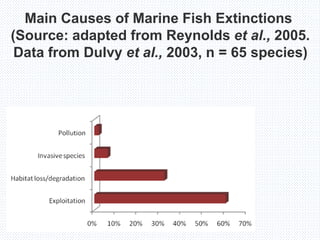
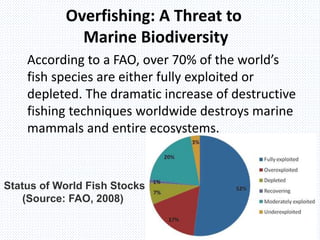
The document discusses the depletion of fish biodiversity along the Indian coast due to overexploitation and environmental changes. It notes that over 70% of the world's fish species are fully exploited or depleted due to poor fisheries management, destructive fishing practices, and excessive bycatch. A study in Kerala found that two popular fish species, Lactarius lactarius and Pampus argenteus, have been depleted. Conservation measures like enforcing bycatch reduction technologies and regulating total fishing efforts are needed to protect marine biodiversity.