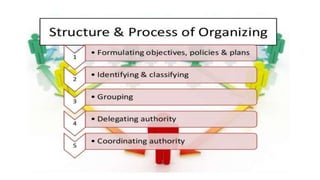
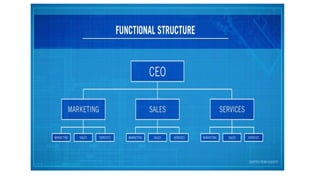
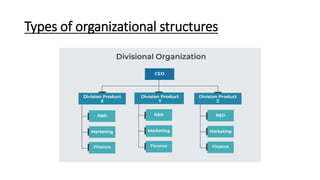
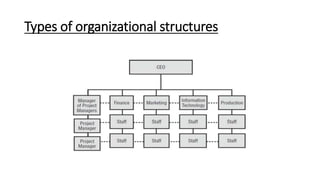
The document provides an overview of organizing as a management function. It discusses the organizing process which includes determining objectives, identifying activities, grouping activities, allocating duties and responsibilities, and delegating authority. It also describes the importance of organizing, types of organizational structures like functional, divisional, and matrix structures. Finally, it discusses concepts related to organizing individuals like responsibility, authority, and delegation.