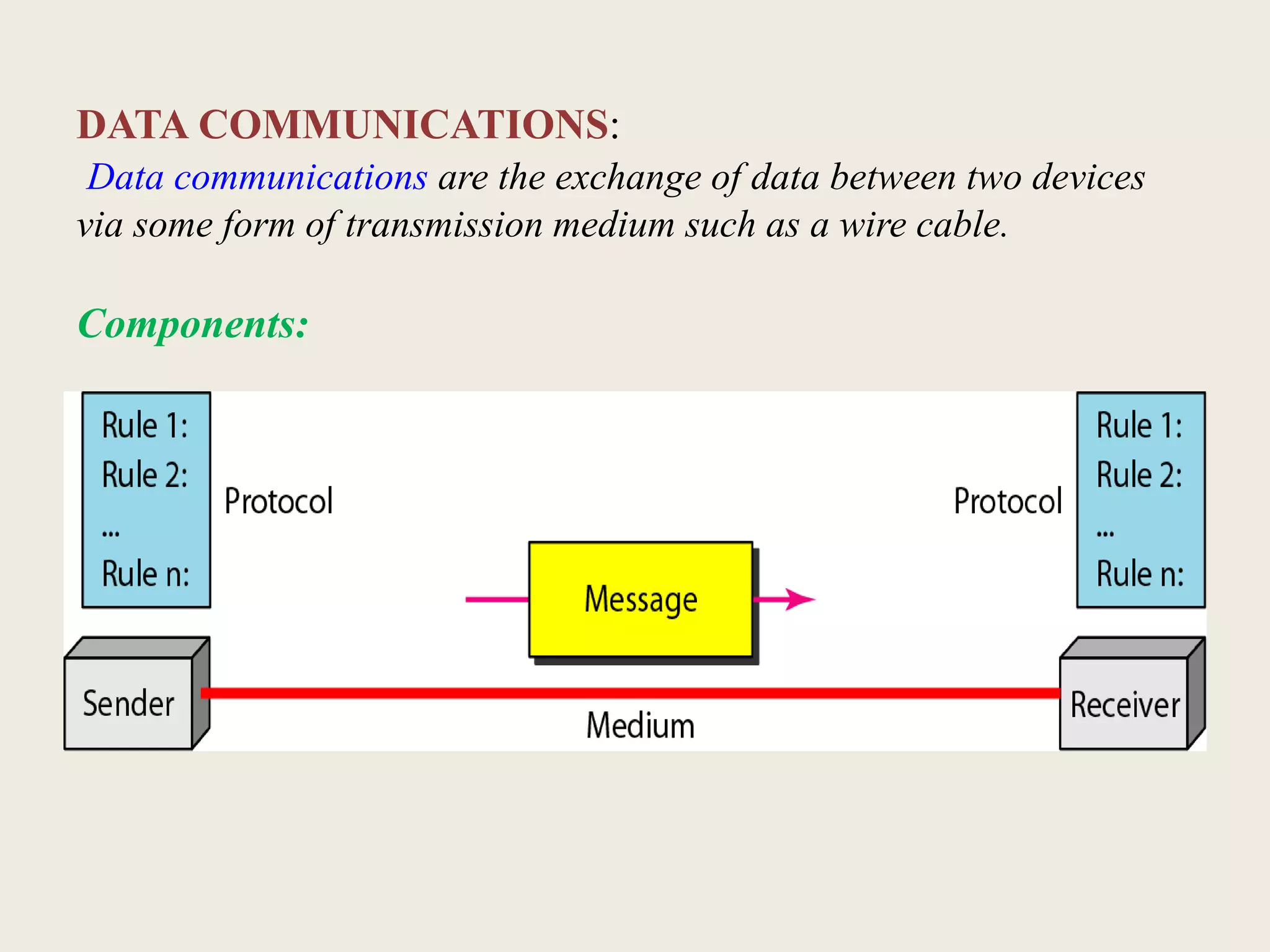
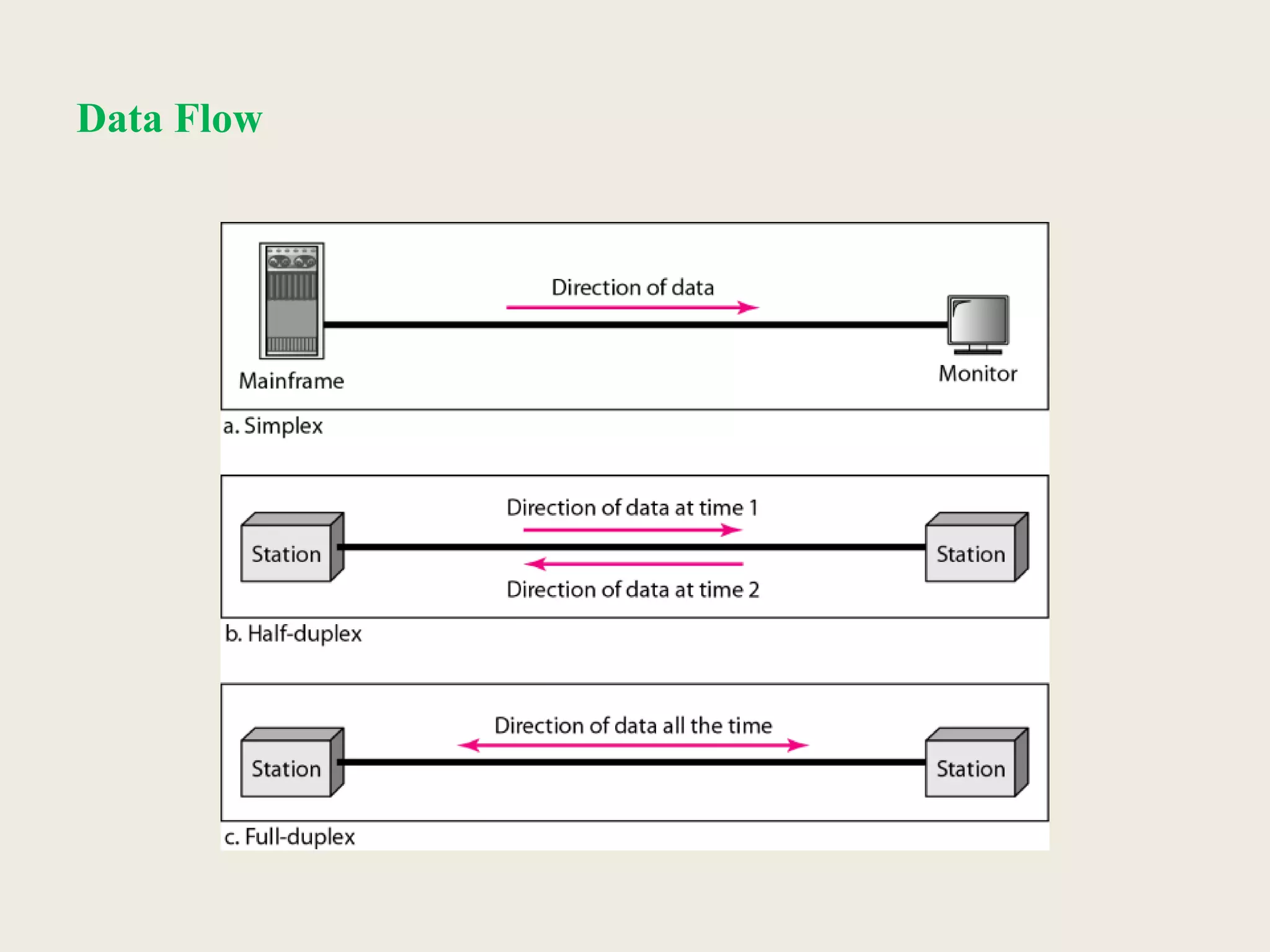
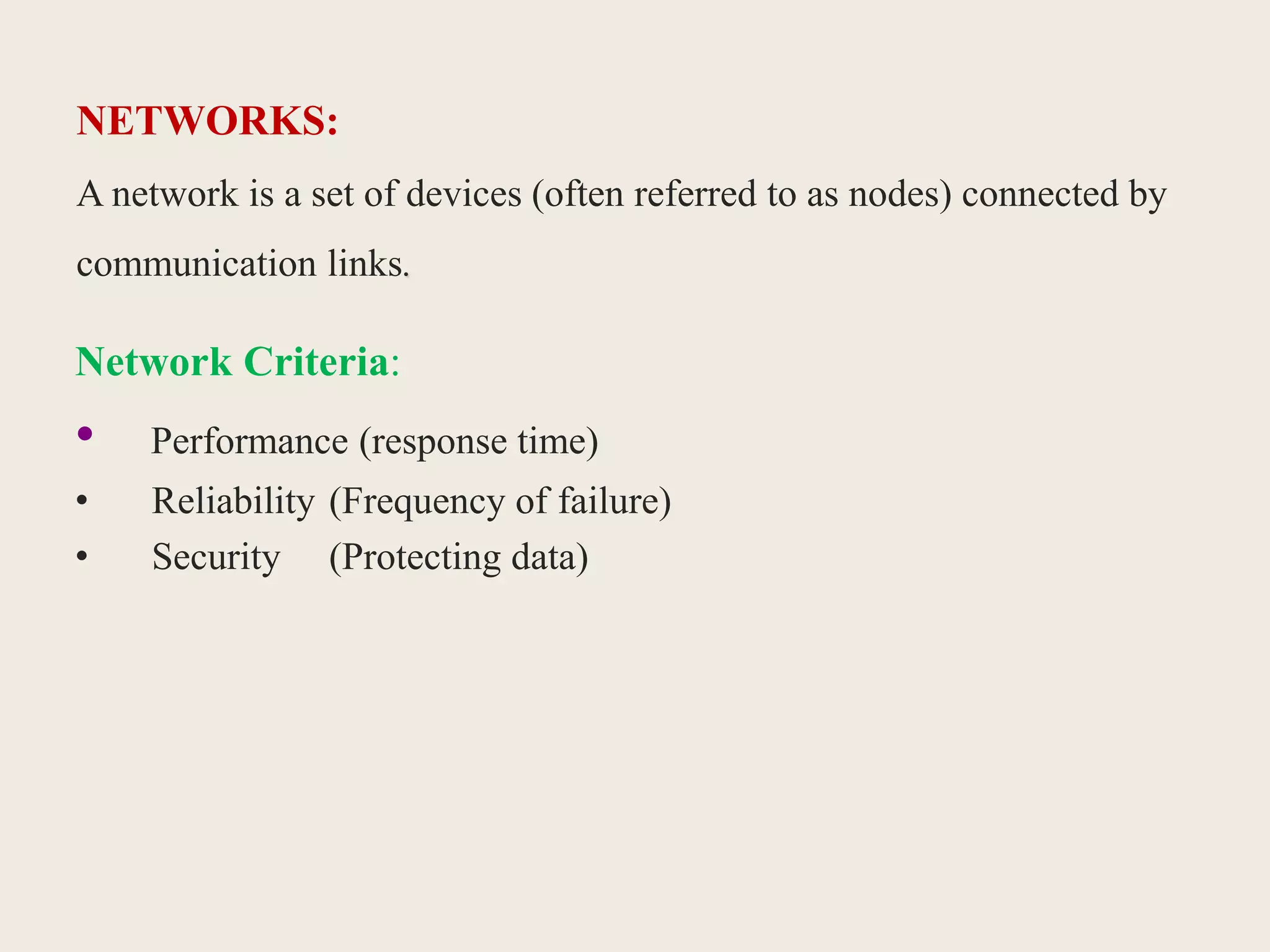
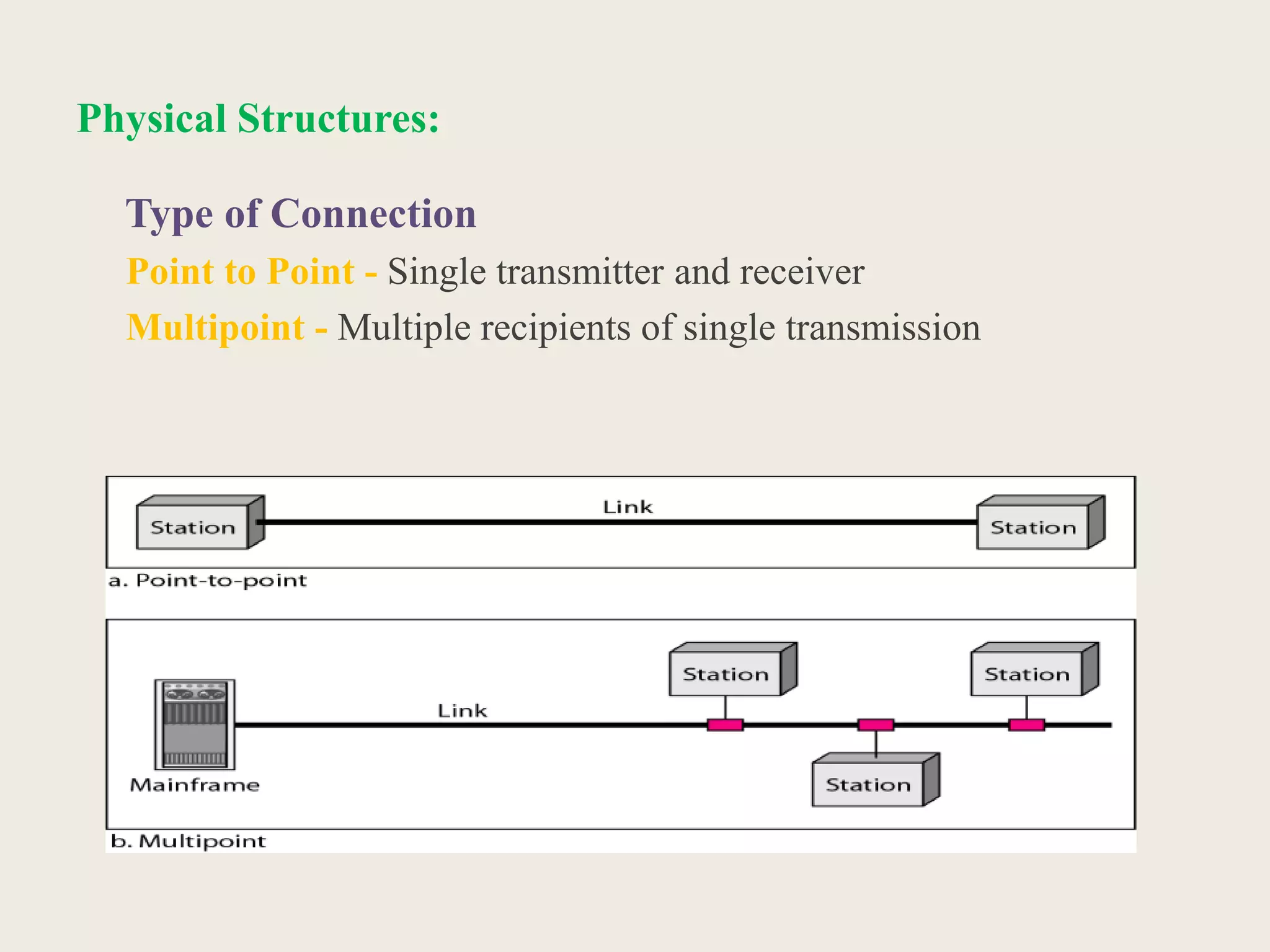
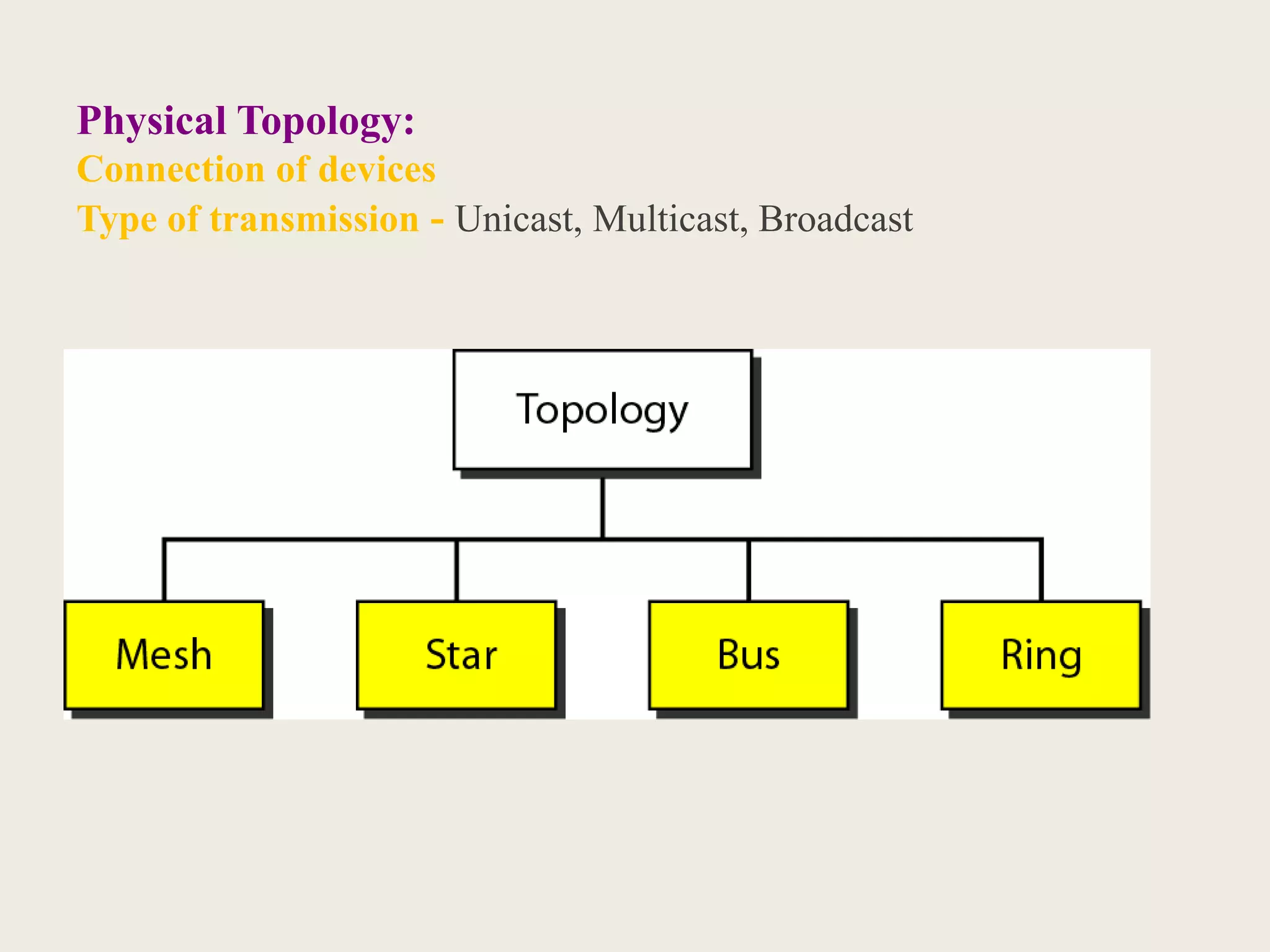
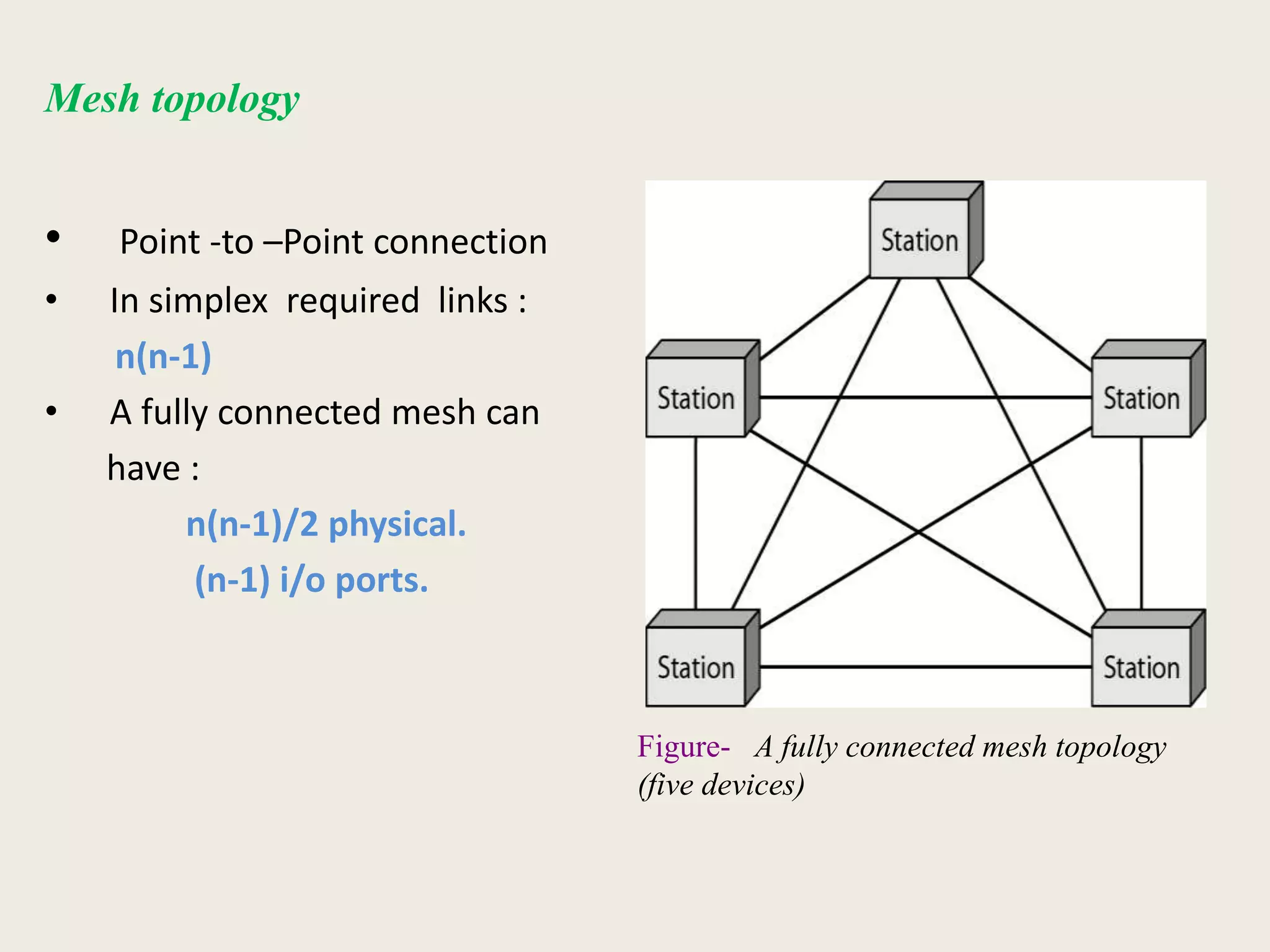
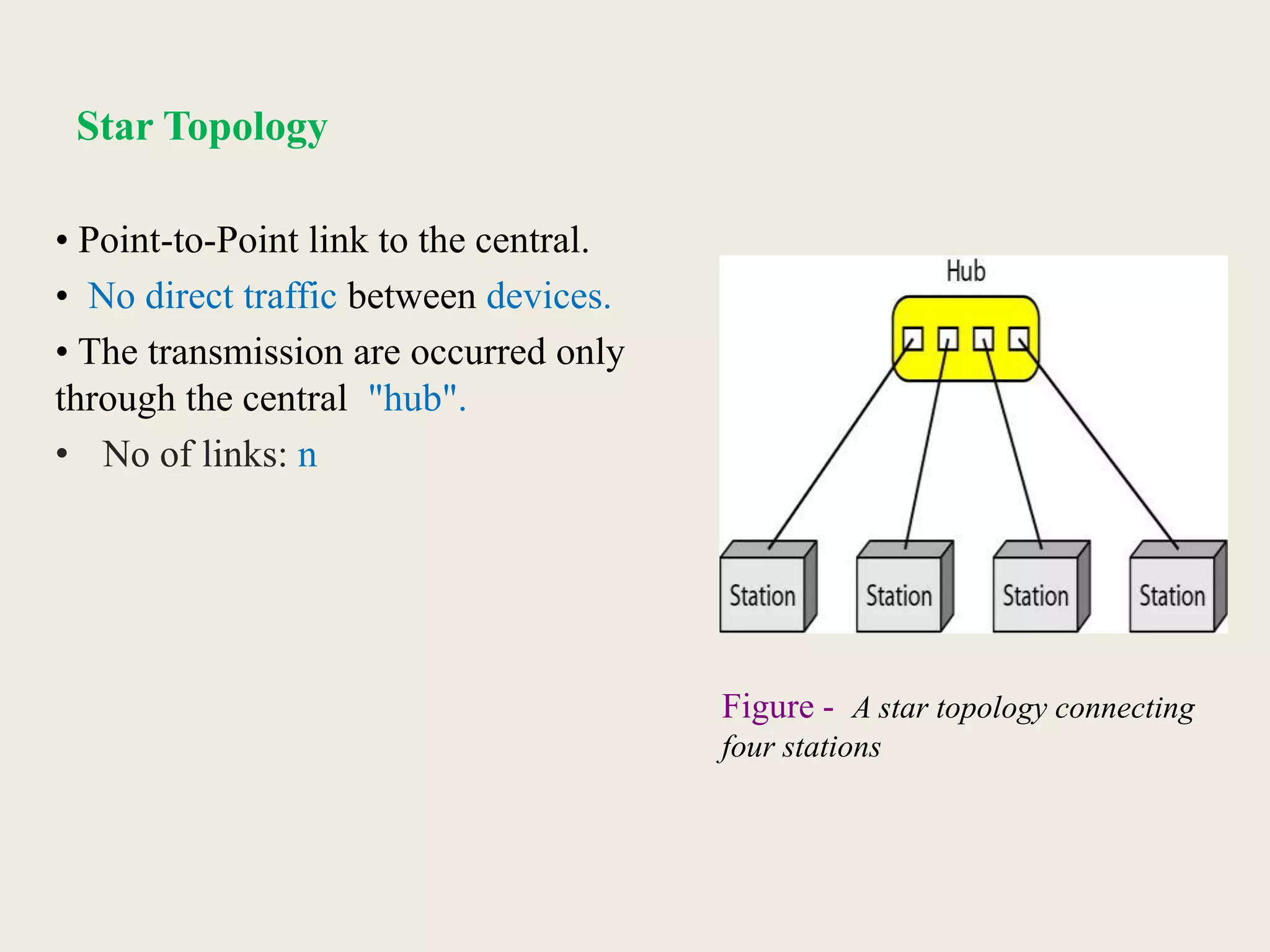
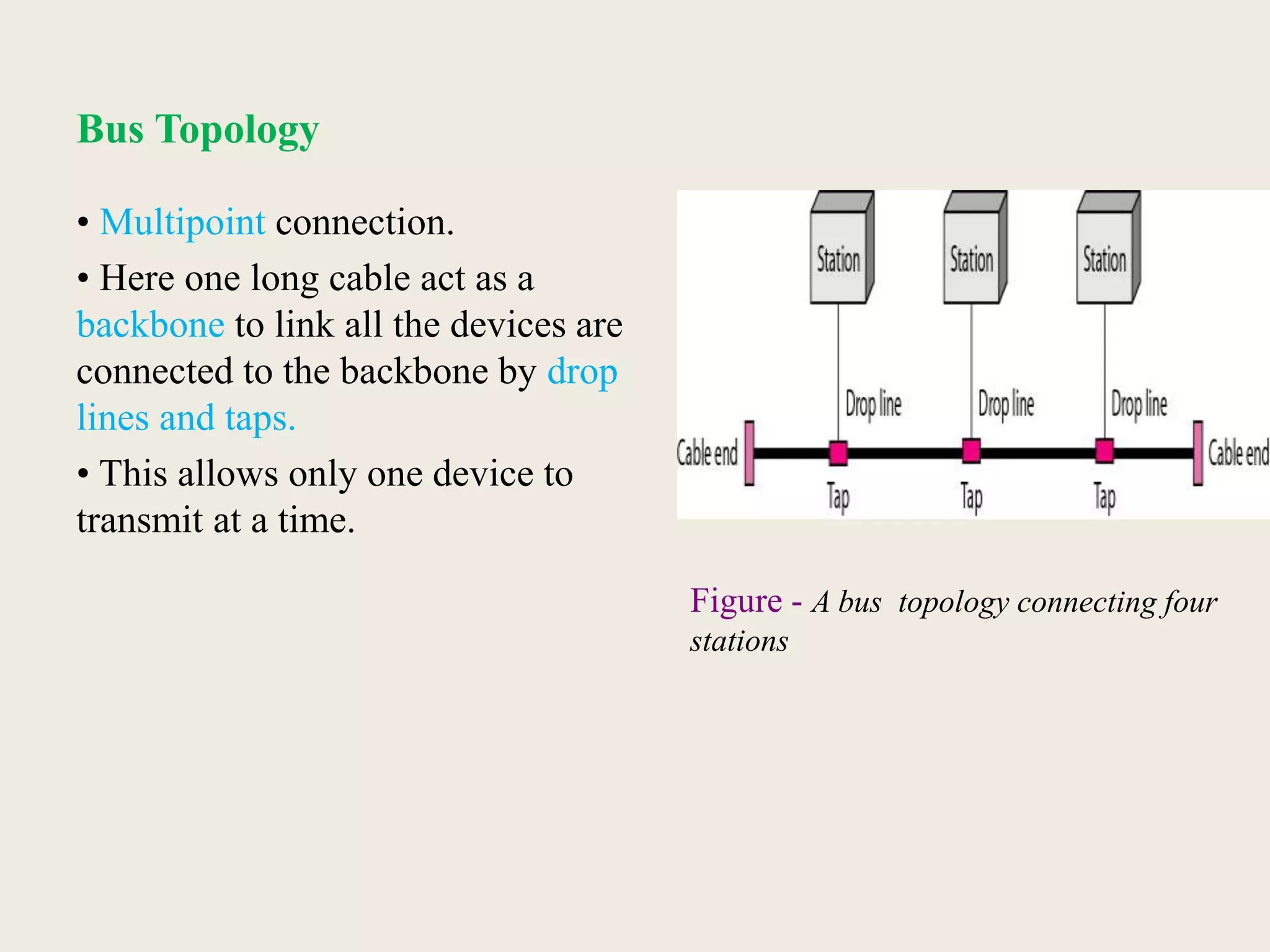
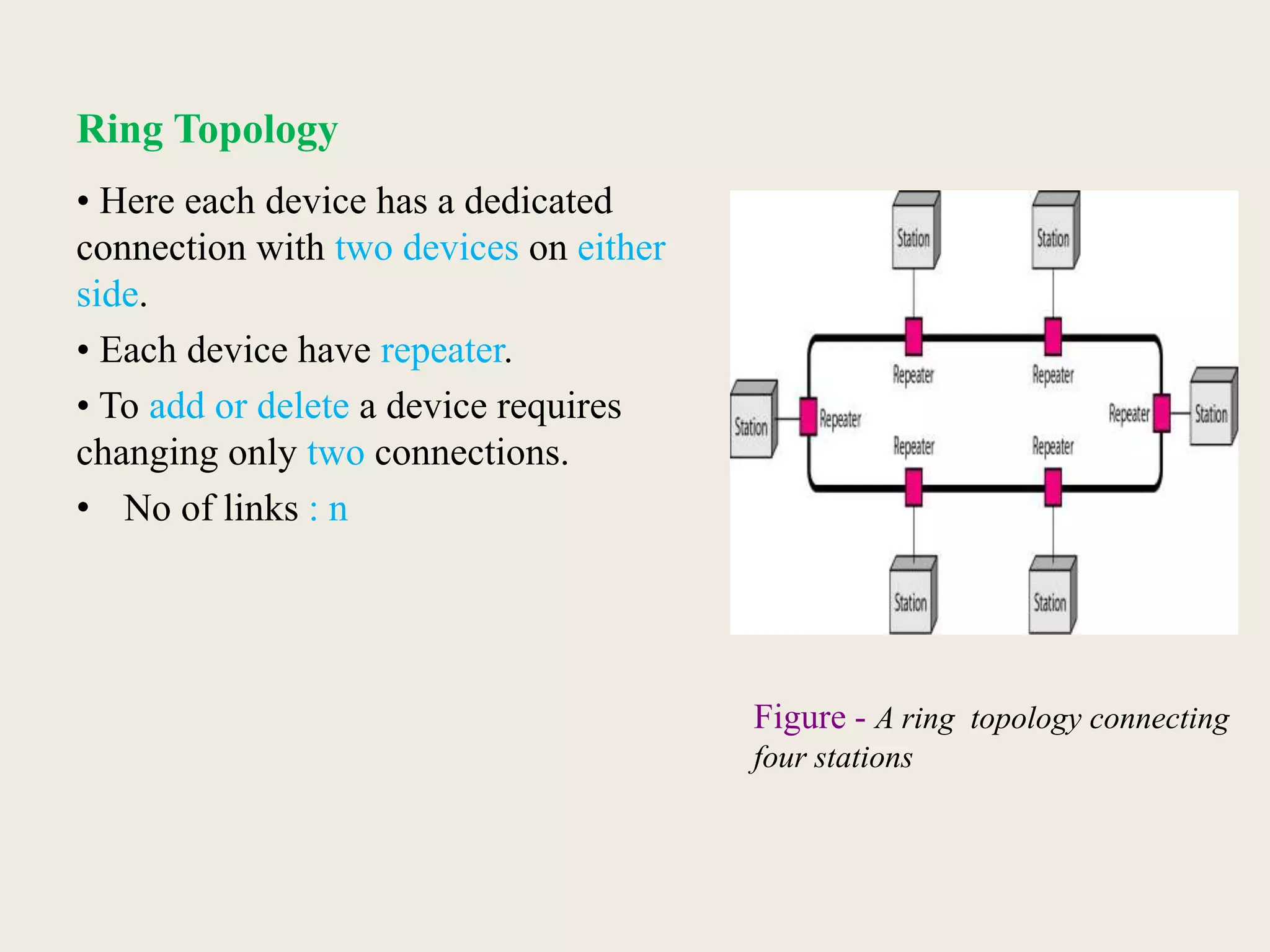
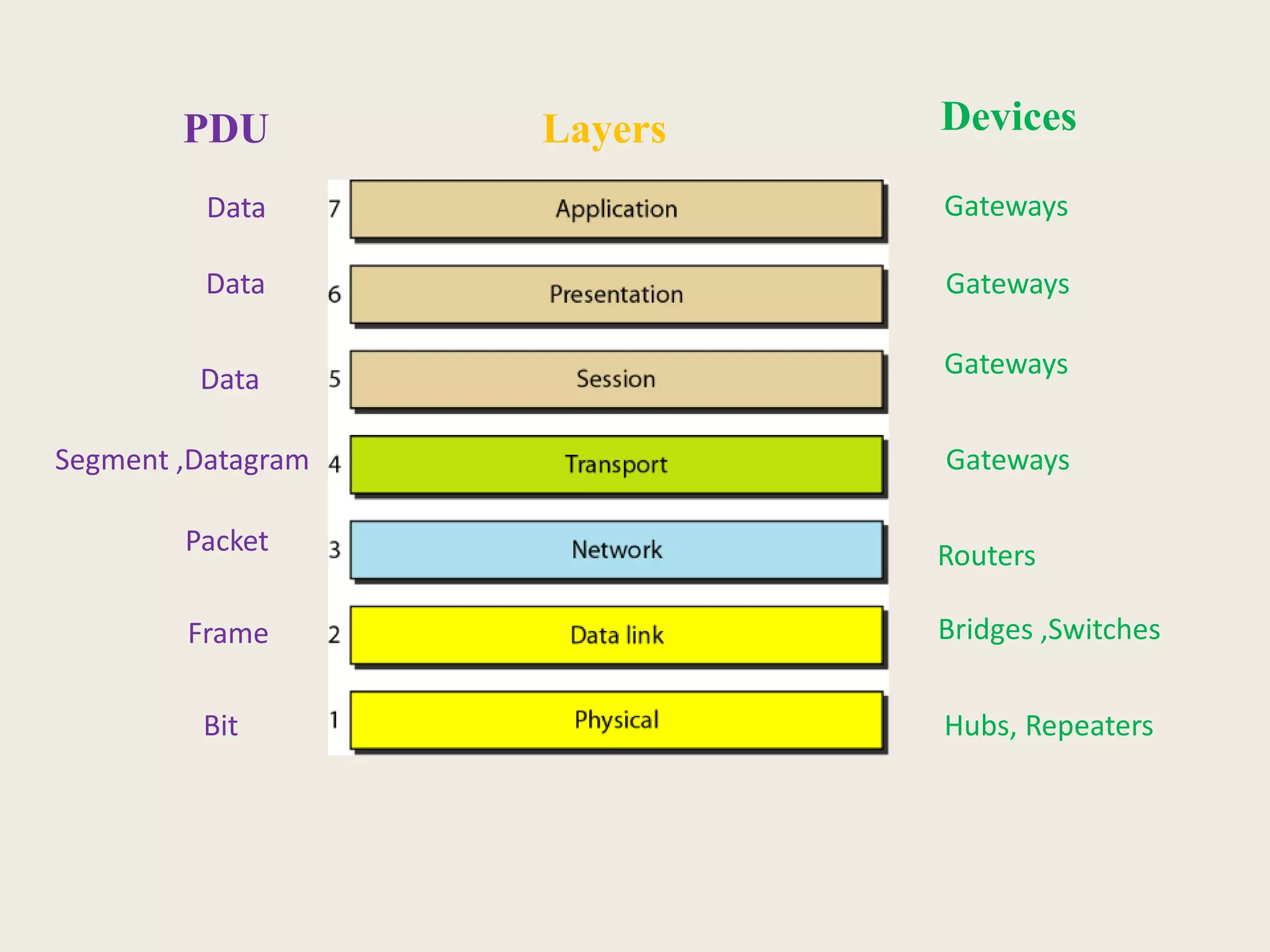
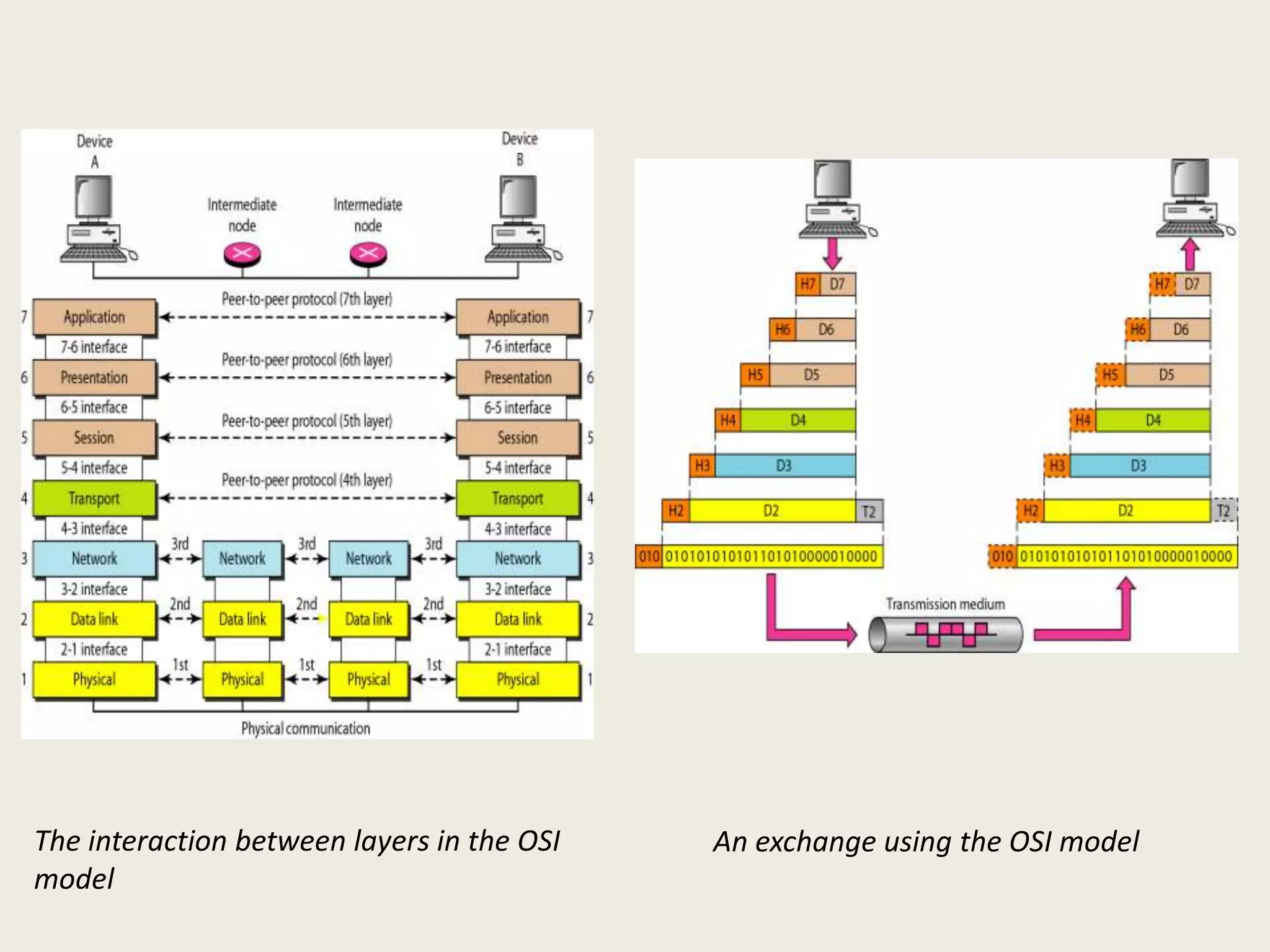
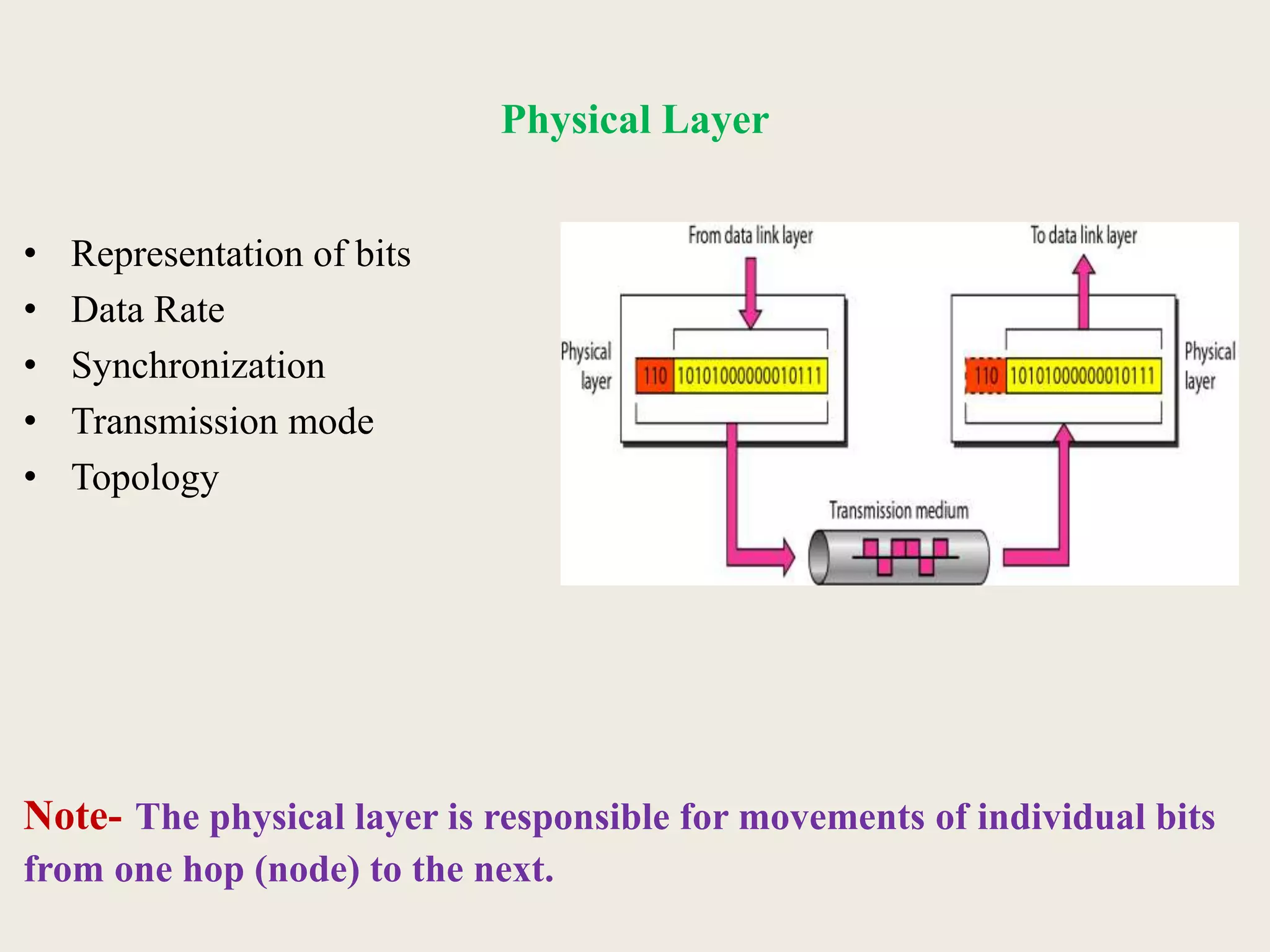
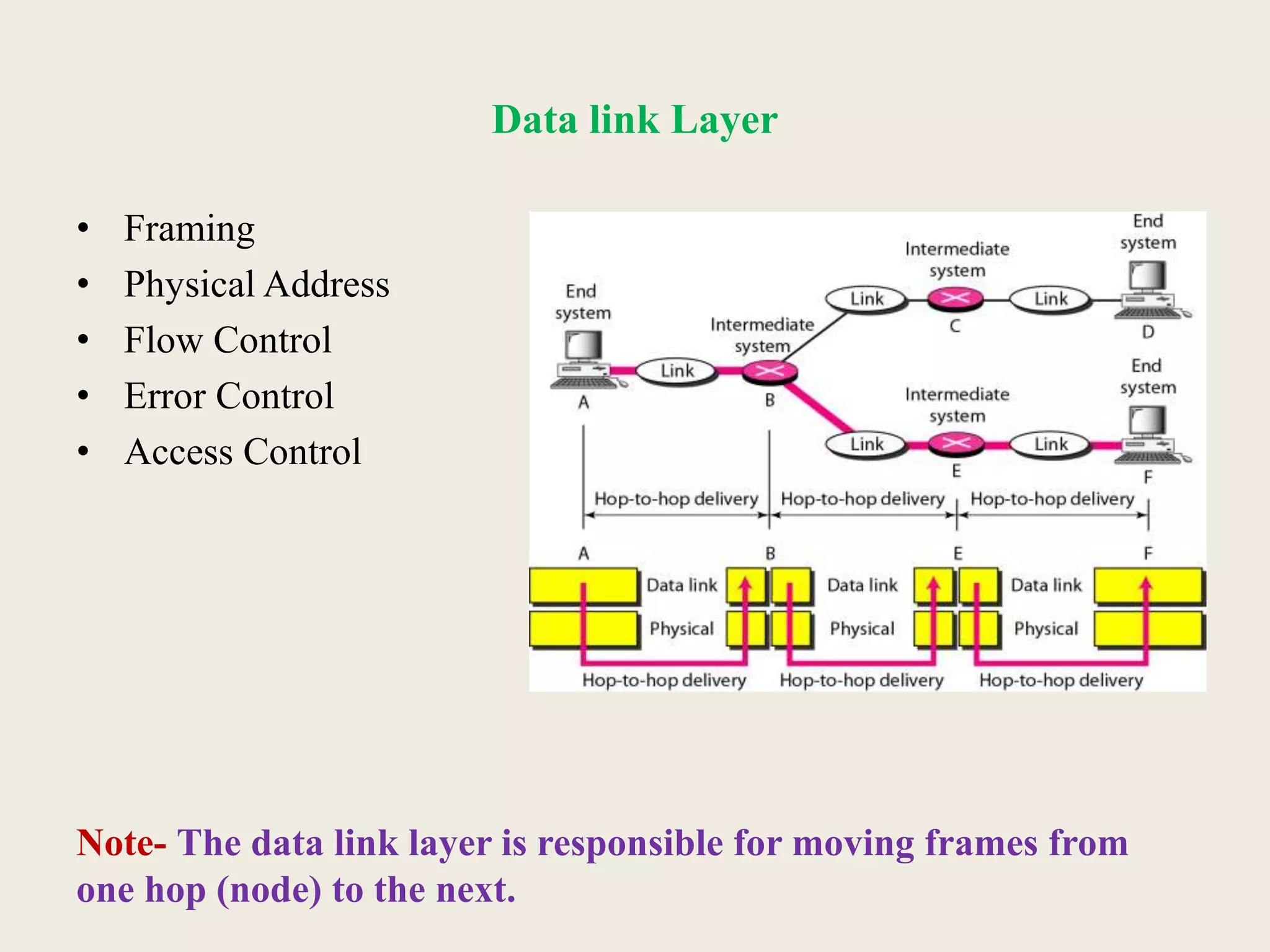
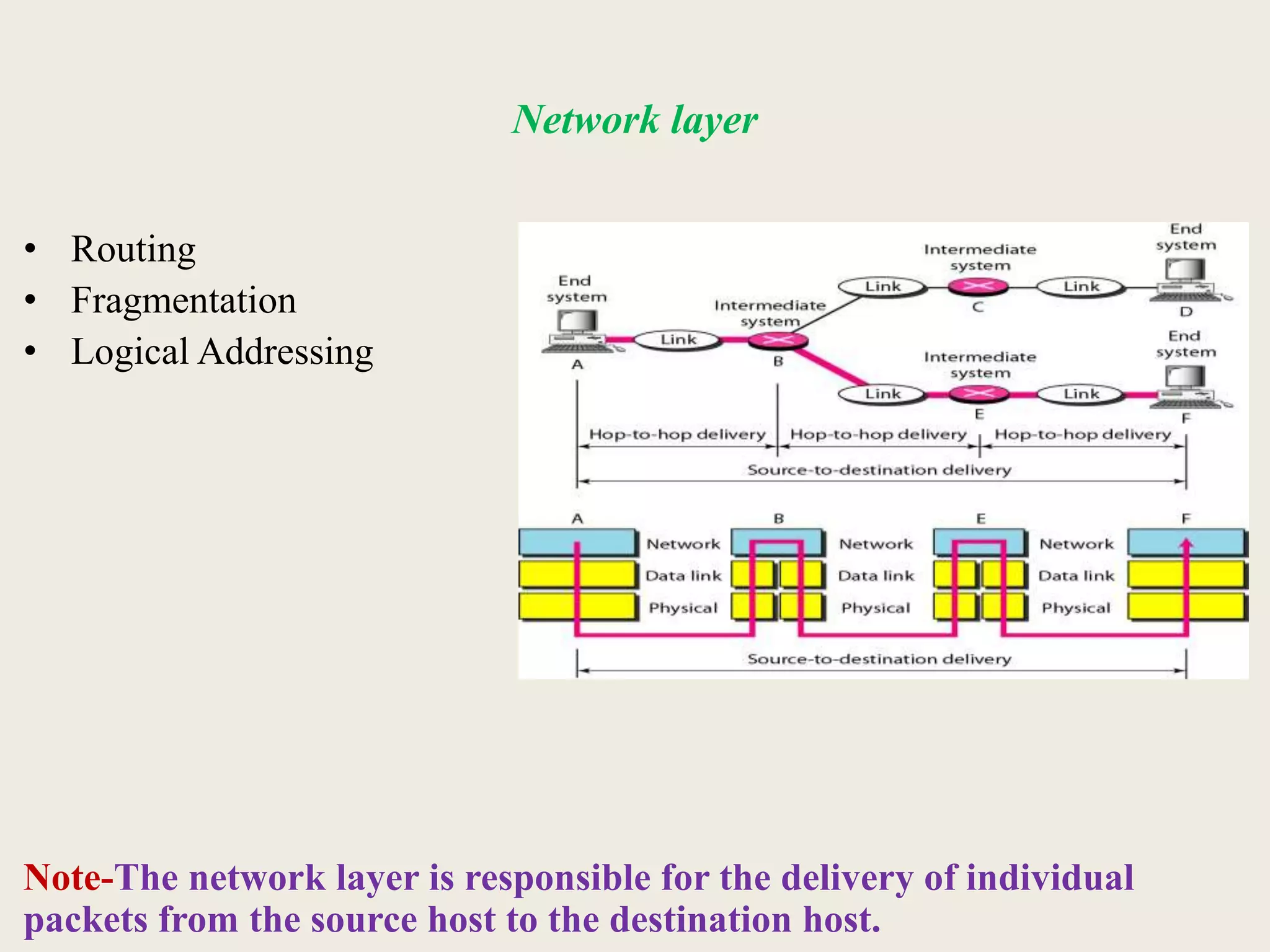
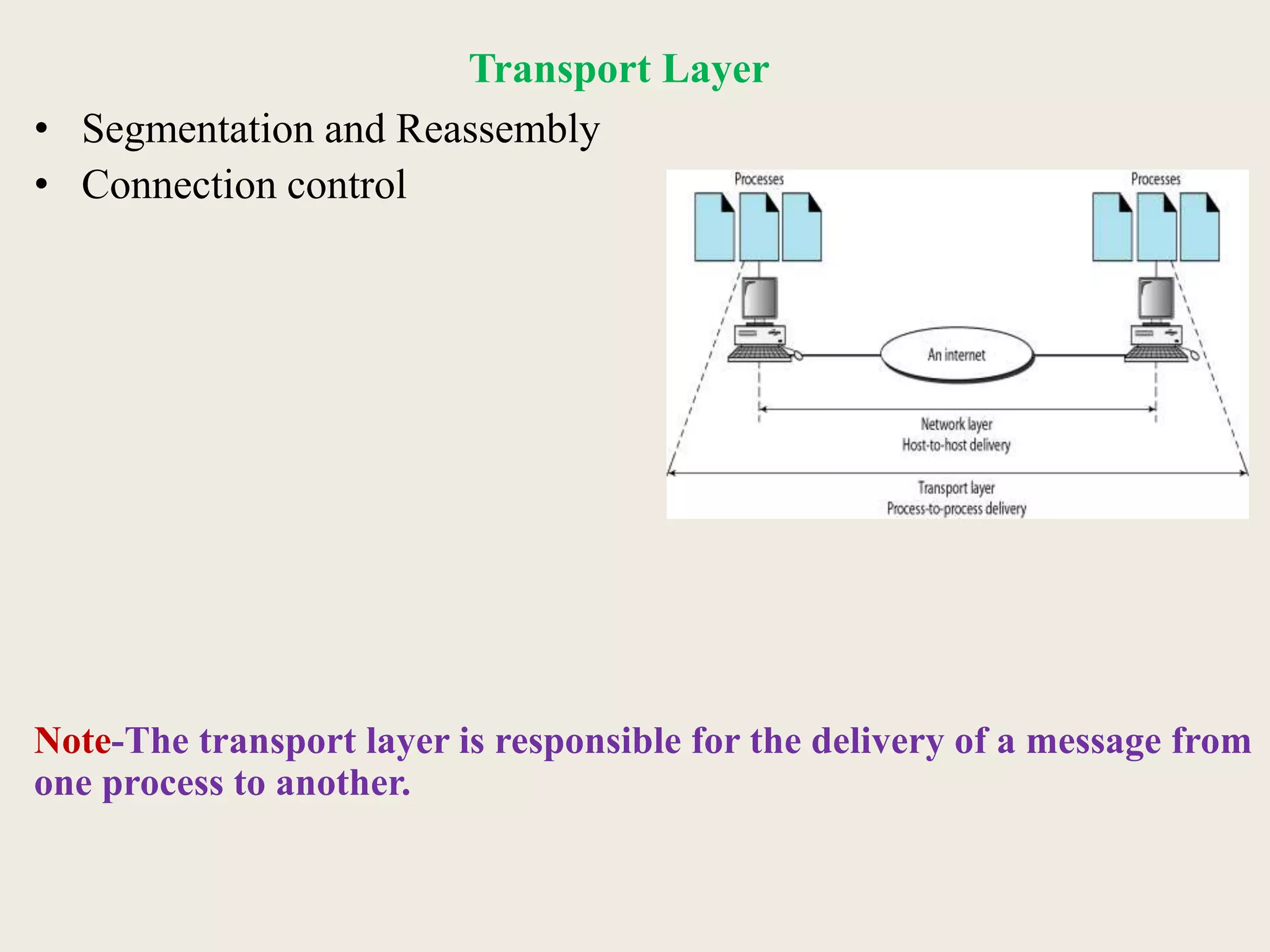
This document provides an introduction to computer networks, including definitions of data communication, networks, and network topologies. It discusses the components of data communication and defines a network. Physical network structures like point-to-point and multipoint connections are described. Common network topologies including mesh, star, bus, and ring are defined along with their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, the seven-layer OSI model is introduced as a standard for network communication, with brief descriptions of the layers and their responsibilities.