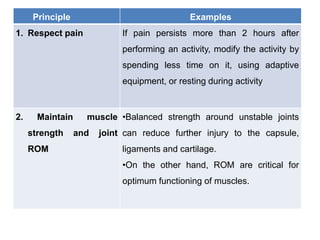
1. Joint protection techniques aim to reduce stress and force on joints to prevent further injury and promote healing. This includes respecting pain limits, maintaining muscle strength and range of motion, using joints in their most stable planes, and proper body mechanics.
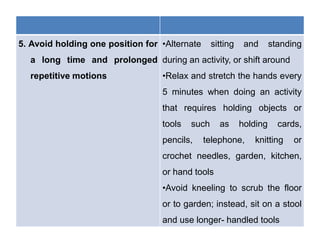
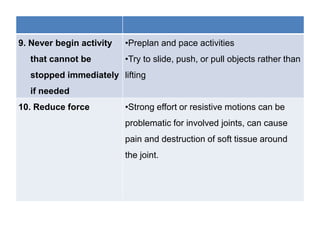
2. Specific techniques include alternating positions, avoiding prolonged repetitive motions and fixed positions, using larger muscle groups instead of joints, balancing activity with rest, and being able to stop activities immediately if needed. Forces should also be reduced on joints.
3. The goal is to modify activities, use adaptive equipment, rest during tasks, strengthen muscles around unstable joints, and move joints through their full range of motion while avoiding positions that cause deformity or excessive pressure on joints.