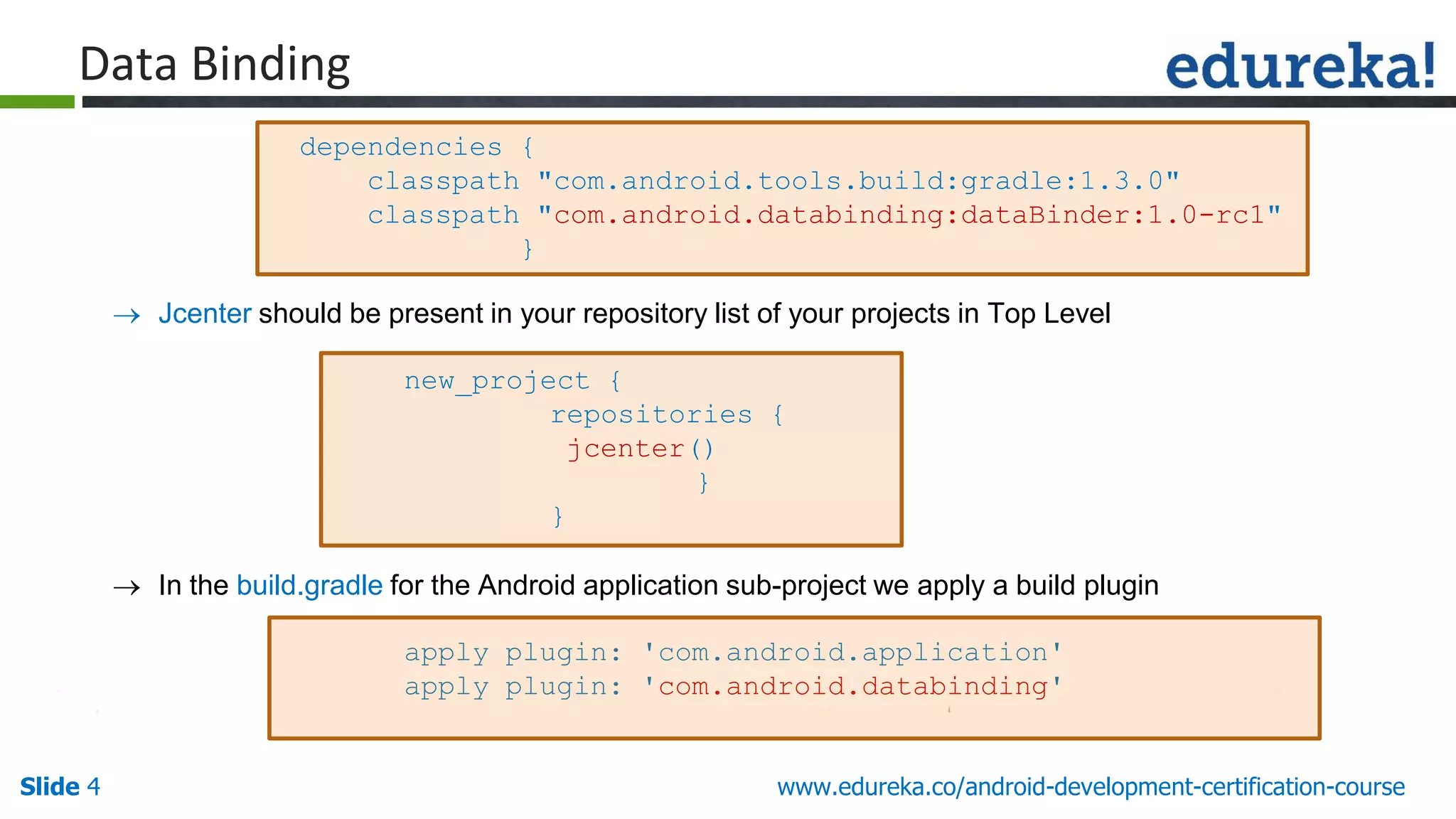
This document discusses features introduced in Android 6.0 Marshmallow. It covers Data Binding, which provides a mechanism for linking UI layouts to data sources. It also discusses Android Percent Layout for setting child view dimensions as percentages. Additionally, it covers Runtime Permissions, which allow apps to request permissions at runtime instead of install time. App Linking and Direct Share are also new sharing features introduced in Android M.