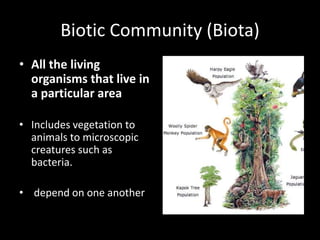
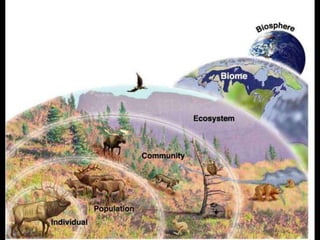
The document outlines the basics of ecology, defining key concepts such as organisms, species, populations, biotic communities, and ecosystems. It distinguishes between abiotic factors (non-living elements) and biotic factors (living organisms) that constitute an environment. Additionally, it explains ecotones as transition areas between ecosystems and biomes as large areas with similar climate and vegetation.