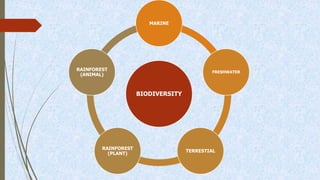
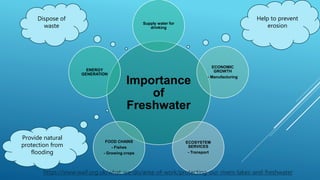
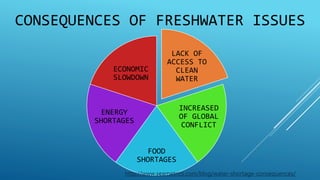
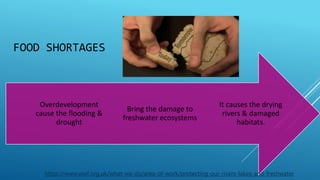
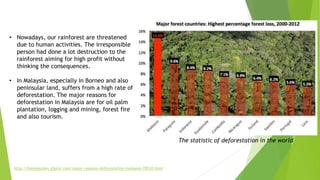
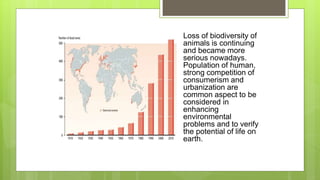
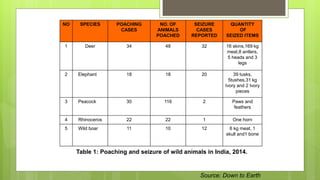
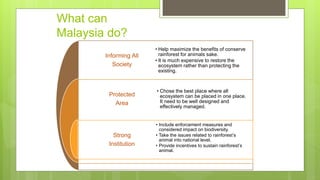
This document discusses terrestrial biodiversity and different terrestrial ecosystems. It provides job assignments for studying different aspects of biodiversity to five students. Che Anis is assigned to study marine biodiversity, Norfatiha freshwater biodiversity, Syaiful Azrie terrestrial biodiversity, Siti Zaiton rainforest plants, and Aida Syazwani rainforest animals. It then introduces biodiversity, its importance, threats like overfishing and deforestation, and the need for conservation.