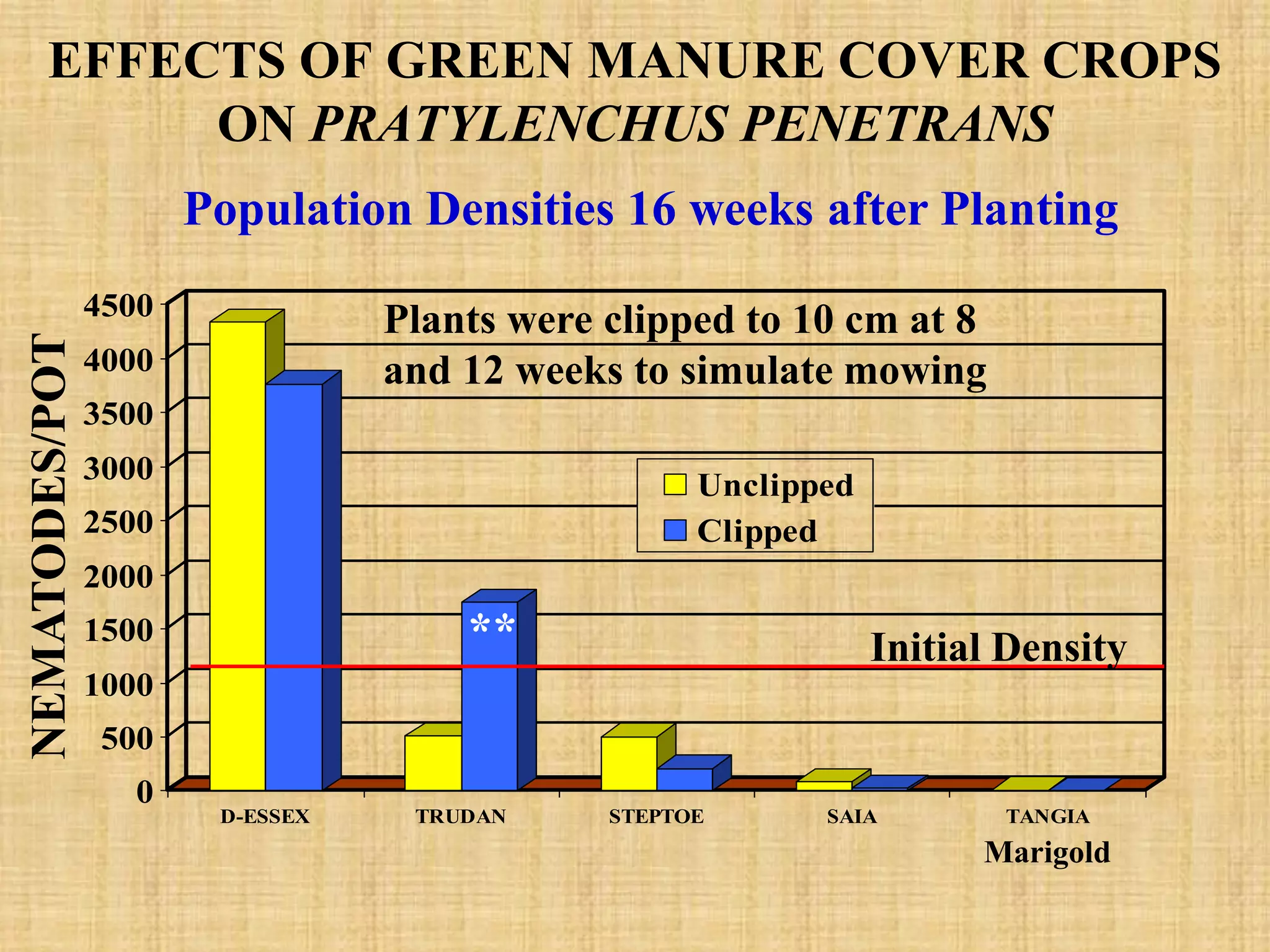
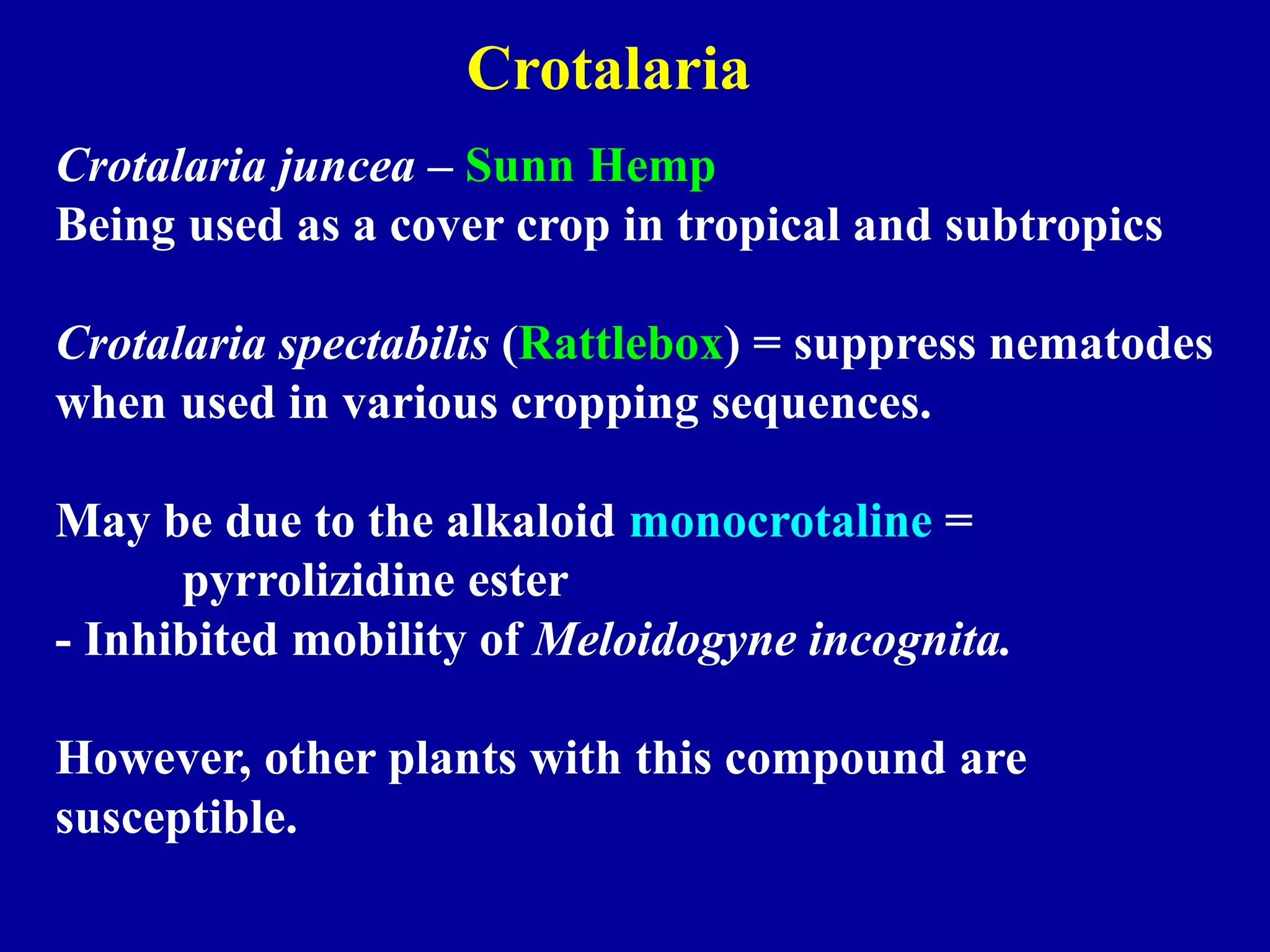
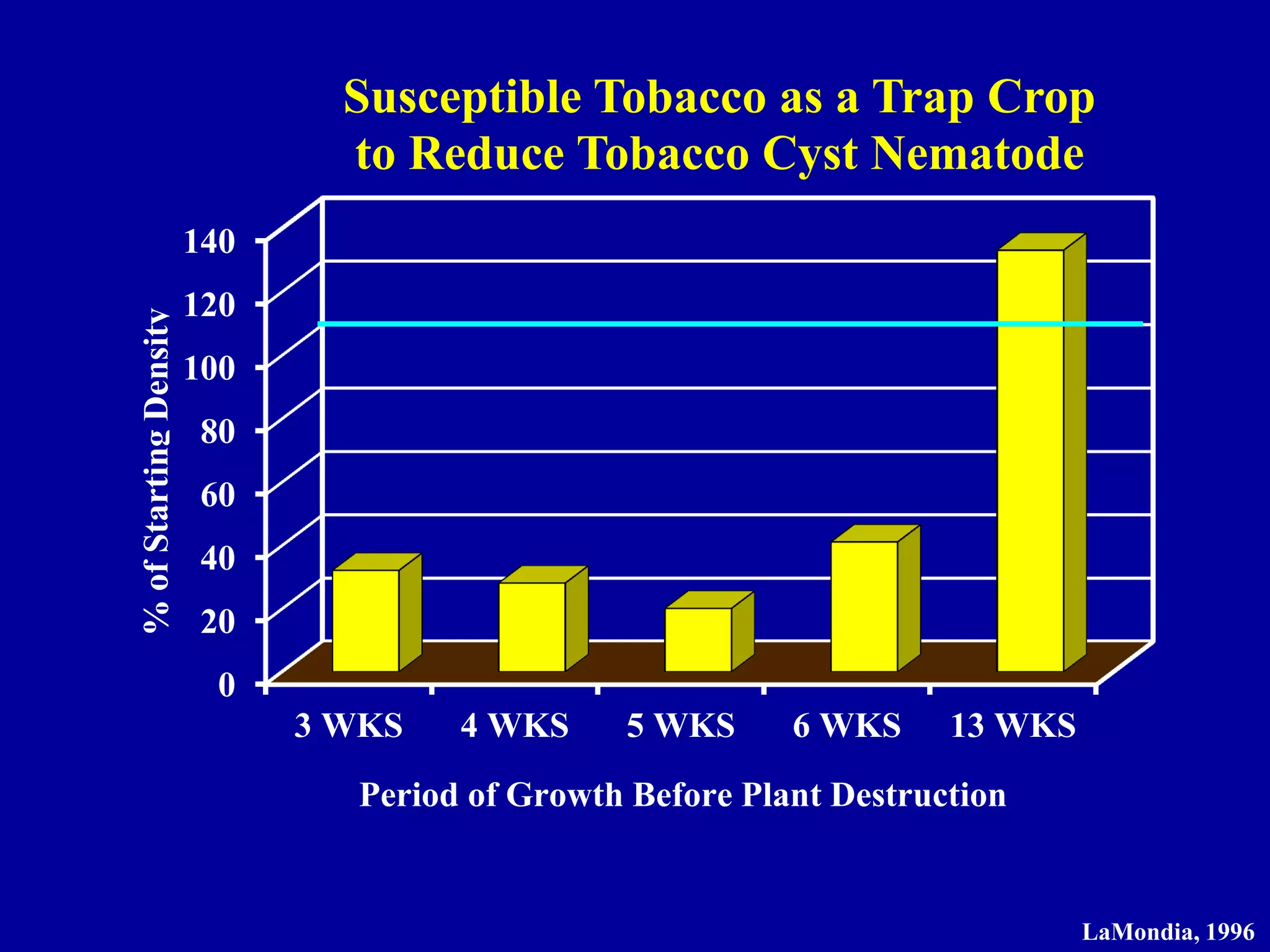
This document discusses various cultural strategies for nematode management using plants, including using non-host crop rotations, green manure cover crops, antagonistic plants, trap crops, and resistant cultivars. It provides examples of different plants used in each strategy and their effects on nematode populations, such as marigolds and cruciferous plants which can reduce populations through nematicidal compounds in root exudates. Trap crops are discussed as a way to attract and trap sedentary nematodes before they can reproduce. Early planting and harvest is also summarized as a strategy to avoid nematode damage by escaping high nematode activity periods.