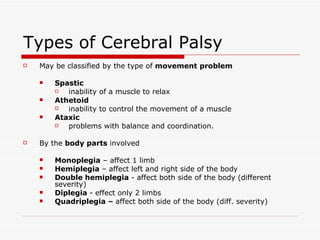
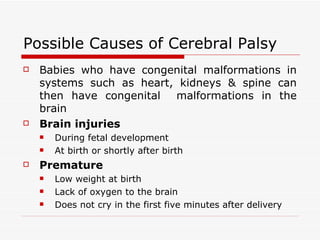
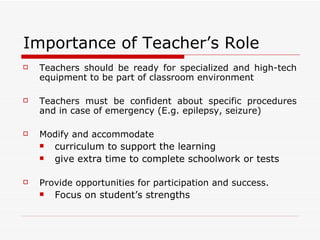
Cerebral palsy is a non-progressive neurological disorder that affects motor movement due to lesions in the brain. It can affect mobility in different parts of the body. Common causes include brain injuries during fetal development, birth complications like prematurity or lack of oxygen, and certain infections or chemical exposures during pregnancy. Teachers can help students with cerebral palsy by modifying instruction, ensuring an accessible classroom environment, encouraging social engagement, and focusing on student strengths. Local organizations in Singapore provide resources and treatment for children with cerebral palsy.