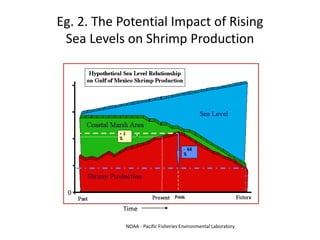
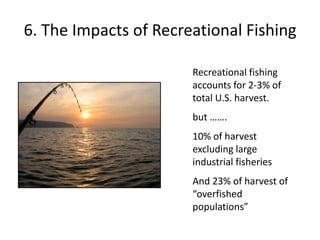
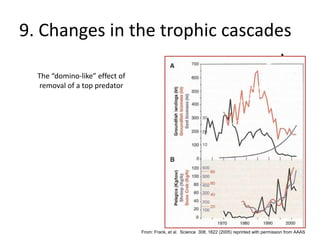
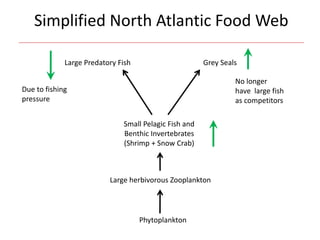
Marine fishery declines are primarily driven by overfishing, use of efficient fishing technologies, bycatch, and overcapacity. Additional factors include global warming and recreational fishing, which impact fish populations and ecosystems. Societal influences such as government subsidies, increasing demand for fish, shifting baselines in fish population perception, and inadequate fisheries data further exacerbate these declines.