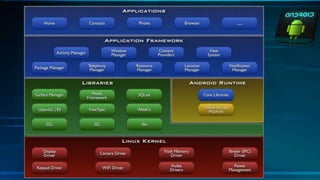
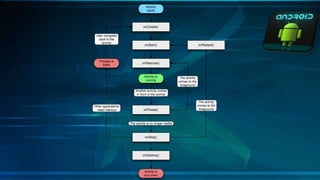
Android is an open source software platform used for mobile device development. It is developed by the Open Handset Alliance and powered by the Linux operating system. The Android software stack consists of four main layers - the application layer, application framework, libraries/runtime, and kernel. Key components for application development include activities, intent receivers, services, and content providers. Activities correspond to screens, intent receivers respond to notifications, services run in the background, and content providers share data across apps. Android offers advantages like customization, notifications, hardware choice, and a large app market. It also faces challenges like inconsistent app designs and battery life issues.

















![REFERENCE
[1]. Hewlett-Packard Education Services Notes
[2]. Android Developers Webpage-
http://developer.android.com/develop/index.html
[3]. Tutorials Point Webpage-
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/android/index.htm
l](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-151126135213-lva1-app6891/85/Overview-of-Android-21-320.jpg)
