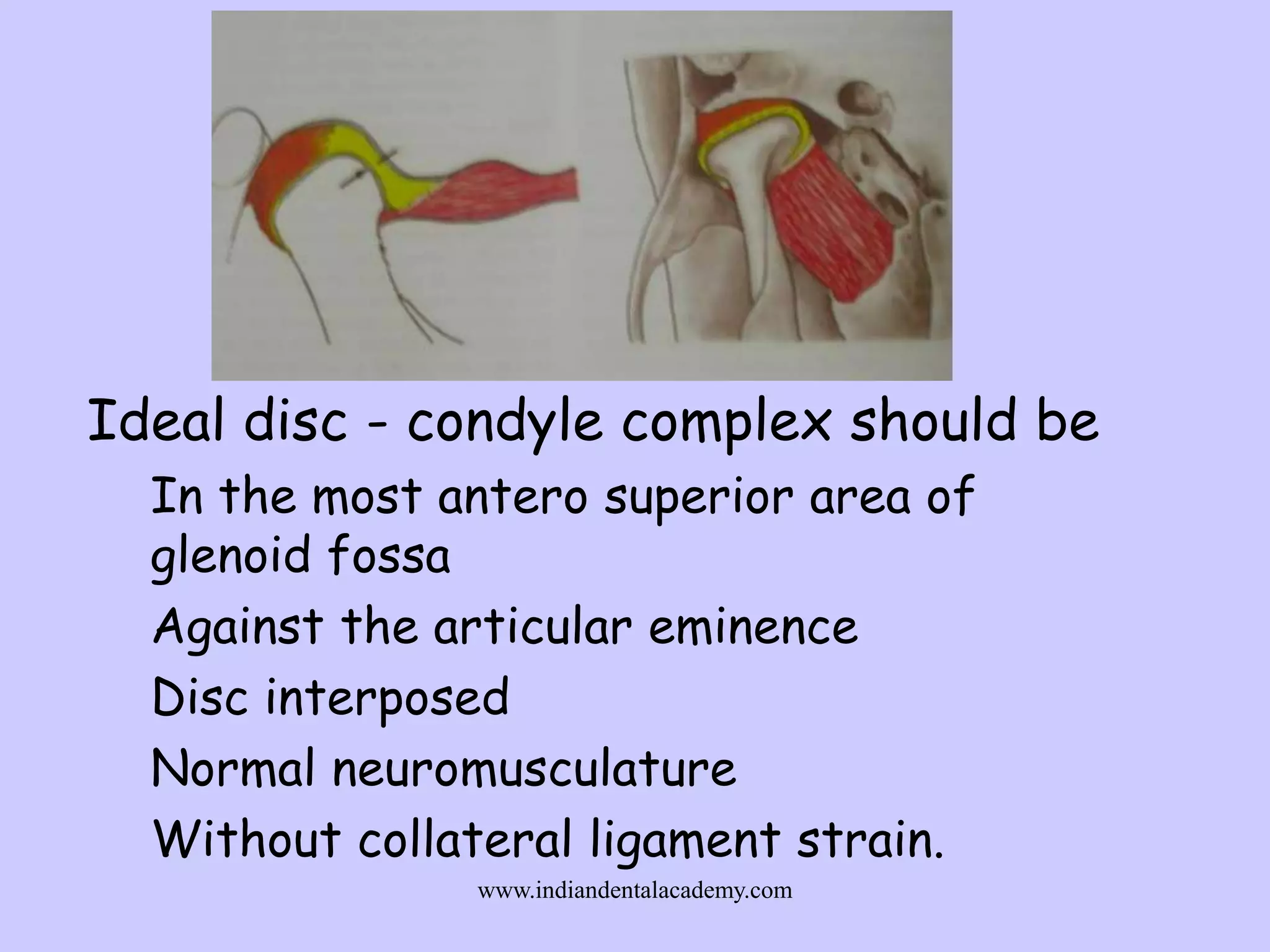
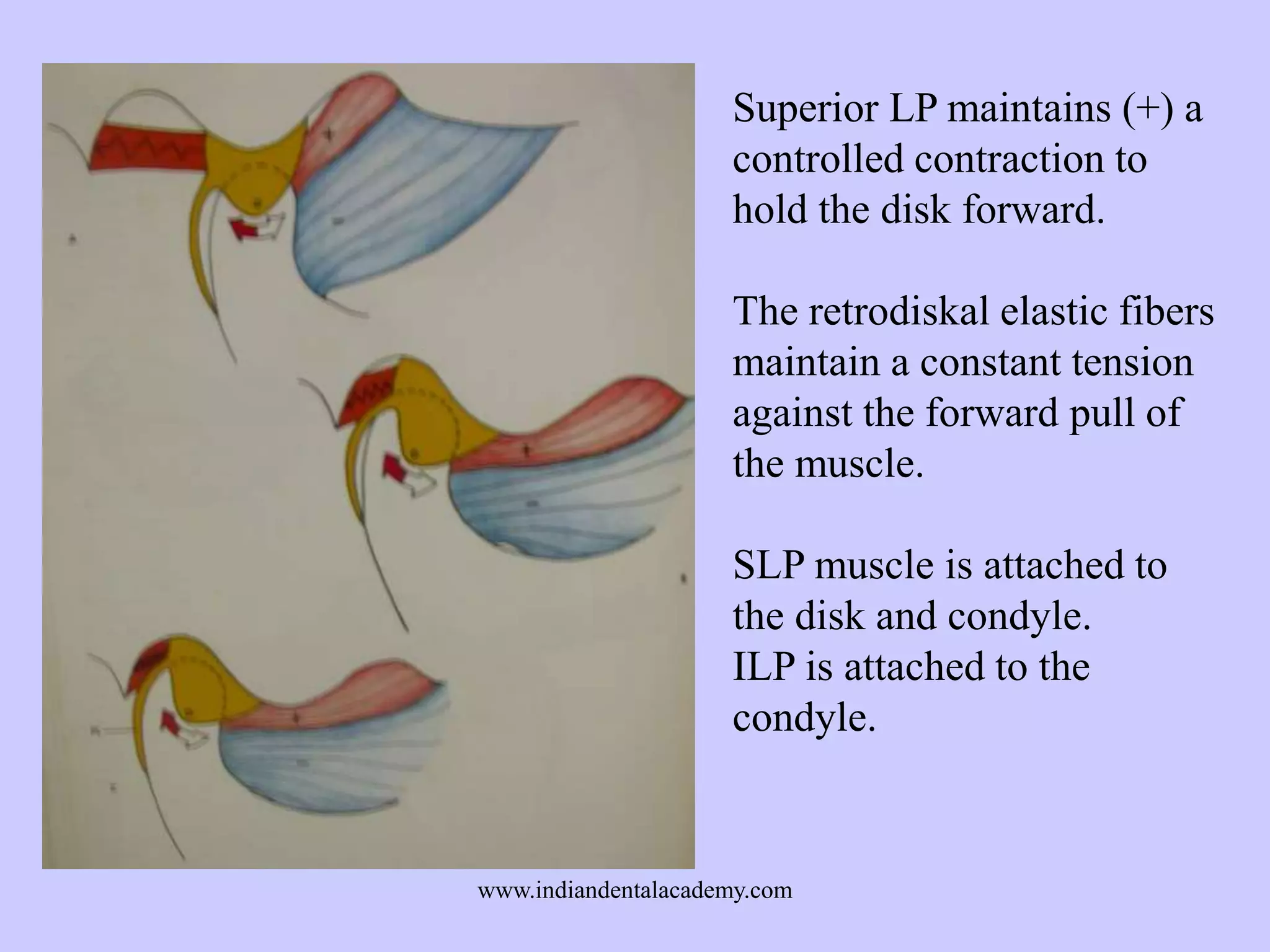
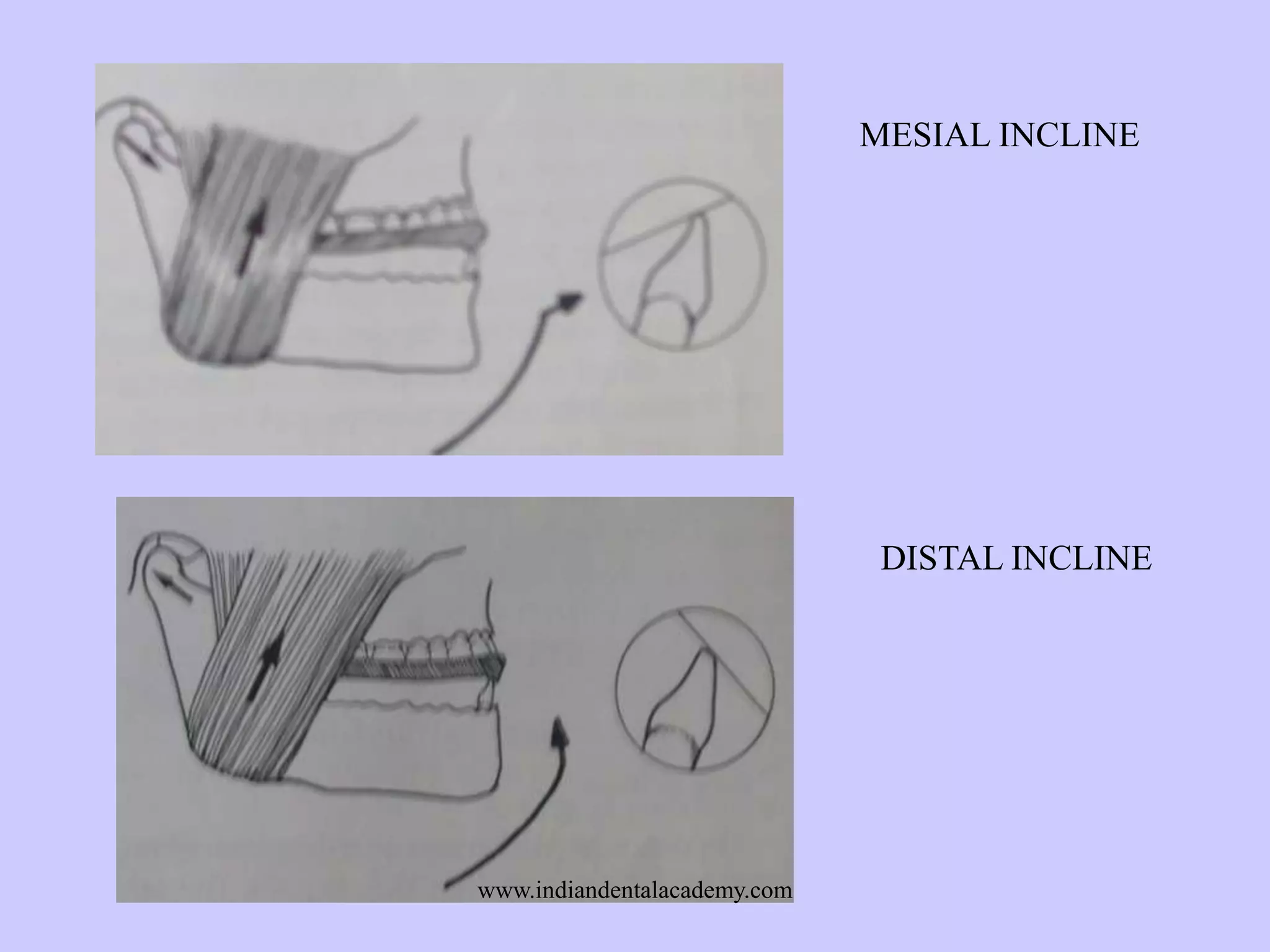
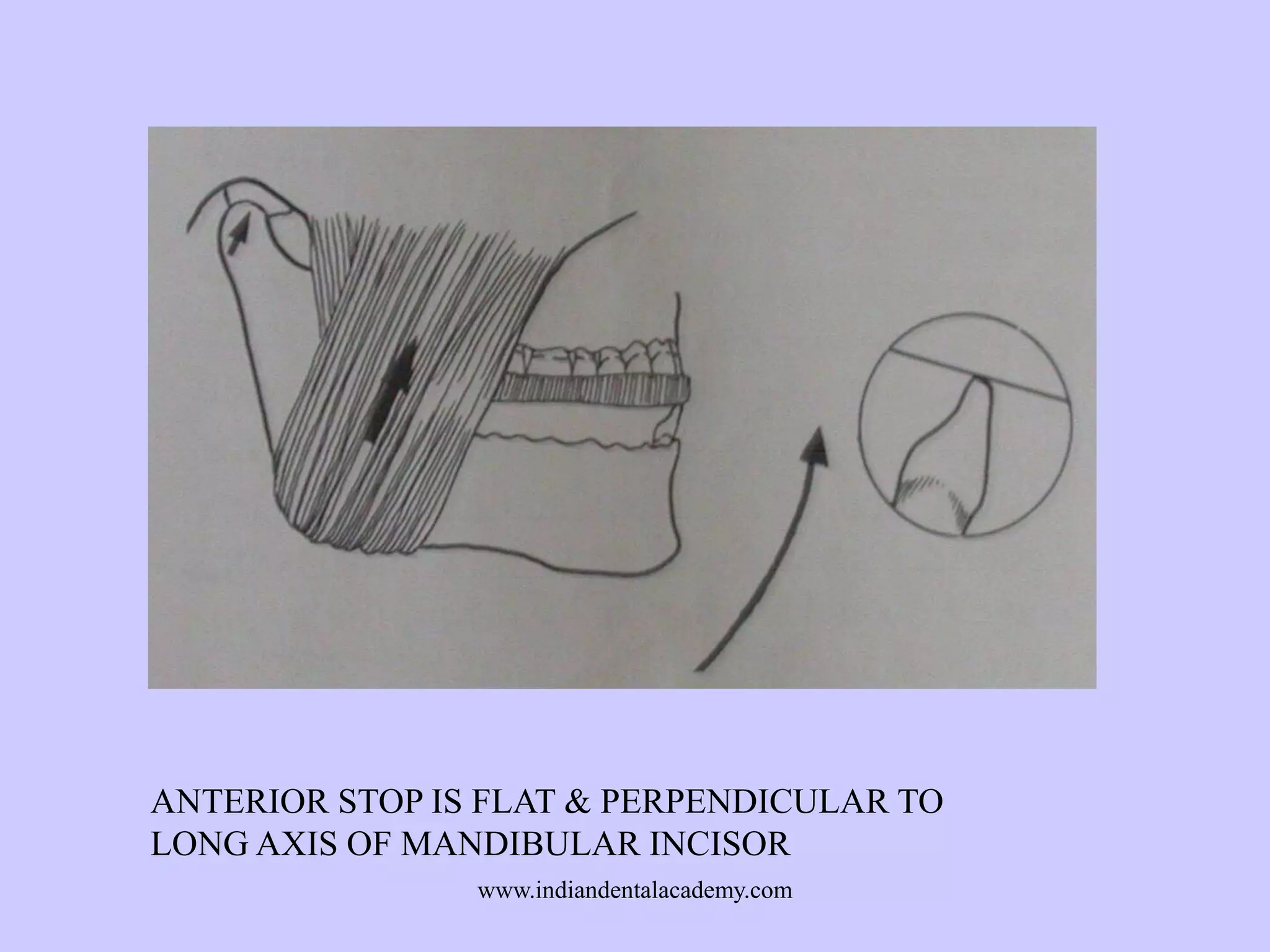
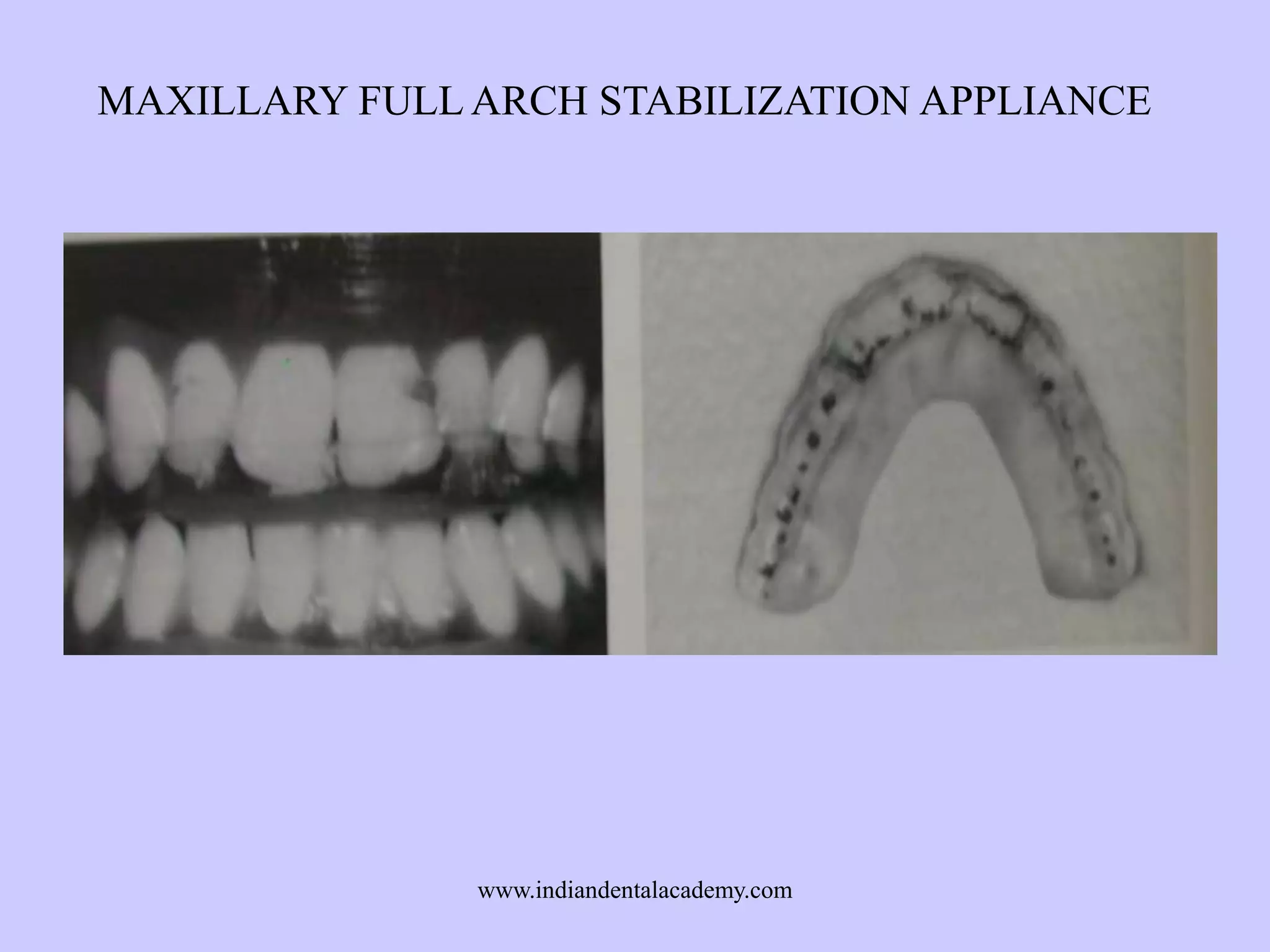
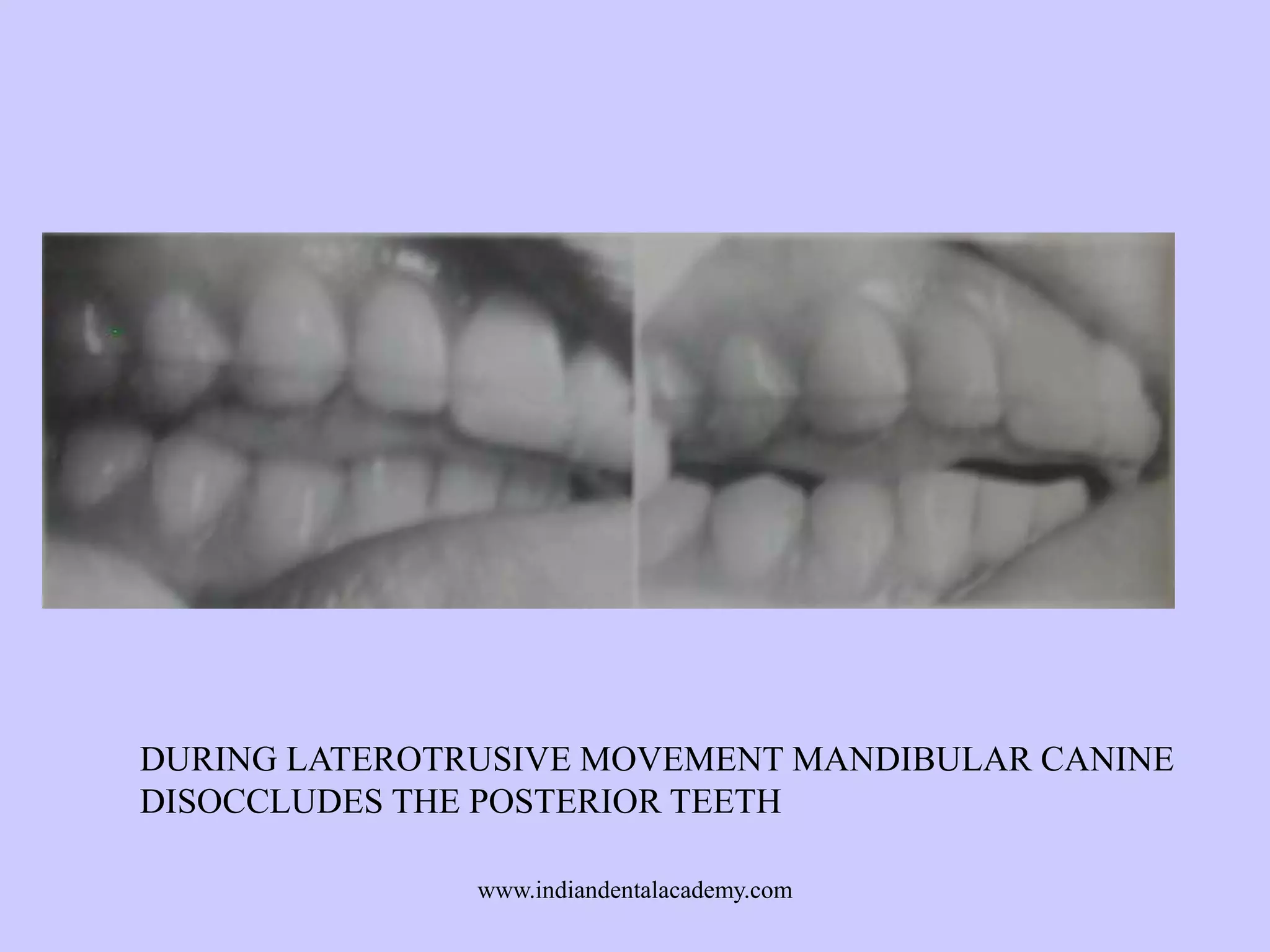
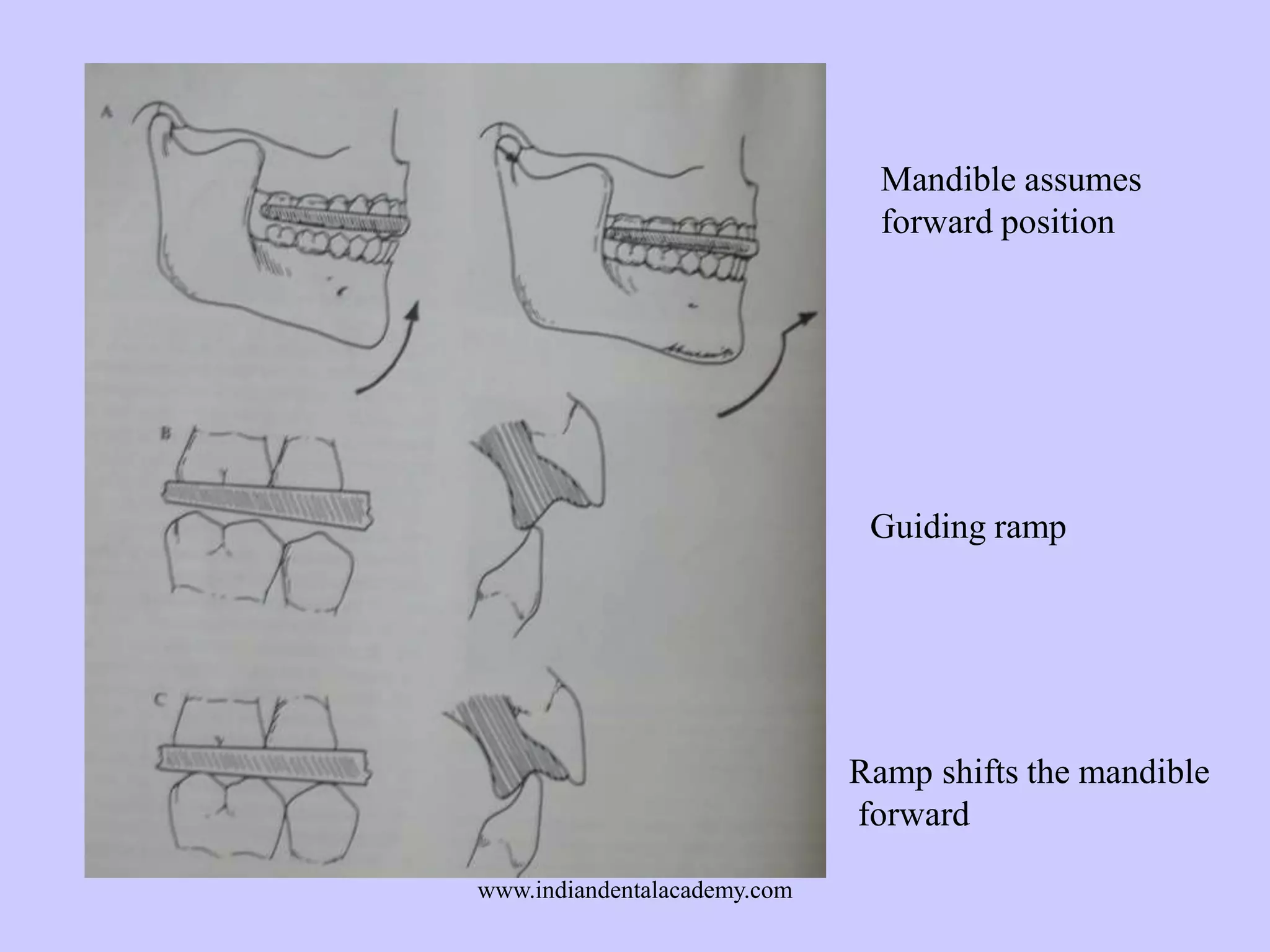
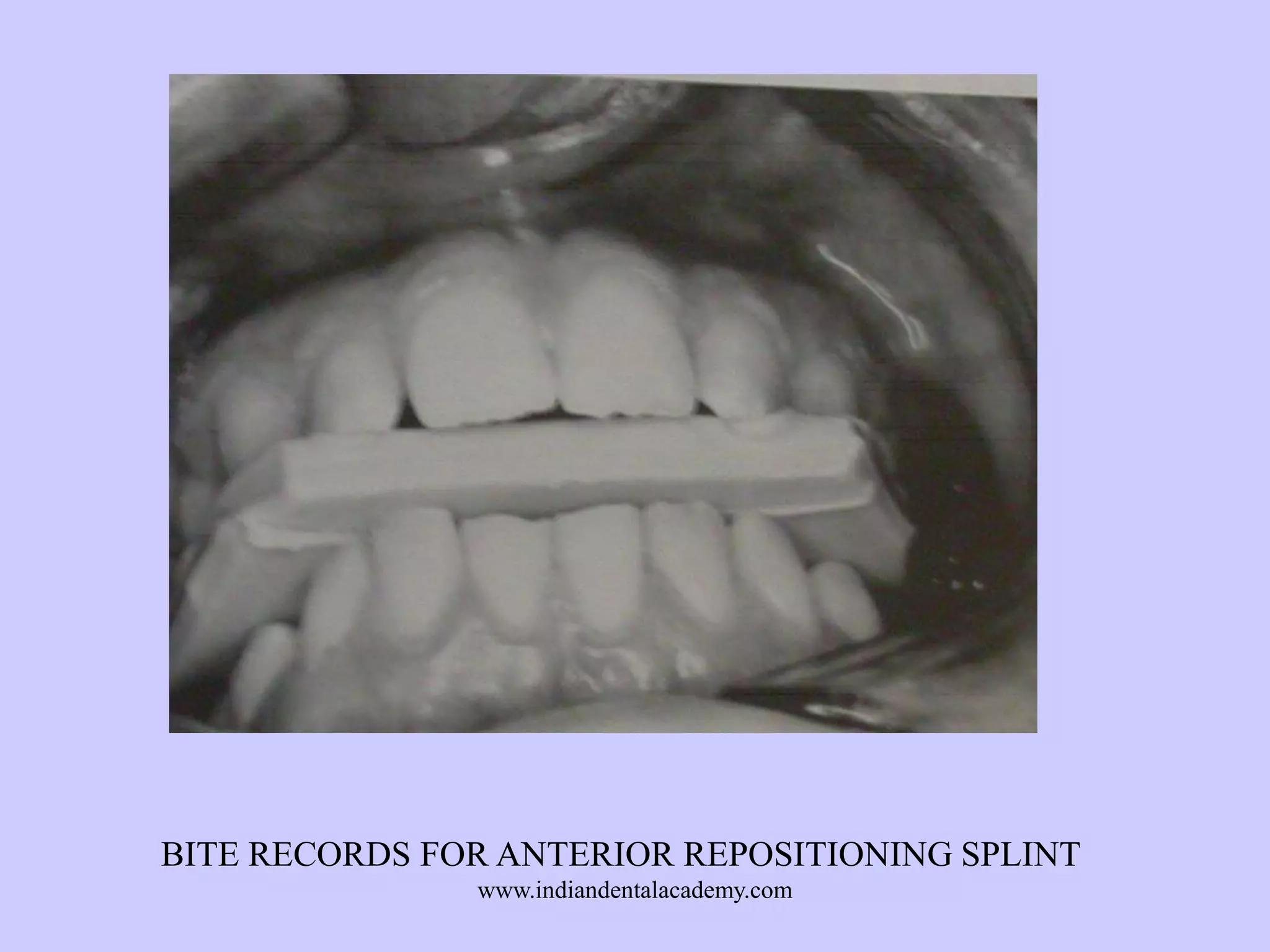
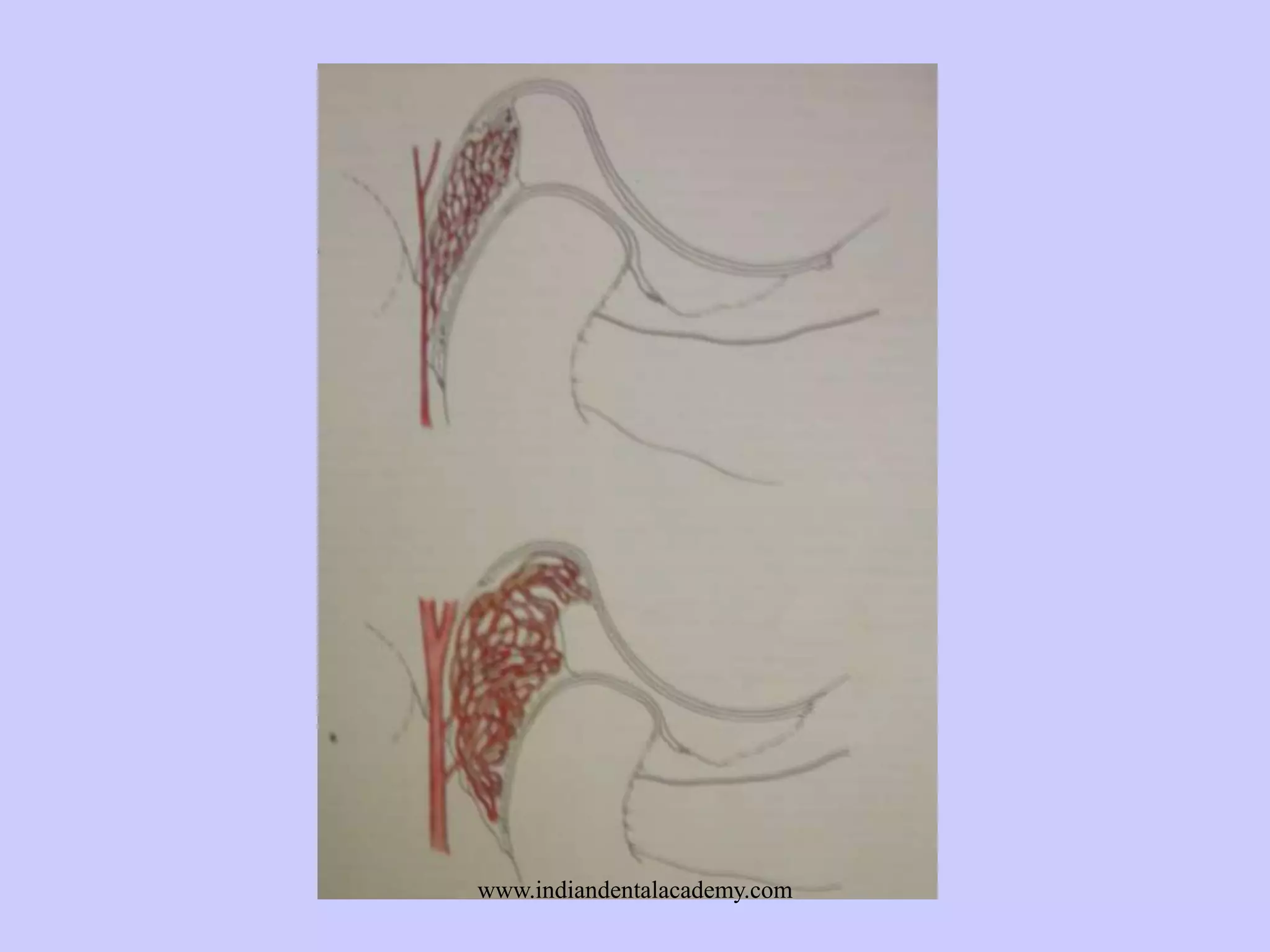
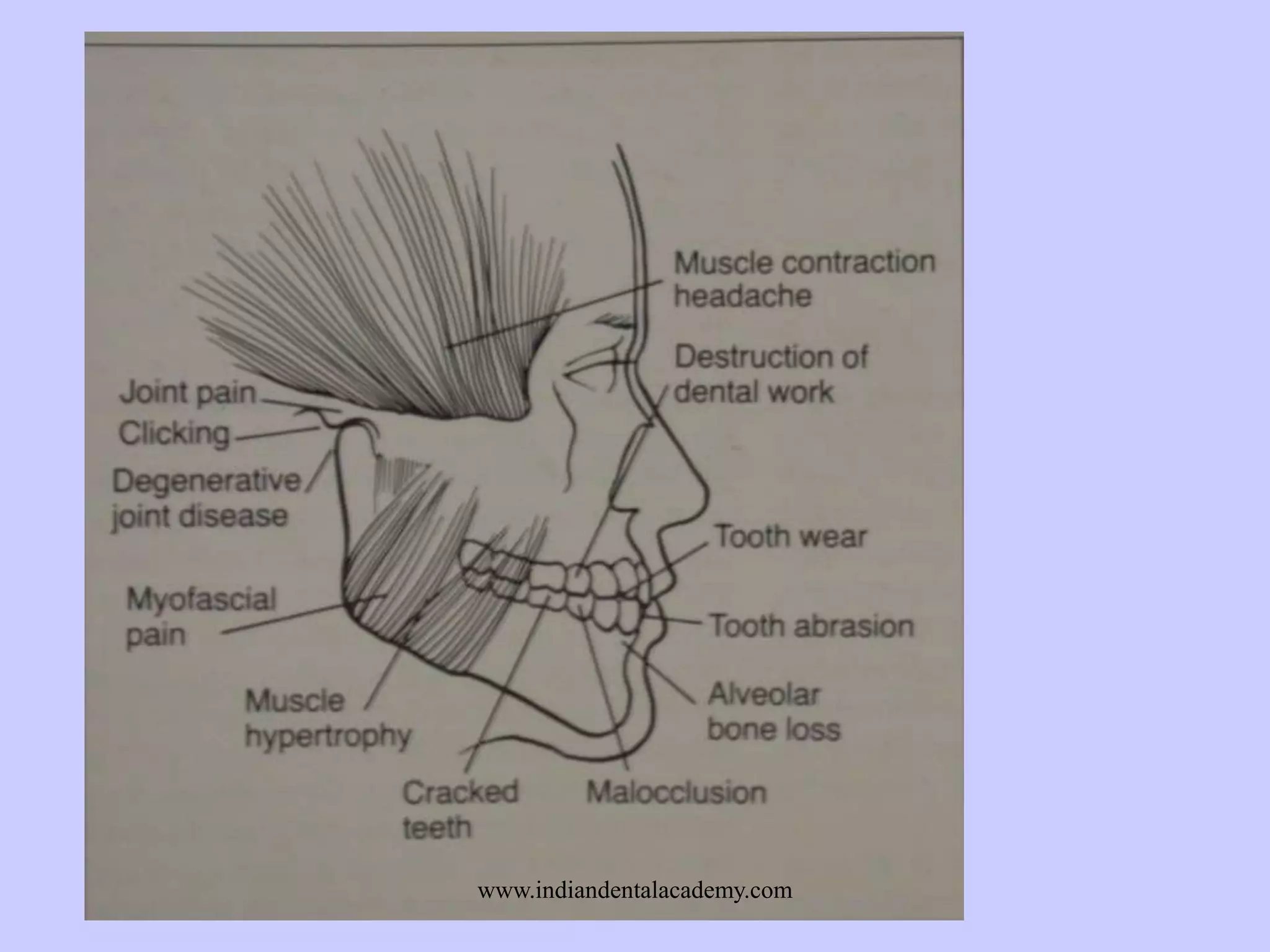
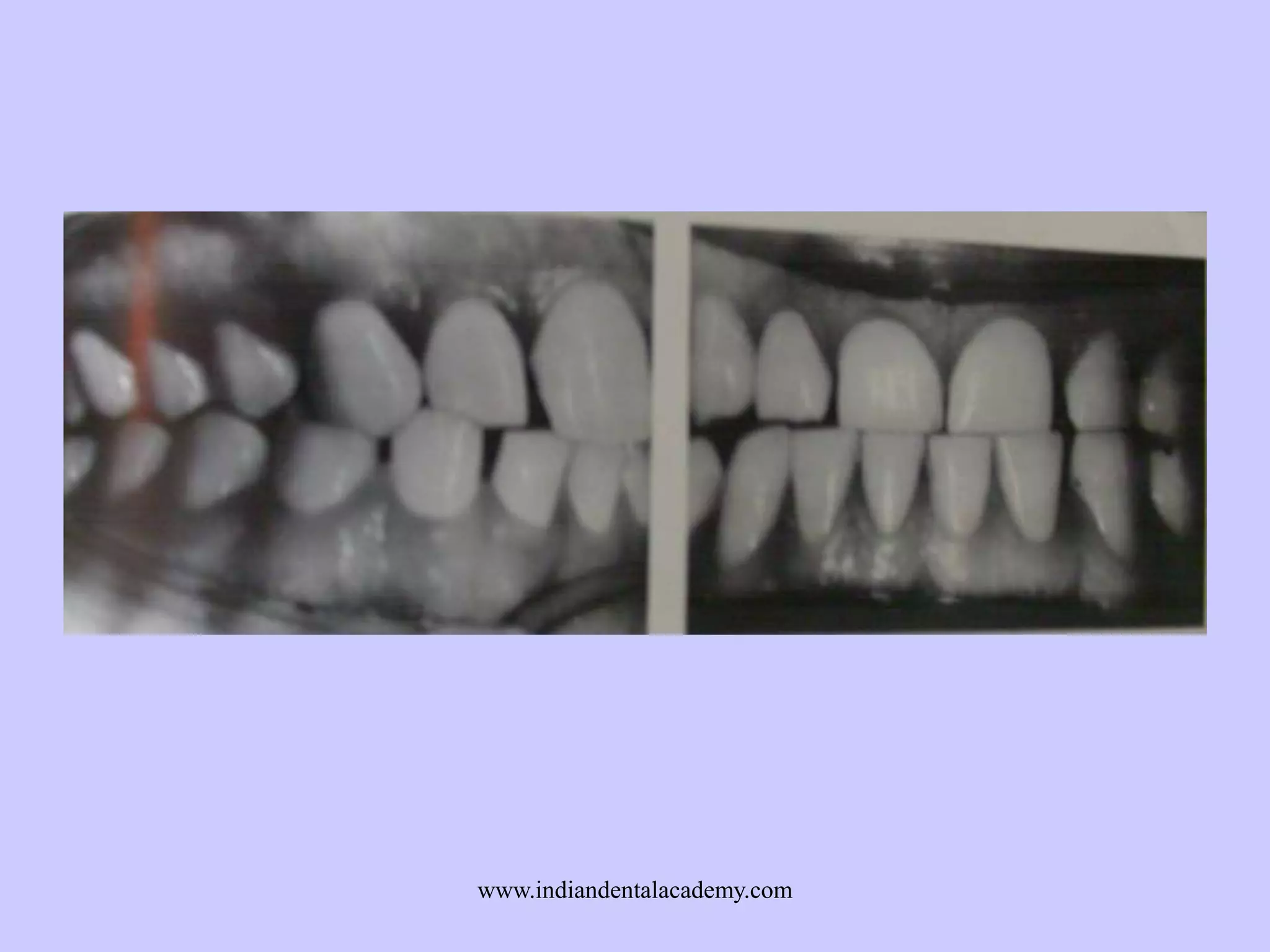
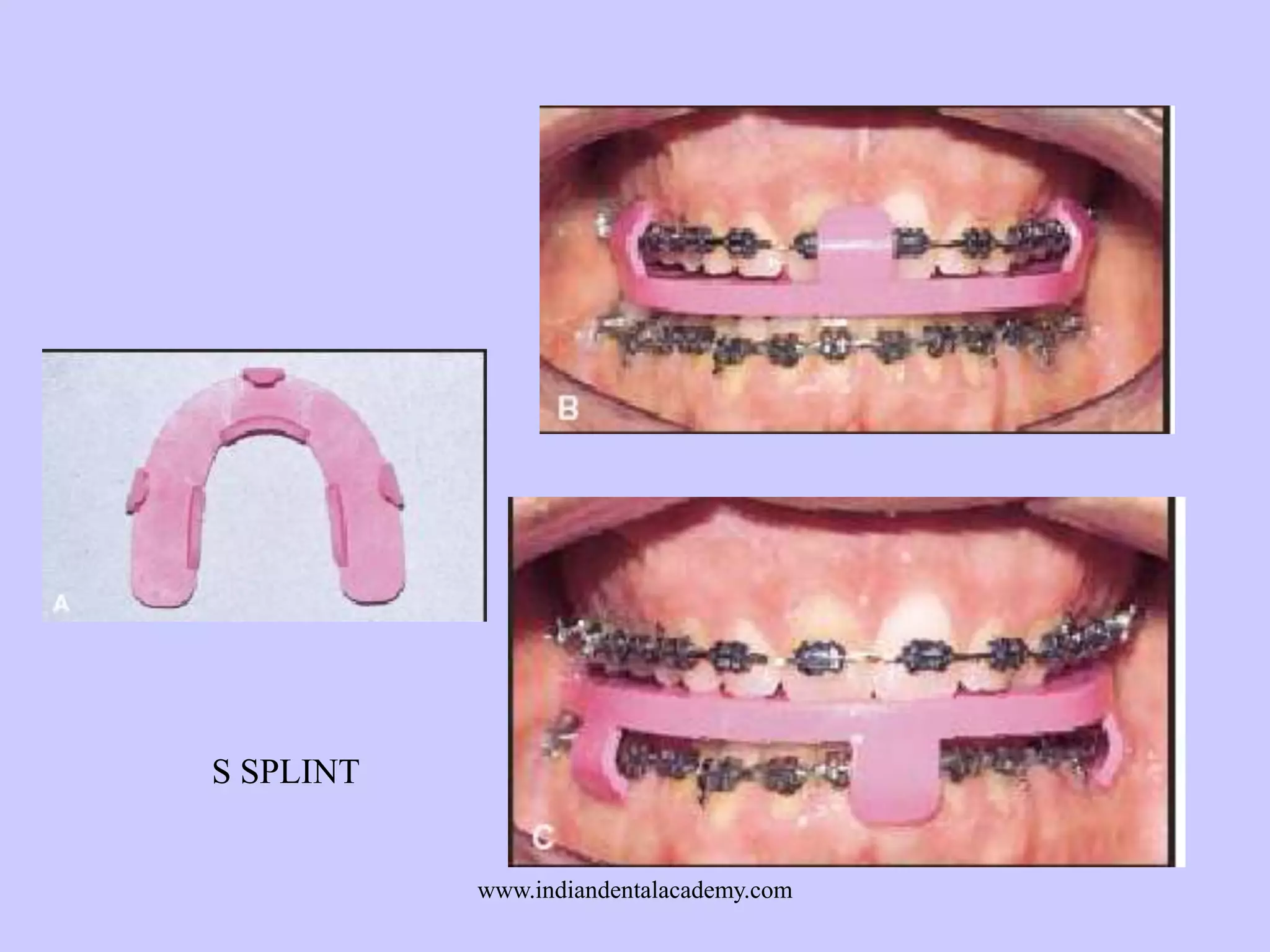
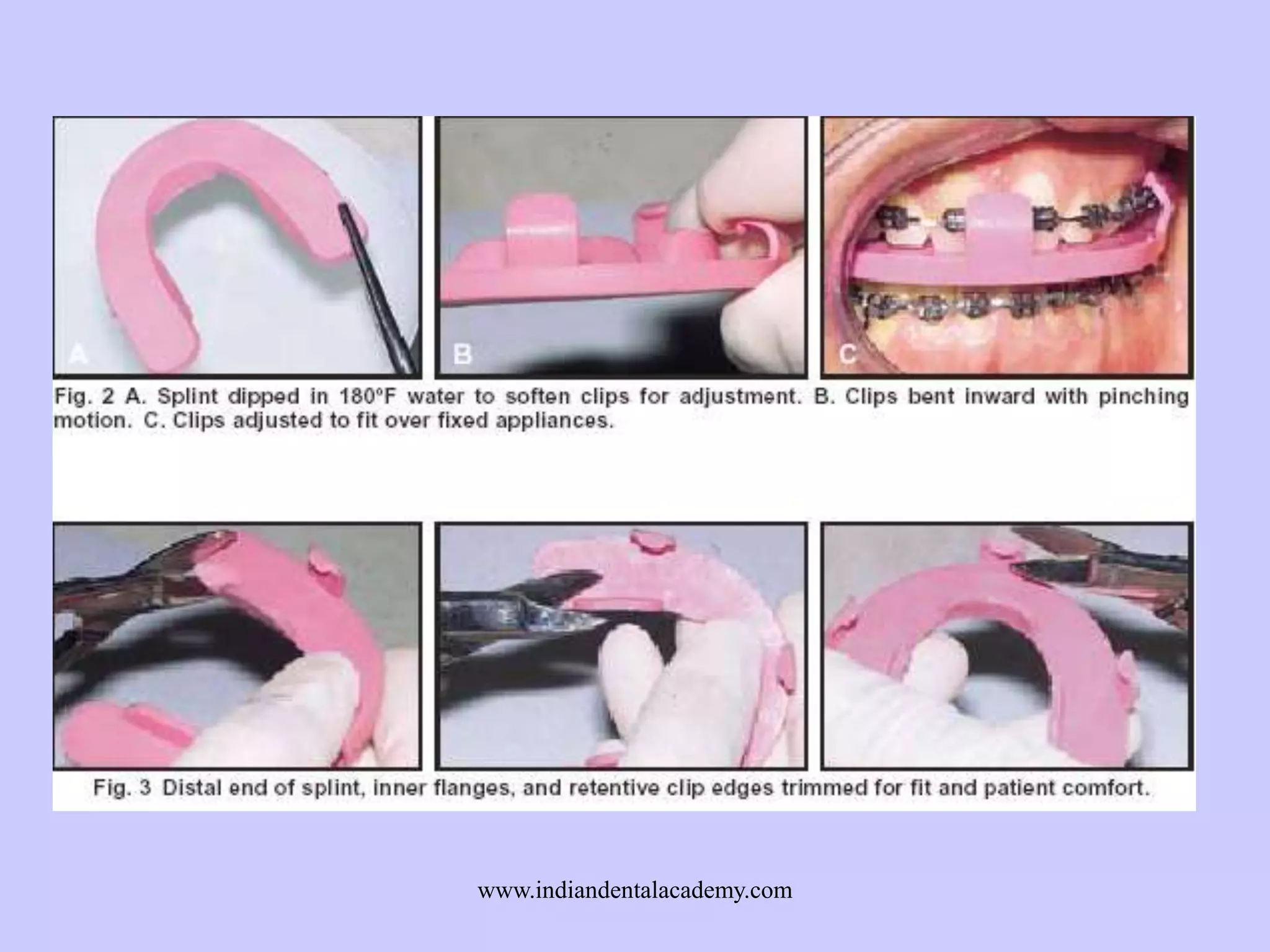
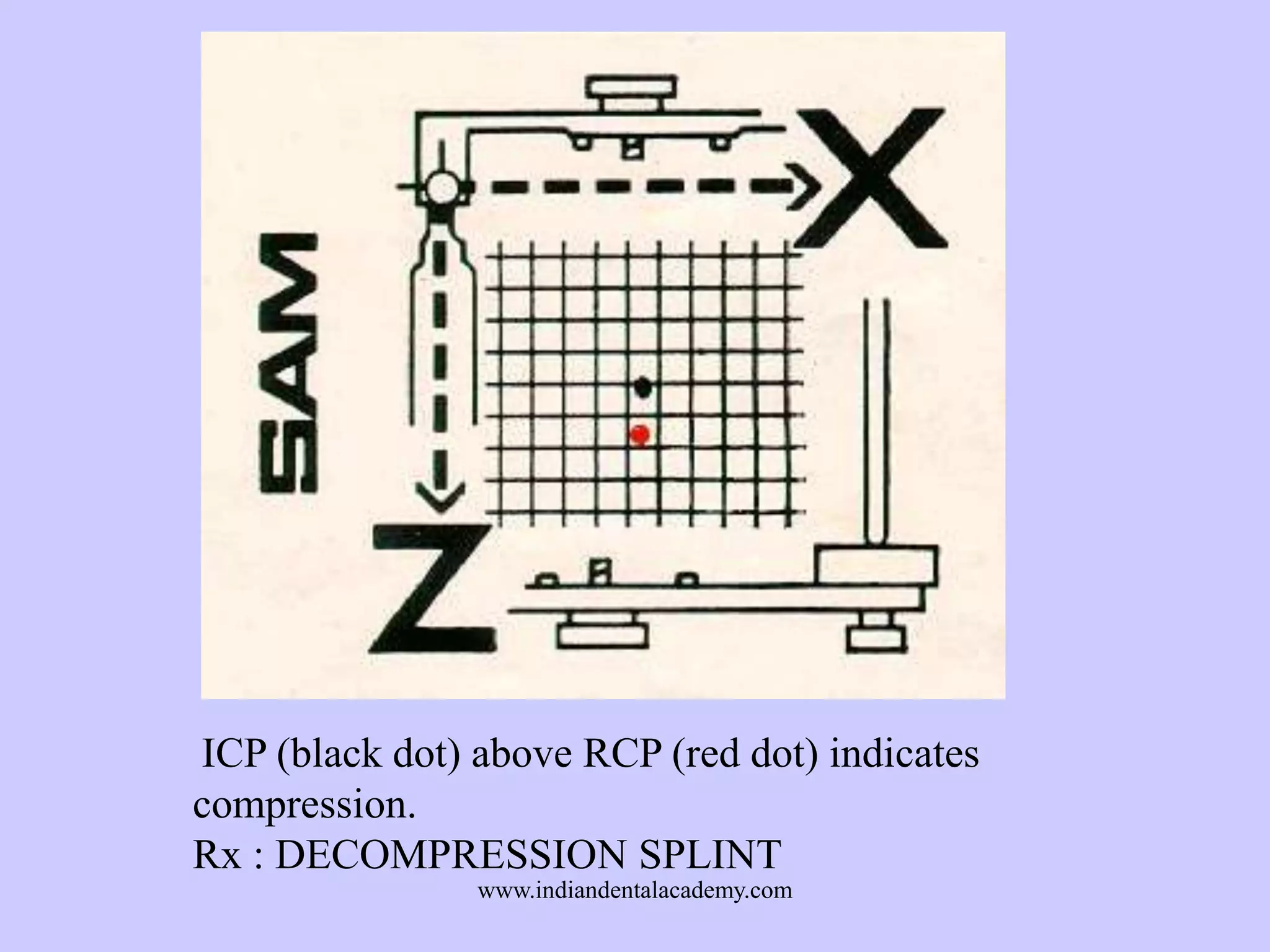
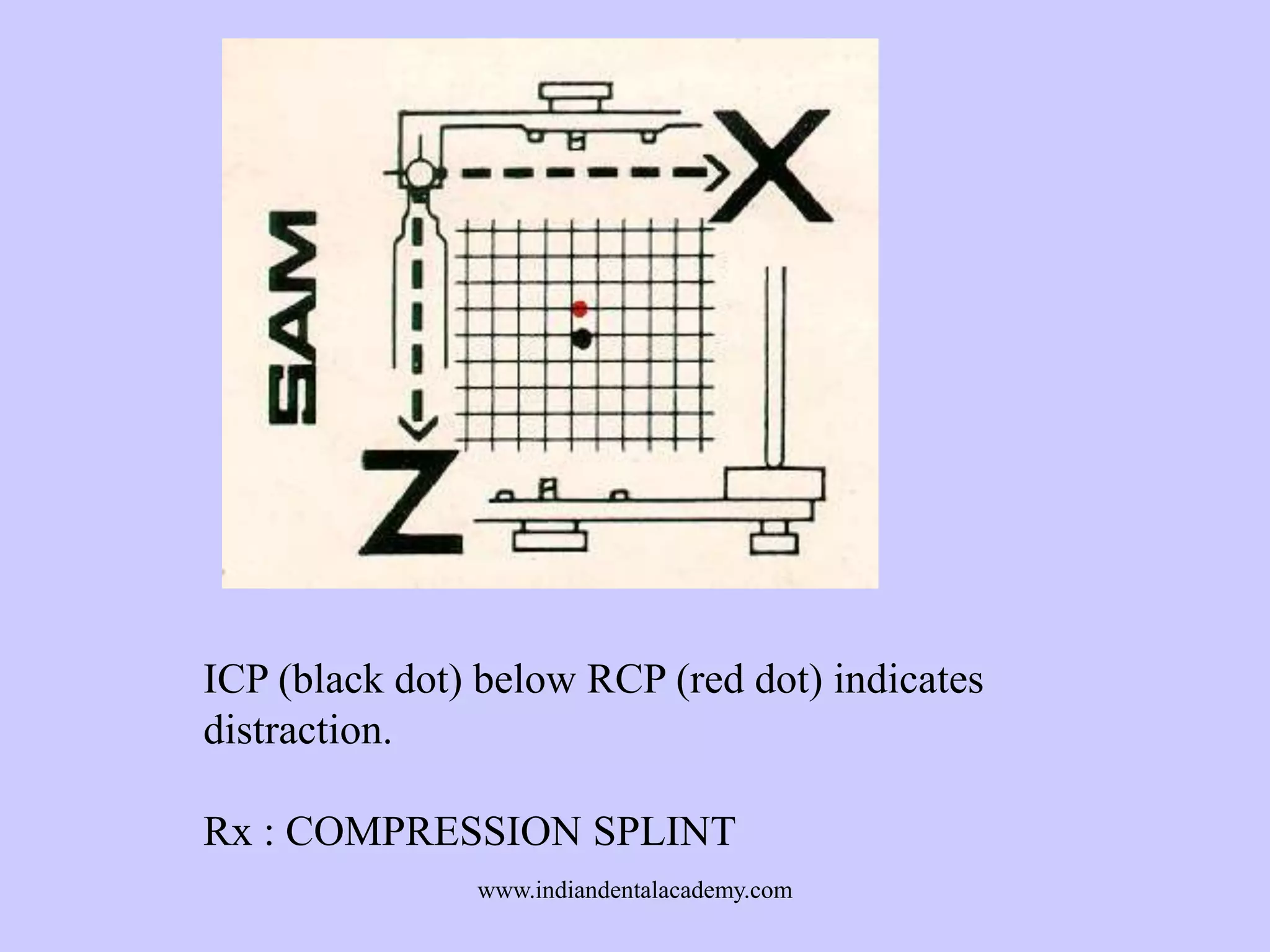
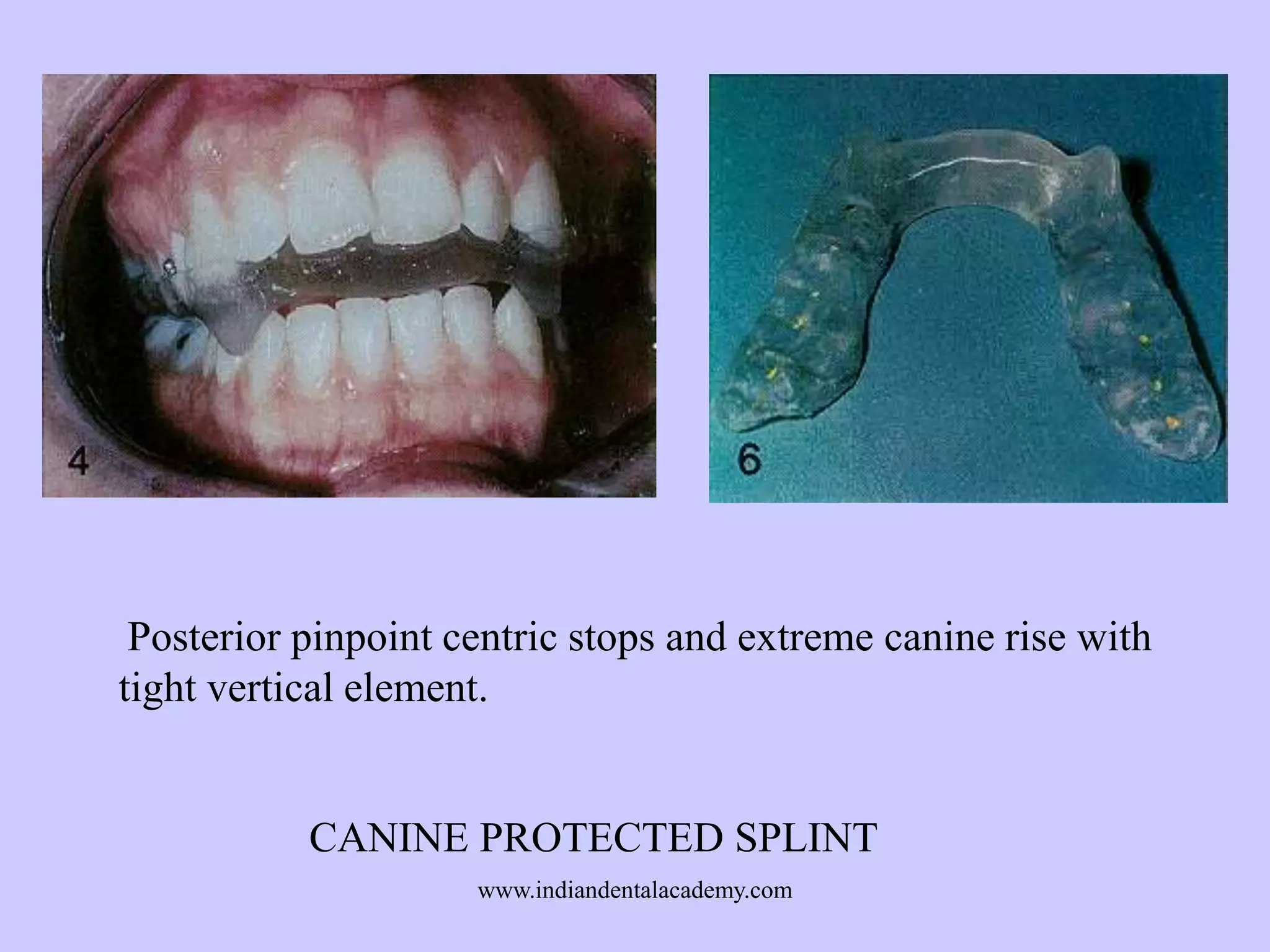
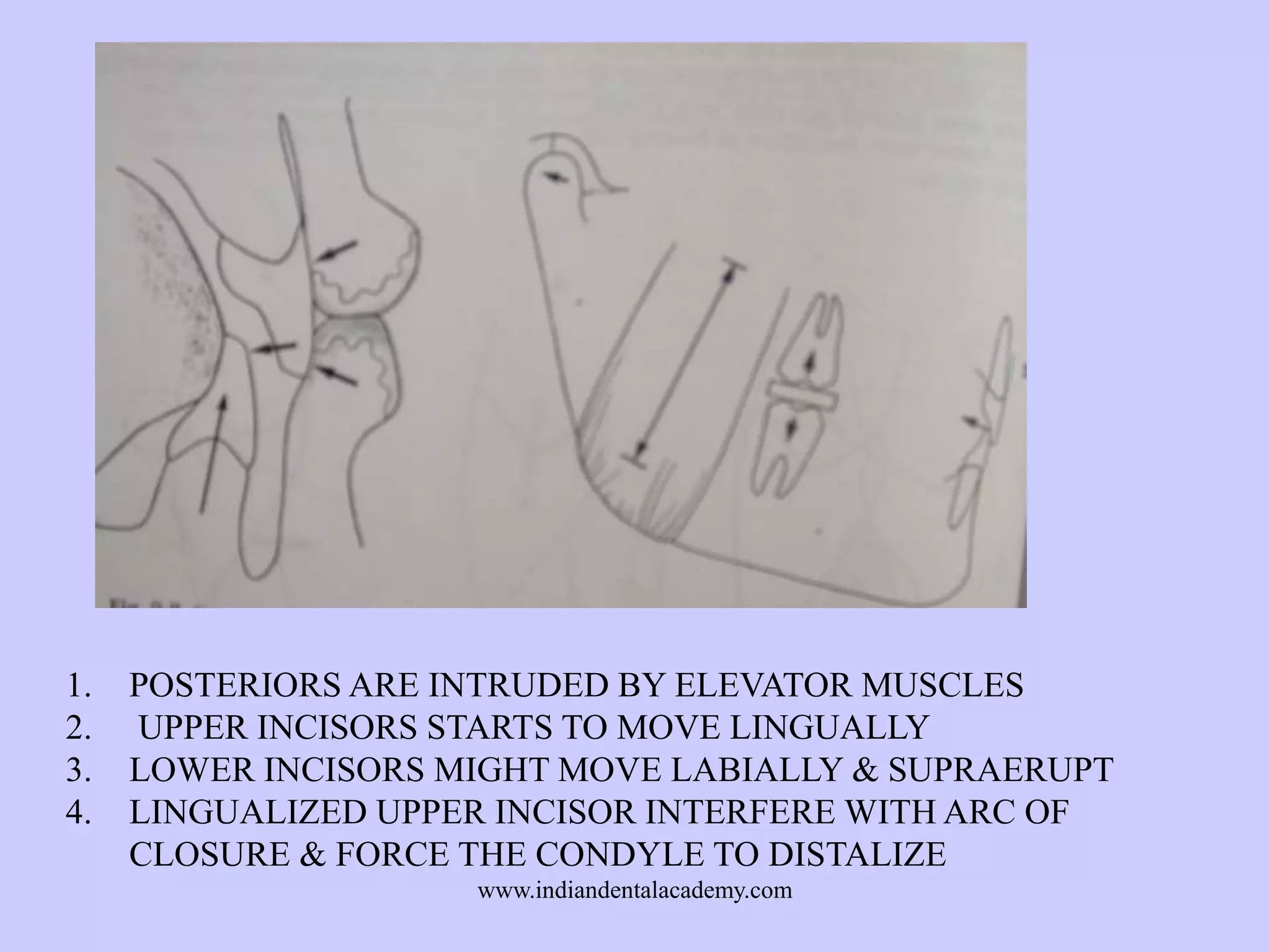
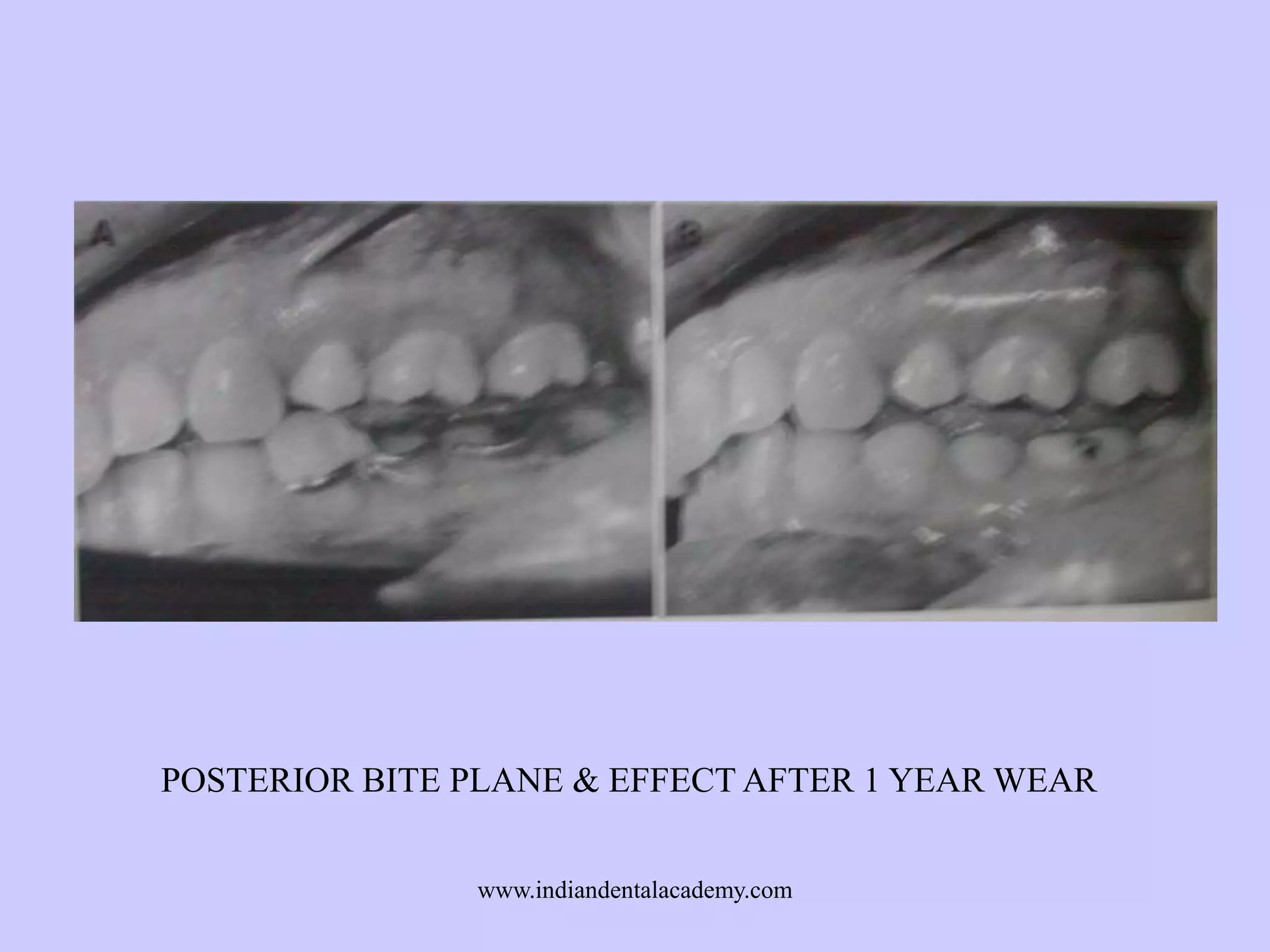
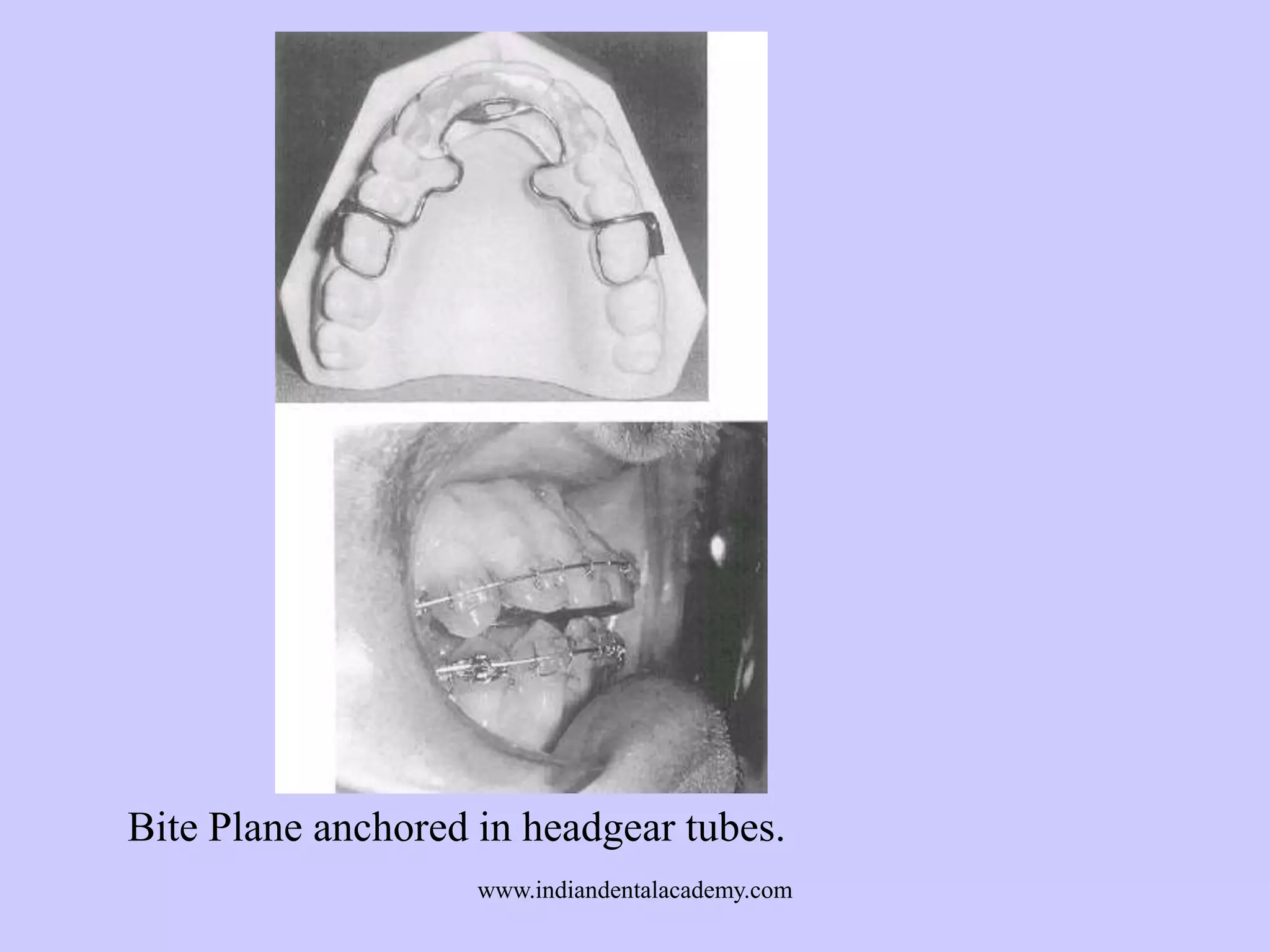
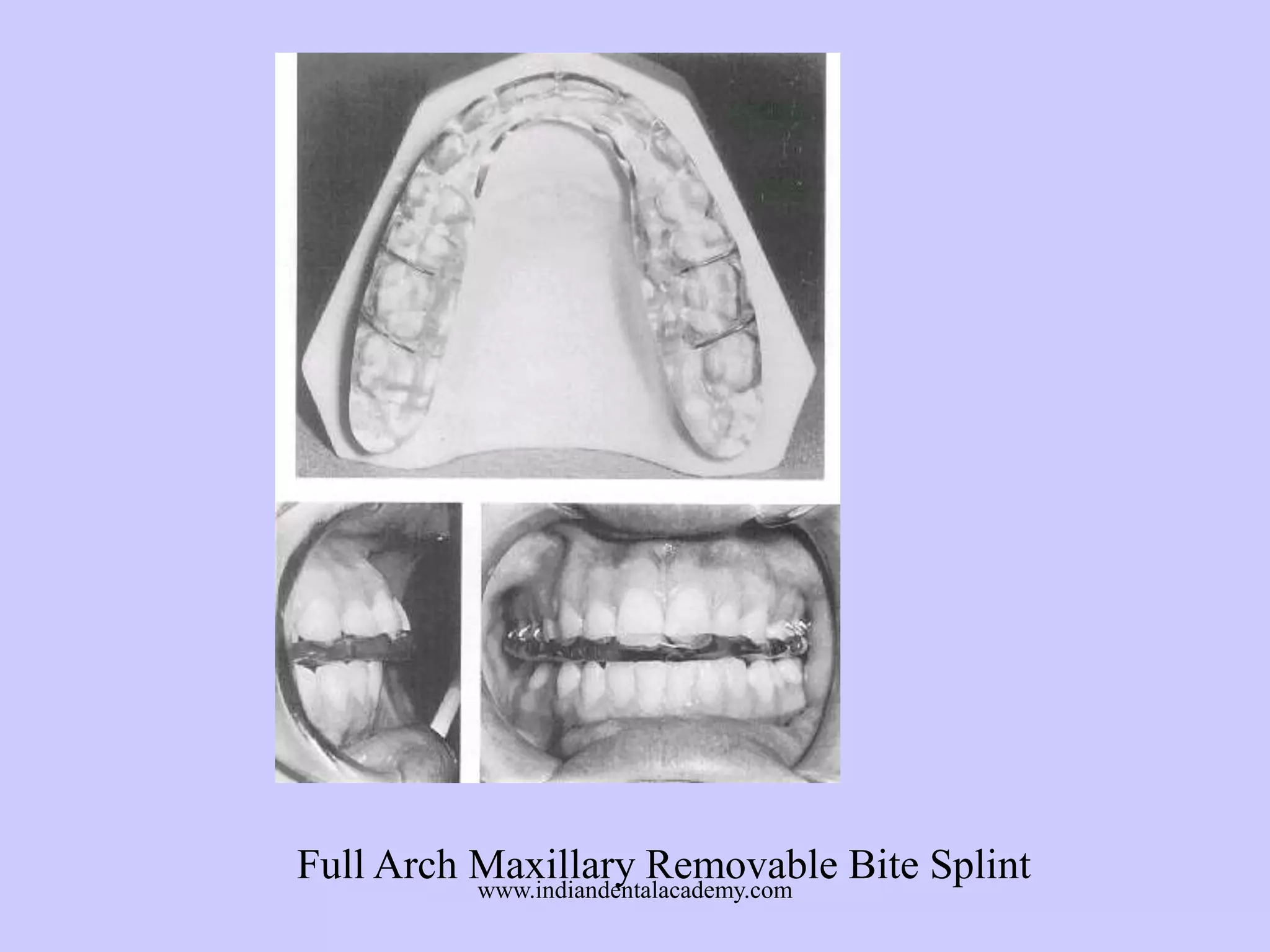
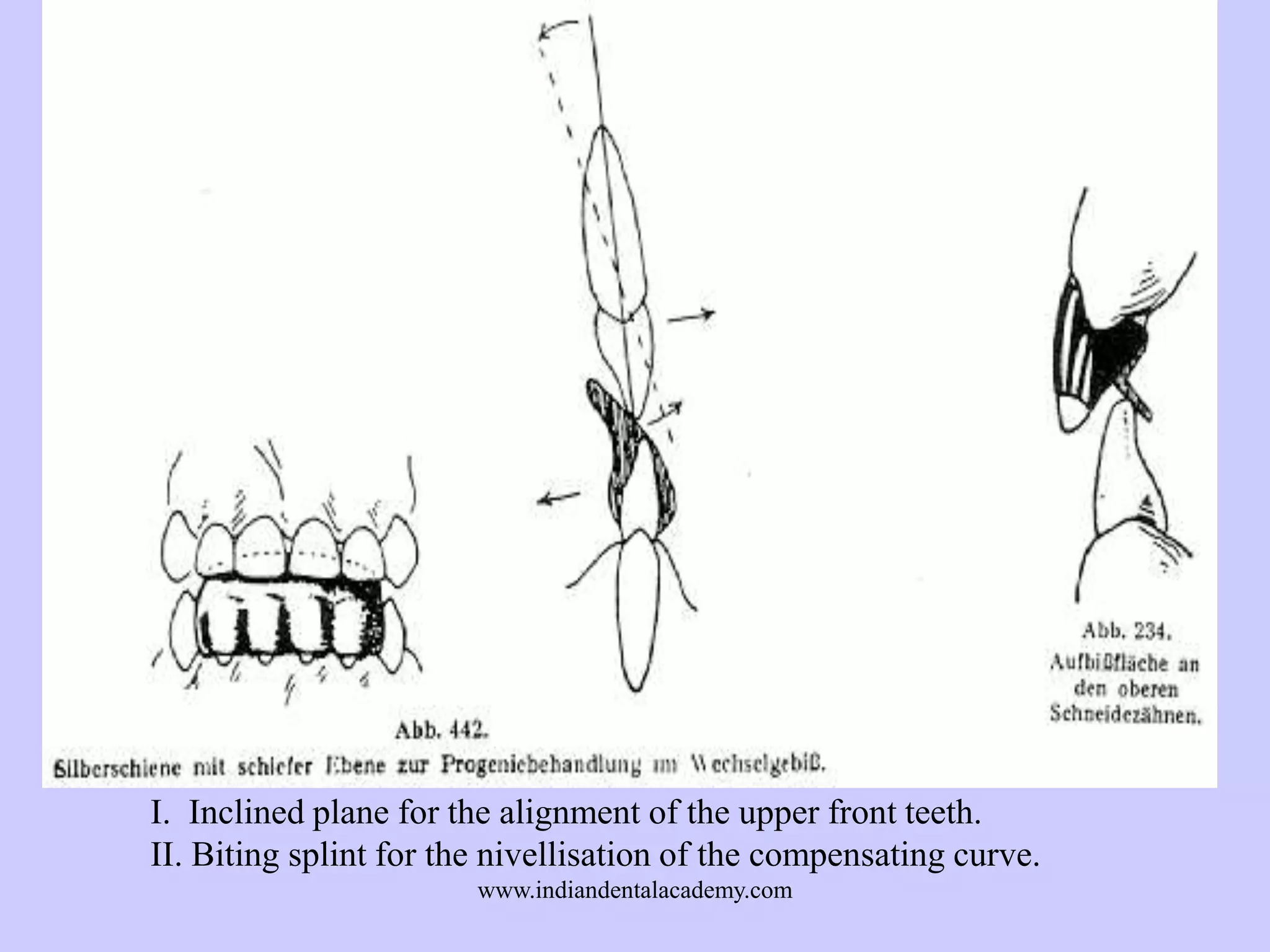
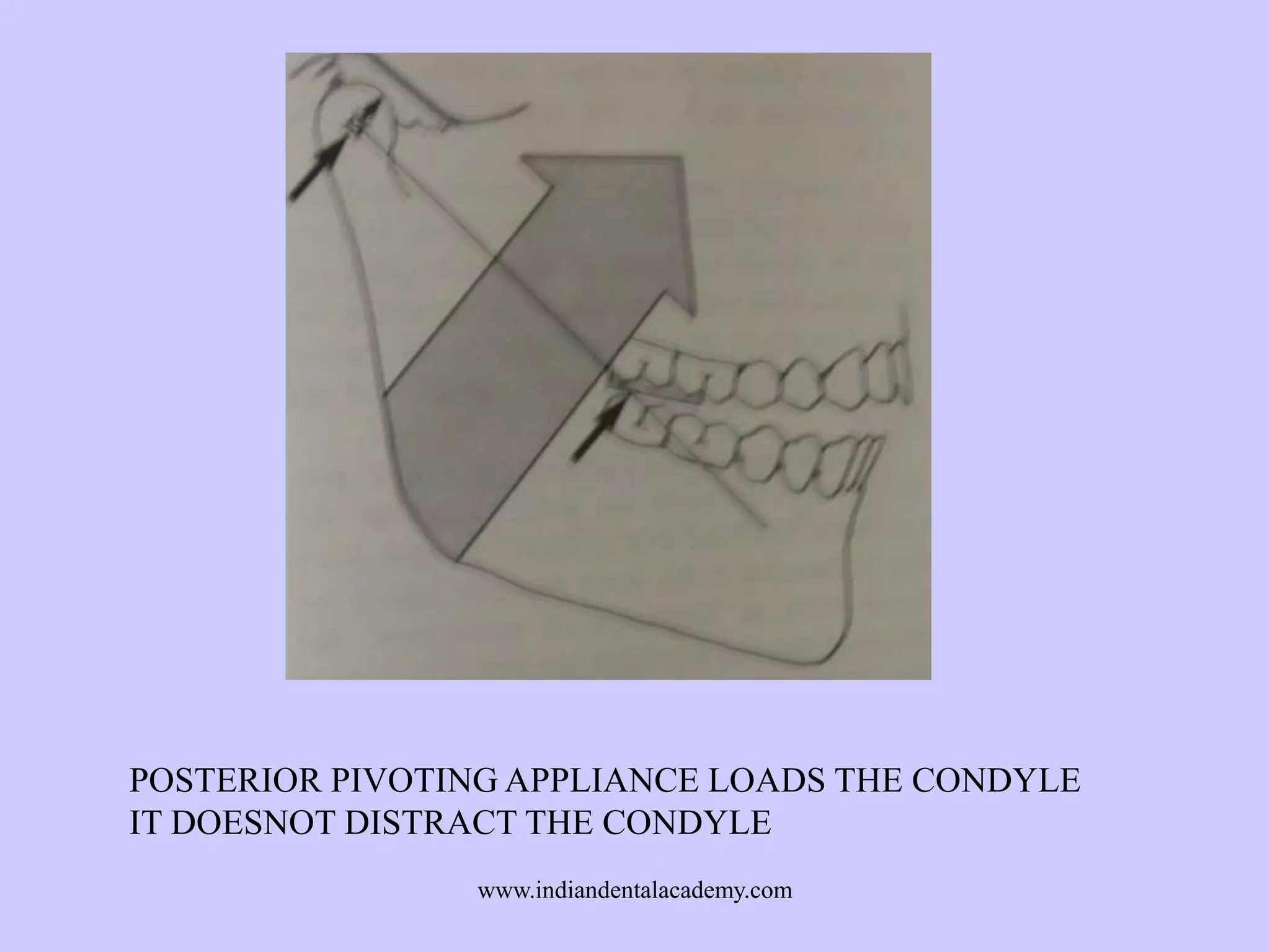
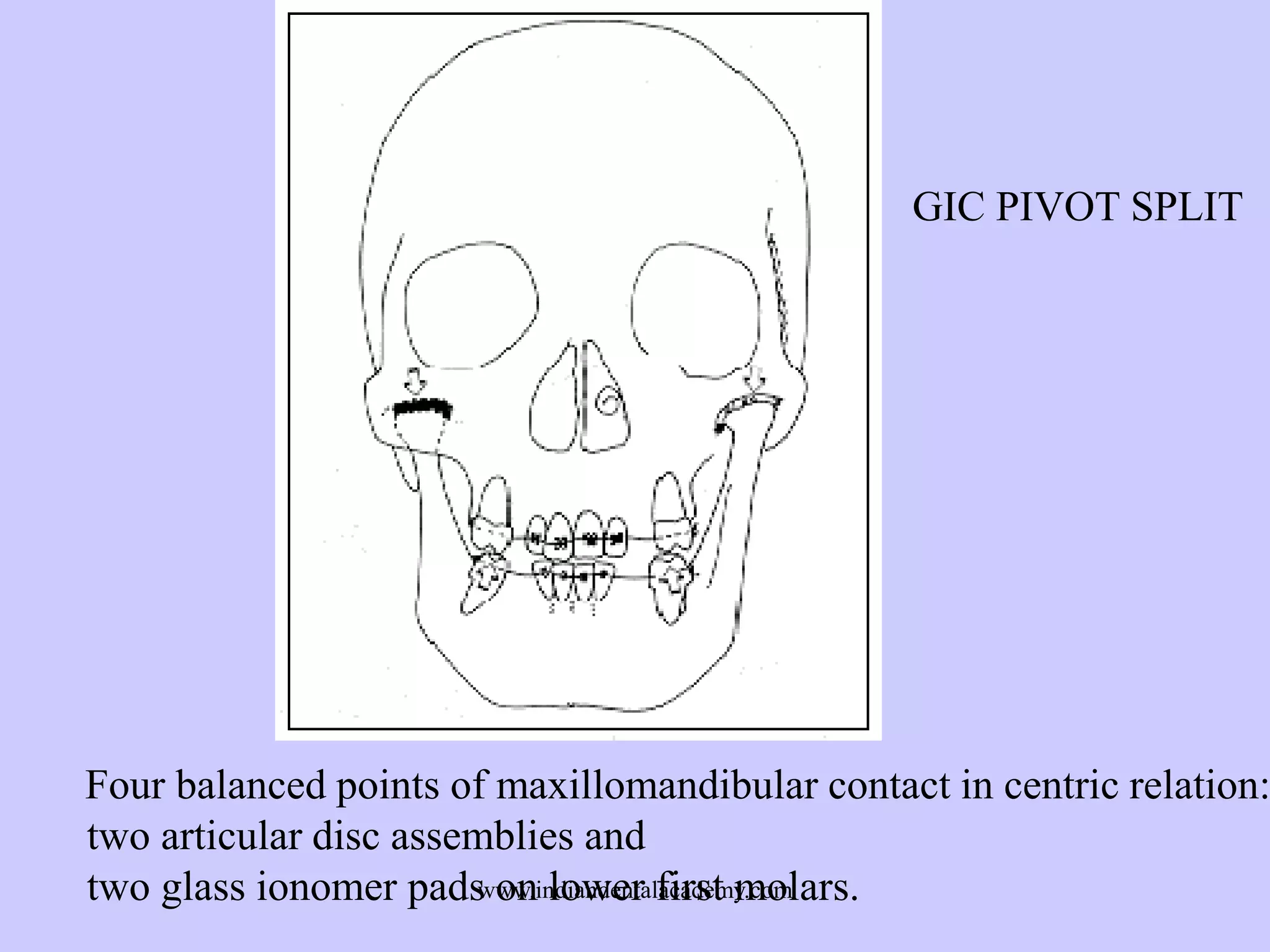
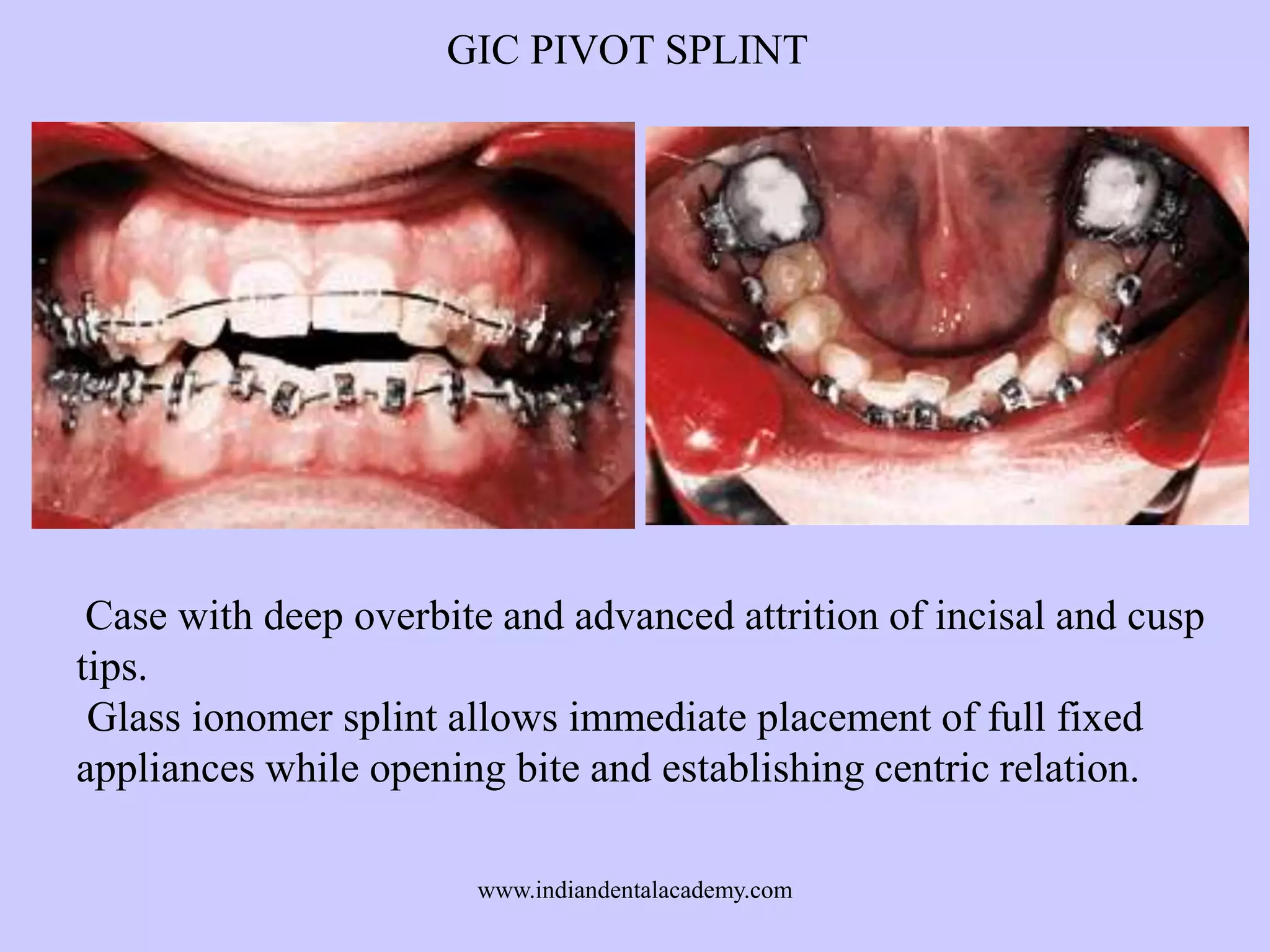
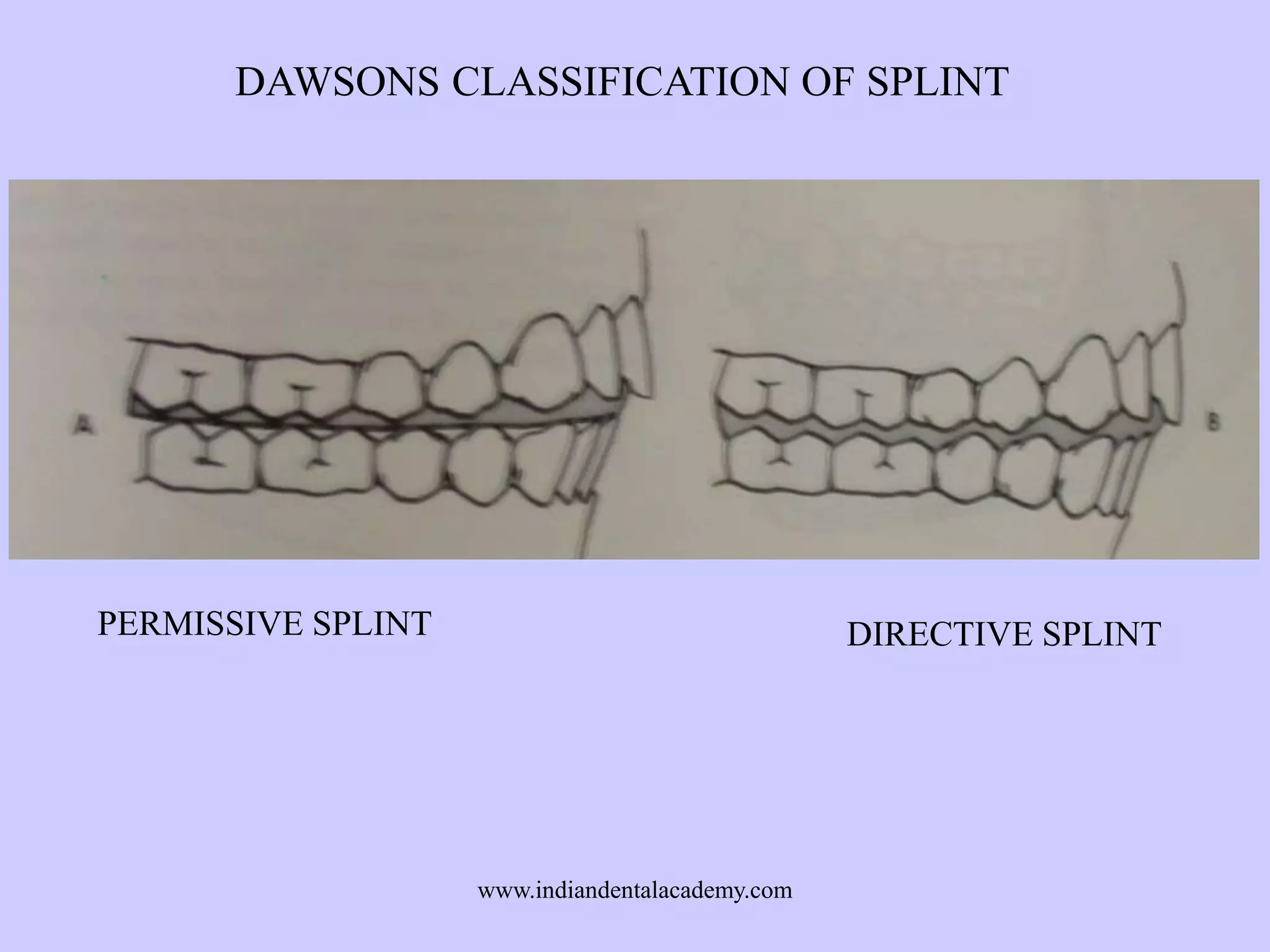
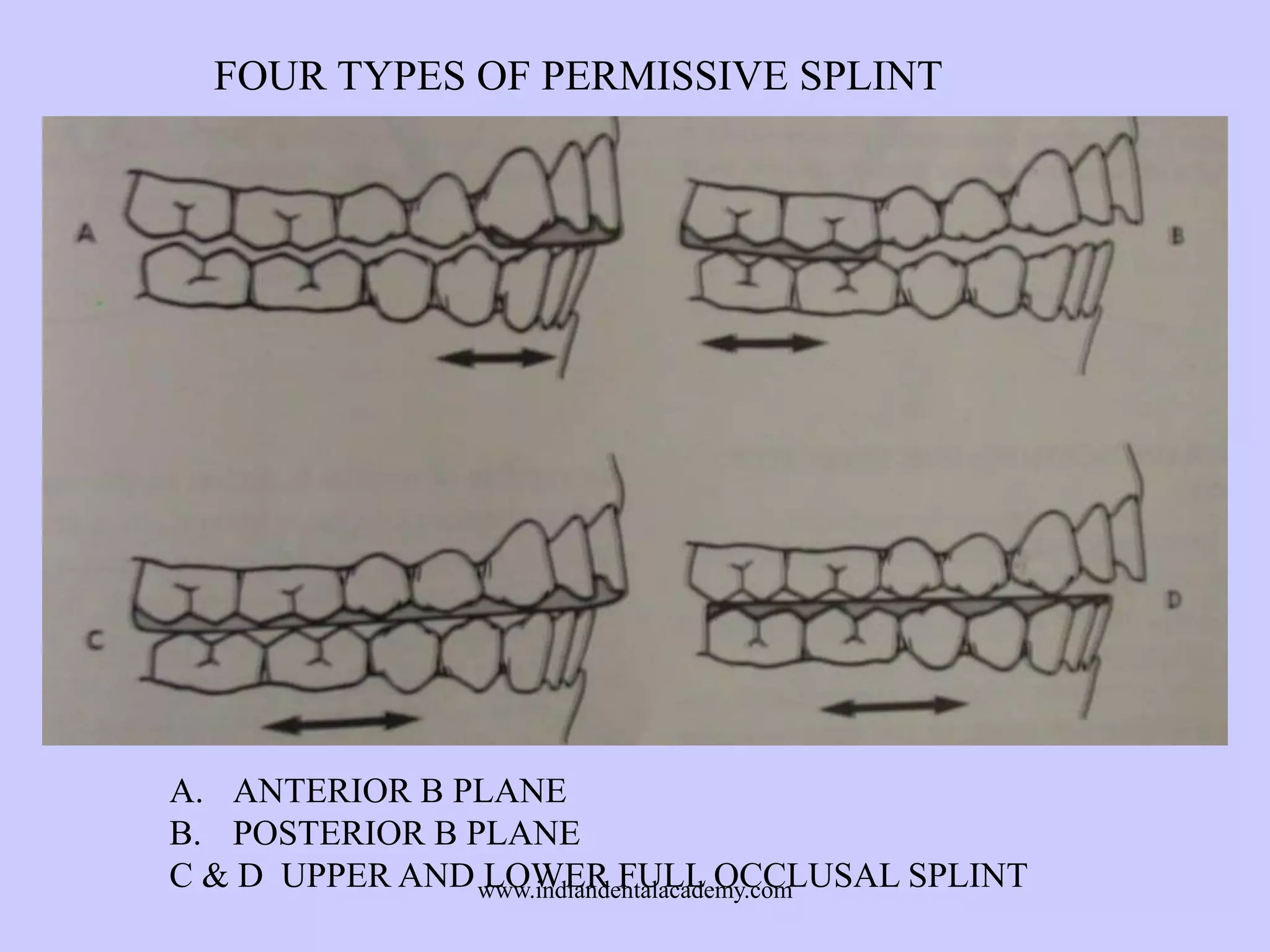
The document provides an overview of splints used in dental occlusion therapy, detailing their types, classifications, and mechanisms of action. It discusses the physiological interactions involved in occlusion and how splints can relieve muscle strain and alter jaw positioning. Additionally, various theories explaining the functionality of splints, as well as specific design considerations and applications, are outlined.