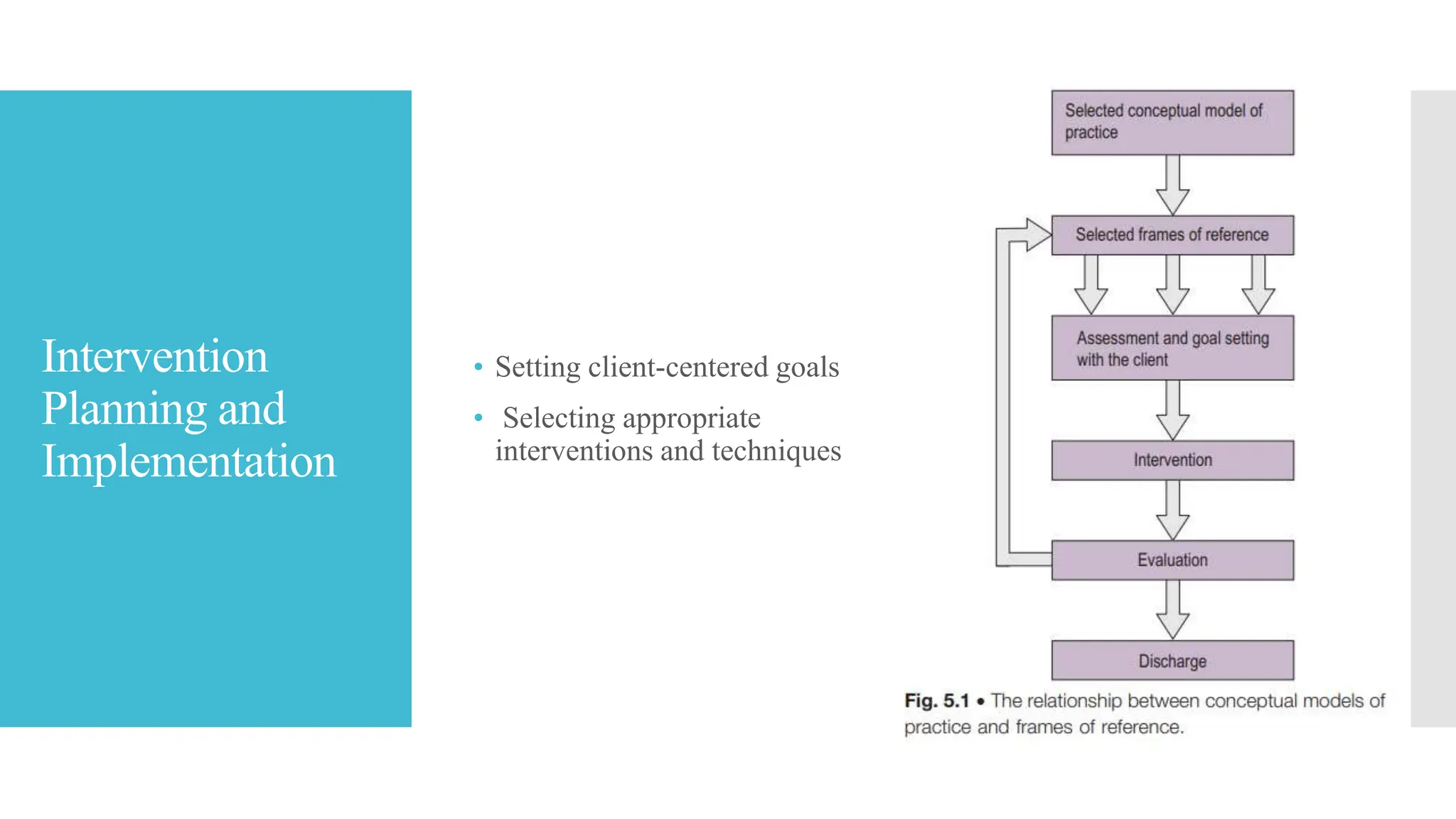
The document discusses the importance of theories and models in guiding occupational therapy practice, explaining how they inform interventions and client-centered care. It outlines how frames of reference utilize theoretical concepts to structure practical applications and treatment approaches while emphasizing the significance of understanding a client's individual goals. Additionally, trends and innovations in occupational therapy, including technology's evolving role, are highlighted.