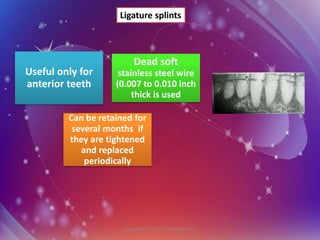
The document discusses splinting, including its history, definitions, aims, principles, indications, classifications, advantages, and disadvantages. Some key points:
- Splinting aims to immobilize and stabilize loose or mobile teeth by redistributing forces across multiple teeth.
- It has been used since ancient Egypt to stabilize teeth and fractures. Modern classifications include temporary, provisional, and permanent splints made of various materials.
- Indications include reducing tooth mobility from trauma, occlusal adjustment, or periodontal disease. Contraindications include active periodontal inflammation.
- Advantages are stabilizing teeth and tissues, but disadvantages include increased risk of decay and difficulties with oral hygiene.