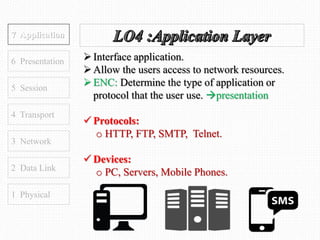
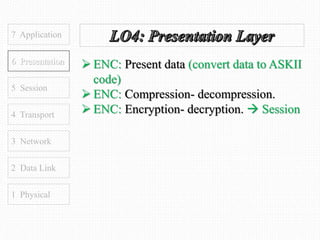
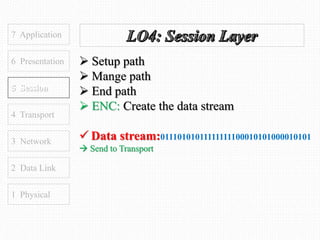
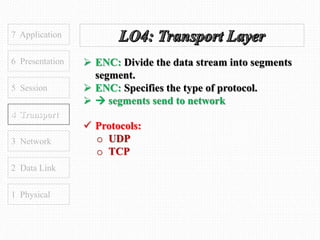
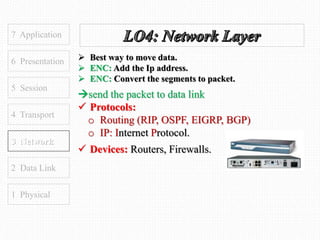
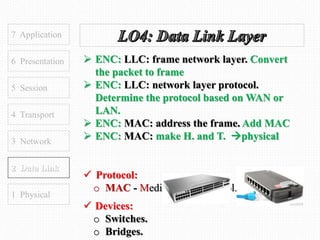
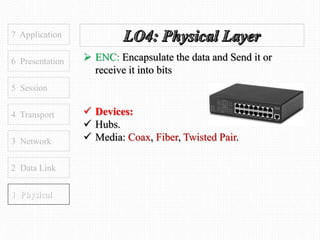
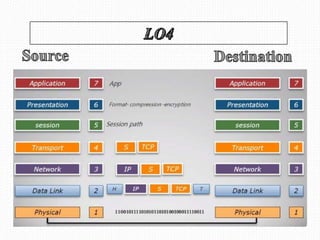
This document discusses the OSI model, which defines 7 layers of network communication. It defines each layer, their functions, and the encapsulation process between layers. Key points covered include defining the 7 layers and their functions, comparing TCP and UDP protocols, and stating that OSI model allows different hardware/software to communicate by organizing networks into well-defined modules. The purpose of OSI is to represent a perfect network and organize it into functional layers to allow troubleshooting and different technologies to work together across networks.




![• For represent a perfect network.
• For organize the network into well defined,
documented, functional modules, in the layered
network.
• Each layer provides specific functionality or
services to the neighboring layer.
• Allows different hardware and software to work
together.
• Essay for Troubleshooting. [1]
• DO YOU TINK TERE IS ANOTHER BENIFT FOR OSI MODEL?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osilayers-171107193713/85/OSI-MODEL-5-320.jpg)





![[1] Zimmermann, H. (1980). OSI reference model--The ISO model of
architecture for open systems interconnection. IEEE Transactions on
communications, 28(4), 425-432.
[2] Handel, T. G., & Sandford, M. T. (1996, May). Hiding data in the OSI
network model. In International Workshop on Information Hiding (pp.
23-38). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
[3] Jacobson, V. (1990). Compressing TCP/IP headers for low-speed
serial links.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osilayers-171107193713/85/OSI-MODEL-20-320.jpg)